Heredity and Evolution
Class 10 -Science & Technology-Part 2-Chapter 1- Maharashtra Board
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Inheritance or heredity : The process of transfer of physical and mental characters from parents to the progeny is called inheritance or heredity.
- The chromosomes made up of nucleic acids and proteins, present in the nucleus of the cell ere the components that carry hereditary characters in living organisms.
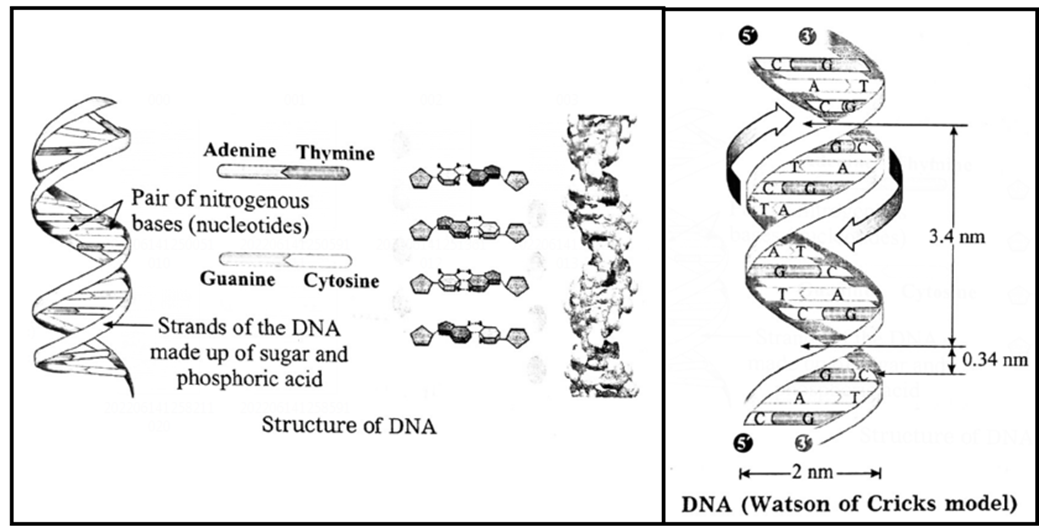
Components of the DNA molecule : DNA molecule is made up of two helical strands consisting of deoxyribose sugar, phosphoric acid and pairs of nitrogenous bases.
Hereditv and hereditary changes:
Heredity : The transfer of biological characters from one generation to the next one with the help of genes is called heredity.
History of genetics: 1) Year: 1886 : Scientist: Gregor Johann Mendal 2) Year: 1901 : Scientist: Hugo de Vries 3) Year: 1902 : Scientist: Waltor and Sutton 4) Year: 1944 : Scientist: Ostwald Avery, Mclyn McCarthy and Colin MacLeod 5) Year: 1961 : Scientist: Francois Jacob and Jack Monad After the processes of protein synthesis was discovered…
The benefits of science of heredity:
- Diagnosis of hereditary disorders.
- Treatment of incurable hereditary disorders.
- Prevention of hereditary disorders.
- Production of hybrid varieties of animals and plants.
- Industrial processes in which microbes are used..
DNA: DNA molecule is a double helix consisting of two strands. Each strand of this helix is made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of a phosphoric acid, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogenous base. Nitrogenous bases are of two types, viz. purines and pyrimidines.
- The purines are of two types, viz. adenine and guanine
- Pyrimidines are of two types viz. cytosine and thymine.
- The adenine always pairs with thymine with double hydrogen bonds
- Cytosine always pairs with guanine with triple hydrogen bond.
- The helices remain bound due to these hydrogen bonds.
RNA:
- RNA is nucleic acid having single strand of ribonucleotides.
- Each ribonucleotide is made up of ribose sugar, phosphate molecules and a nitrogenous base.
- There are four types of nitrogenous bases, viz. adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. RNA is found both in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm.
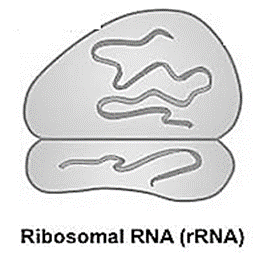
- According to the functions RNA is of the following three main types: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA.
mRNA : It carries the information for protein synthesis from genes on DNA chain in nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Therefore, it is called messenger RNA.

rRNA : It is the component of the ribosome. It helps in protein synthesis.
tRNA is present in the cytoplasm. According to the message of the mRNA, it carries the specific amino acid up to the ribosomes as per the message coded on mRNA.

Genetic disorders : Genetic disorders are caused due to abnormalities in chromosomes and mutations in genes. Some important causes of genetic disorders are as follows :
- Increase or decrease in number of chromosomes causing numerical change.
- Deletion of any part of the chromosome
- Translocation of chromosomes.
- Sudden change or mutation occurring in a normal gene, turning it into a defective gene.
- Mutations in ‘more than one gene at the same time causing polygenic disorder.
Examples:
- Disorders due to numerical changes in the chromosomes : (1) Down’s syndrome (2) Turner’s syndrome (3) Klinefelter’s syndrome.
- Monogenic disorders caused due to mutations: Hutchinson’s disease, Tay-Sachs disease, galactosaemia, phenylketonuria, sickle cell anaemia, cystic fibrosis, albinism, haemophilia, night blindness, etc.
- Polygenic disorders: Cleft lip, cleft palate, constricted stomach, spina bifida (a defect of the spinal cord), etc. are polygenic disorders. Diabetes, blood pressure, heart disorders, asthma, obesity are also polygenic disorders.
Transcription, Translation and Translocation :
(i) Transcription : Synthesis of mRNA as per the nucleotide sequence present on the DNA molecule, is called the process of transcription.
- The nucleotide sequence present in the DNA molecule is called gene. Genes control the structure and functioning of cells of the body.
- Information required for the synthesis of proteins is stored in the genes i.e. in the nucleotide sequences of DNA. The proteins are synthesised according to the need of the body.
- Central Dogma: Synthesis of proteins by DNA through the RNA is called central dogma.
- DNA Transcription →RNA Translation→ Protein
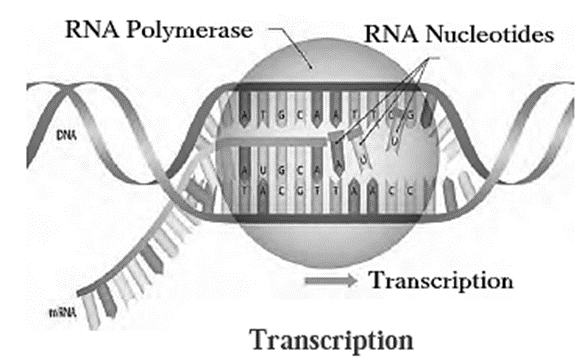
- Genetic information is thus used from DNA to RNA, then through RNA for protein synthesis.
- mRNA is produced according to the sequence of nucleotides on DNA.
- During transcription only one of the two strands of DNA is used.
- The sequence of nucleotides present on DNA strand gets copied in mRNA. Hence there is always complementary sequence produced on the new mRNA molecule.
- RNA molecules have uracil instead of thymine present in DNA.
- Thus by transcription MRNA molecule which is complementary to DNA is produced.
Role of different RNA in protein synthesis :
See below figure -
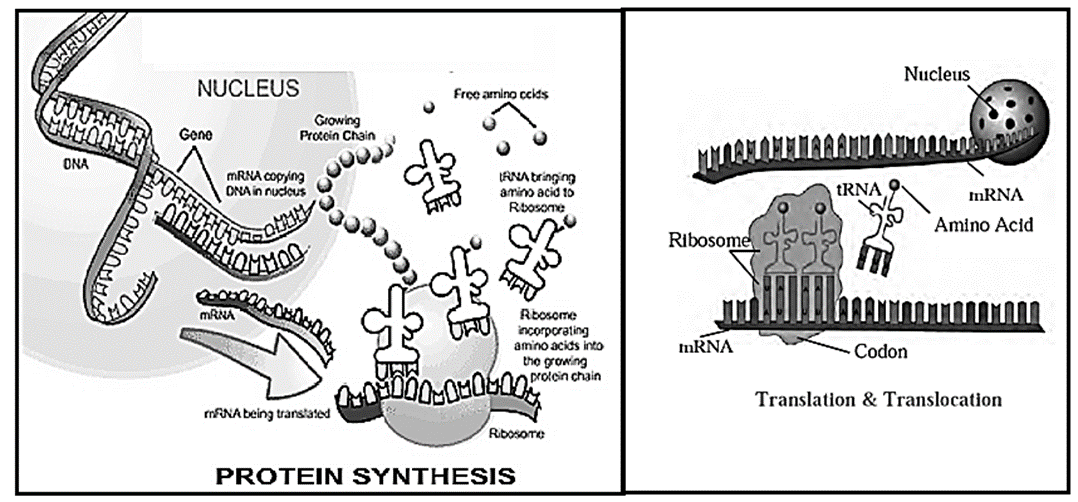
Triplet codon :
- The code for each amino acid consisting of three nucleotides, is called ‘triplet codon’.
- mRNA formed in nucleus brings the coded message from DNA when it comes in cytoplasm. This message contains the codes for amino acids.
- Dr. Har Govind Khorana, made an important contribution in discovery of triplet codons for 20 amino acids. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1968 for this work, along with two other scientists.
- Thousands of triplet codons are present in each mRNA molecule. As per the message on mRNA, amino acids are supplied by the tRNA.
(ii) Translation : As per the codon on mRNA, the tRNA molecule with complementary ‘anticodon’ is brought near mRNA, this process is called ‘translation’.
Formation of peptide bonds: Every tRNA brings specific amino acid. These individual amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds with the help of rRNA.
(iii) Translocation : The ribosome keeps on moving from one end of mRNA to other end by the distance of one triplet codon. This process is ‘translocation’.
Many such polypeptide chains come together to form different and complex proteins. The proteins are essential for controlling various functions of body of living organisms.
Mutation :
- Sudden change occurring in the genetic material is known as mutation.
- Due to transmission of parental genes to offspring, there is remarkable similarity between parents and their offspring. But if there is mutation in any nucleotide then there are changes in the characters of the offspring.
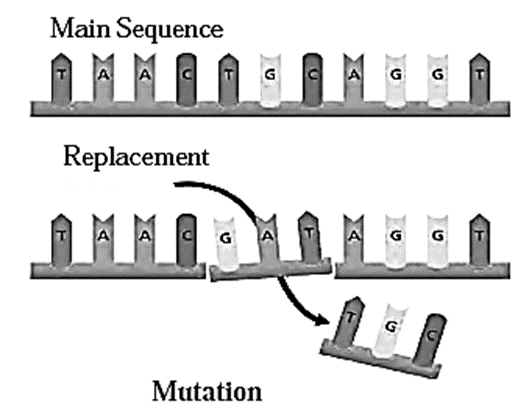
- Mutations are of two types, viz. minor and major. Minor mutations can also bring about considerable changes. E.g. Genetic disorders like sickle cell anaemia is caused due to mutation.
- Mutation is an everlasting process which leads to the process of evolution. It also offers proof for Darwin's theory of natural selection.
Q. What is the function of the appendix of our digestive system?
Ans. Appendix of human digestive system is a functionless or vestigial organ.
Q. Are our wisdom teeth really useful for chewing the food?
Ans. Wisdom teeth are not useful for chewing the food.
Q. Why did the huge animals like dinosaur become extinct?
Ans. Dinosaur could not adapt to the environment. in which they were trying to | survive. There was beginning of ice-age which resulted in scarcity of food. The starvation was one of the reasons for extinction. According to one theory, a meteor collided with the earth and this resulted in catastrophic death of the dinosaurs.
Q. Why are many species of animals and birds getting extinct?
Ans. There is continuous and rapid change in the environment which is causing threat to the natural habitats of the animals and birds. Pollution, climate change, increasing urbanization etc. are the factors causing depletion of food and shelter of animals and birds. Moreover, hunting and poaching has also resulted in extinction of many species.
Evolution :
The gradual change occurring in living organisms over a long duration is called evolution.
- Evolution results in the development of organisms. Transformations ranging from changes in the stars and planets, to the changes in biosphere on the earth are studied in field of evolution.
- Due to evolution, there is formation of new species. Due to natural Selection, there are continuous changes in specific characters of several generations of living organisms.
Approximately 3.5 billion years ago, life was not present on the Earth. The living organisms have been developed according to the following phases:
(1) Simple elements → (2) Organic and inorganic compounds → (3) Complex Organic compounds such as proteins and nucleic acids → (4) Mixture of different types of organic and inorganic compounds. → (5) First primitive type of cells → (6) Processes to take up surrounding chemicals developed leading to growth of cells in numbers → (7) First living organism → those organisms that could adjust and adapt to the surrounding conditions, survived and grew. This is according to the principle of natural selection. Some of them that could not adjust, perished.
- Ranging diversity in animals: From unicellular amoeba and paramoecium to giant whale and man.
- Ranging diversity in plants : From unicellular Chlorella to the huge banyan tree.
- Existence of life on Earth: From equator to both the poles on the entire earth, living ; organisms are seen in air, water, land, rock, etc.
- Theory ‘of ‘Gradual development of living organisms’ is accepted worldwide.
Theory of Evolution :
- According to the theory of evolution, first living material was in the form of protoplasm which was formed in ocean.
- Gradually, it gave rise to unicellular organisms. Changes took place in these unicellular organisms which made them evolve into larger and more complex organisms.
- All evolutionary changes were very slow and gradual taking about 300 crore years to happen.
- Different types of organisms were developed as the changes and development that occurred in living organisms was all round and multi-dimensional.
- Hence, this overall process of evolution is called organizational and progressive.
- Variety of plants and animals developed from the ancestors having different structural and functional organization during the process of evolution.
‘Evidences of evolution :
Evolution is an everlasting process of changes. The proofs to support this process are called evidences of evolution. Following are various proofs available in support of the theories mentioned above.
(i) Morphological Evidences :
- Similarities in the external and visible features are called morphological evidences.
- In animals, similarities in the structures such as mouth, nostrils and ear pinnae, position of eyes, thickly distributed body fur or hair.
- In plants, similar characters such as leaf shape, leaf venation, leaf petiole, etc.
- These similar features indicate that origin of different animal or plant groups must be the same having a common ancestor.
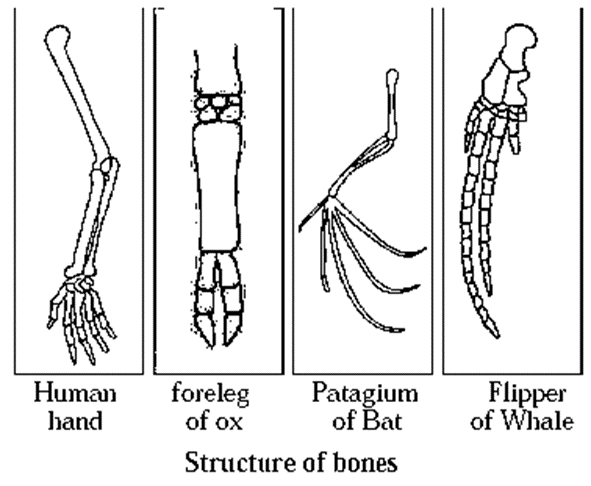
(ii) Anatomical Evidences :
- Human hand, cat’s foreleg, flipper of whale and patagium of bat show difference in their features. .
- These organs also have different uses.
- However, the structure of bones and bony, joints in organs of each of those animals show similarity.
- This is an indication that all these animals originated from a common ancestor.
Organs :
Types of organs in body of organisms :
Higher organisms show different body organs and systems that carry out specific functions. Each system consists of definite organs.
- In the thoracic cavity, there are lungs and heart.
- In skull, brain is located.
- In abdominal cavity there is stomach, intestine, liver, kidney, etc.
Functions :
- Each important vital organ performs specific function which is necessary for survival. Brain controls and coordinates all the vital activities.
- Heart is responsible for the circulation of blood throughout the body.
- Lungs perform respiration.
- Kidneys filter out nitrogenous waste products from the blood.
- In this way, each organ performs its own function. Only few organs such as appendix do not perform any function.
Vestigial Organs : The degenerated or underdeveloped organs which cannot perform any function are known as vestigial organs.
- Existing organs undergo gradual changes during evolutionary process. Thus, they form new tissues, organs, etc.
- Under certain environmental conditions such changes are necessary. However, some structures become useless in newly changed conditions.
- Due to natural selection, such structures undergo degeneration and after a very long time span they vanish.
- Appendix may be useful for grazing, ruminating herbivores but it is vestigial for man.
- Other vestigial organs in human body are tail bone (coccyx), muscles of ear pinna, wisdom teeth, and body hairs.
Paleontological Evidences :
Fossil: Fossils are remnants of living organisms or their impressions which are preserved deep down in the earth’s surface. Various natural calamities buried organisms in this way. Fossils throw light on the evolutionary process as they offer direct evidence of evolution.
Carbon dating : Carbon dating is a technique to understand the age of a fossil. When alive, animals and plants consume carbon continuously but this process ends after their death. Later their body carbon in the form of C-14 undergoes continuous decaying process. C-12 is not radioactive. Therefore, the ratio between C-14 and C-12 changes continuously.
By calculating the following three aspects, the age of the fossil can be determined by knowing
- I-The time passed since the death of a plant or animal.
- II-Measurement of the radioactivity of C-14.
- III- The ratio of C-14 to C-12 present in the body.
Uses of carbon dating:
- Study of palaeontology
- Understanding anthropology
- Determining the age of human fossils and manuscripts.
- Calculating the age of fossils and placing them in geological time scale
- Deducing the information about other former organisms. e.g. Invertebrates gave rise to vertebrates gradually during evolution.
Willard Libby : Willard Libby developed the technique of carbon dating method which is based upon the radioactive decay of naturally occurring C-14. For this contribution he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1960. In the journal ‘Radio Carbon’ the data about the ages of the materials determined is compiled and published.
Connecting Links : Some organisms share morphological characters of two groups and hence they are called ‘connecting links’.
(i) Peripatus : It shows characters of Annelida and Arthropoda and thus it is the connecting link between these two phyla.
- Annelid characters : Segmented body. thin cuticle, and parapodia-like organs.
- Arthropod characters : Tracheal respiration and open circulatory system.
(ii) Duck billed platypus: Duck billed platypus is the connecting link between Reptiles and Mammals.
- Reptilian characters: Egg laying habit, scales on body.
- Mammalian characters : Presence of mammary glands and hair.
(iii) Lung fish: Lung fish is the connecting link between fishes and amphibians.
- Fish characters : Fish like body.
- Amphibian characters: Respiration with lungs.
The above connecting links prove that arthropods evolved from annelids, amphibians evolved from fish and mammals evolved from reptiles.
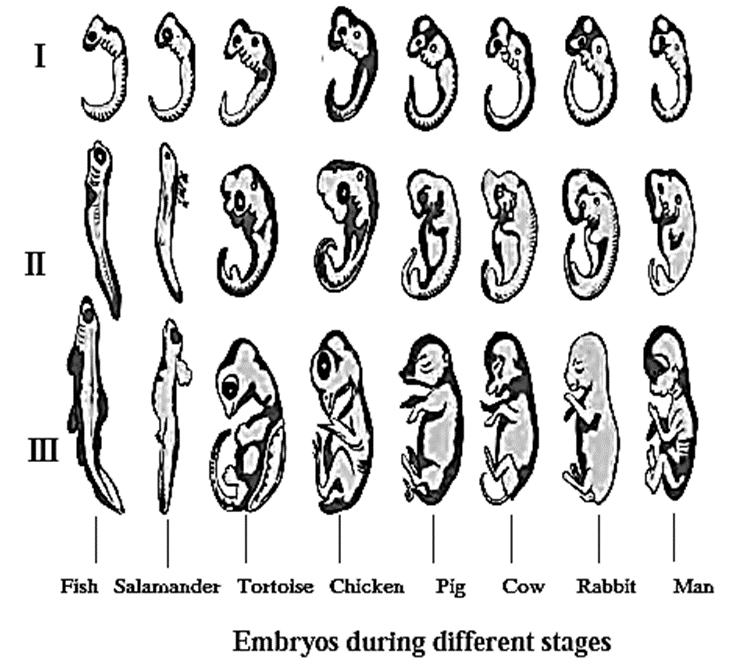
Embryological Evidences : All vertebrate embryos show extreme similarities during initial stages of development. These similarities disappear gradually in later development. This initial similarity indicates that there may be a common origin of all these animals.
Darwin's theory of natural selection :
Charles Darwin: (1809-1882) proposed the theory of natural selection. This theory is an important milestone in the study of evolution.
- Theory of natural selection : ‘The survival of fittest’, i.e. organisms which are fit for survival, evolve while those that are not, perish. The natural selection thus acts to produce new species.
- Theory of natural selection is given in the book, ‘Origin of Species’ which is written by Darwin.
- For this study of evolution, Darwin had collected and observed innumerable specimens of plants and animals.
Important explanation of Theory of natural selection :
- All living organisms reproduce prolifically.
- There is competition with each other or struggle for survival.
- Organisms that show essential modifications for survival, sustain while remaining perish.
- Survival of the fittest and elimination of misfit is the ‘natural selection’.
- Well adapted, sustaining organisms reproduce more such offspring and in turn produce new species having specific characters.
Objections to Darwin’s theory:
- Some more factors are responsible for evolution and not just the natural selection.
- Any explanation about useful and useless modifications was not provided by Darwin.
- Causes of slow and abrupt changes was not explained by Darwin.
Lamarckism :
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744-1829) : Lamarck proposed principle of ‘use or disuse of organs and ‘theory of inheritance/ancestry of acquired characters’. His concepts are Known as Lamarckism.
- Every living organism tries to evolve. During its lifetime, it acquires certain characters through adaptations and modification. These characters are passed to the next generation.
- Depending upon the activities or laziness of that organism these changes occur.
Examples of acquired characters :
- For several generations, giraffe extended the neck for browsing on leaves from heights. Due to such extension of neck, giraffe became long-necked.
- Due to frequent hammering movements. Shoulders of the ironsmith became very, strong.
- Flightless birds like emu and ostrich have weak wings as they do not fly.
- Due to Wading and swimming in water the hind limbs of aquatic birds such as swan and duck became fitter for such mode.
- Due to burrowing habit, snakes lost the limbs.
According to Lamarck such acquired characters are inherited by the next generation.
Objections to Lamarckism :
- The view that unused organs degenerate and used ones evolve Was accepted but inheritance of such Characters was not agreed by the scientists,
- Modifications formed are not transferred to the next generation.
- Ancestry/Inheritance of acquired Characters: This concept states that the living organism is able to transfer the characters which it has acquired, to the next generation.
Speciation :
Species: The group of organisms that can produce fertile individuals through natural reproduction is called species.
Speciation.Due to evolution, new species of plants and animals are formed. The process of formation of new species from earlier ones is called speciation.
- Each species possesses specific characters.
- Each species differs in its geographical conditions, food preference, habitat, reproductive ability and period, etc. Therefore, the specific characters are retained.
Speciation depends upon following factors :
- Genetic variation
- Geographical changes
- Reproductive changes
- Geographical or reproductive isolation for a long period.
Human Evolution :
Evolutionary history of modern man :
Approximately around 7 crore years back the ice age began on the earth. In such conditions, dinosaurs became extinct. The evolution and diversity of mammals started during this time. Due to change in climate the forest cover also declined rapidly.
- Ancestors of humans developed from animals which resembled lemur like animals.
- Around seven crore years ago, monkey-like animais evolved from some of these lemur like animals.
- Then after about 4 crore years ago, in Africa the tails of these monkey like creatures very gradually disappeared.
- Simultaneously, there was enlargement in their body and brain volume too. The hands also improved and were provided with opposable thumb. In this way, ape-like animals were evolved.
- These ape-like animals independently gave rise to two lines of evolution, one giving rise to apes like gibbon and orangutan in the South and North-East Asia and gorilla and chimpanzee which stayed in Africa around 2.5 crores of years ago.
- The other line of evolution gave rise to human like animals around 2 crore years ago.
- The climate became dry and this resulted into reduction of forest cover. This made arboreal apes to descend on the land and start terrestrial mode.
- Due to this, there were changes in the lumbar bones and vertebral column. The hands were also freed from locomotion and thus they became more manipulative.
- Later, journey of hominoid species started from around 2 crores years ago.
- The first record of human like animal is ‘Ramapithecus' ape from East Africa.
- Ramapithecus from Africa → Australopithecus → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon are the important steps in human evolution.
- Neanderthal man was said to be the first wise man. The increasing growth of brain made man more and more intelligent and thinking animal.
- Later, more than biological evolution, it was cultural evolution, when man started agriculture, animal: rearing. There was development of civilizations, arts and science etc.
- About 200 years ago there were industrial inventions and thus man rules the earth.
Stages of human evolution and its time :
Click on below link to give online test and judge yourself. Get instant result in your inbox
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : MSBSHSE -Class 10th Science Text Books – Chapter wise Text Book PDF of all chapter for download Videos : MSBSHSE Class 10th Science & Technology-2-Videos - Chapter wise Videos of all chapter. Next Chapter : Chapter 2. Life Processes in living organisms Part -1 - Online Notes |

Okay
Which redio activity elements in human body?
radioactive elements-Potassium 40, Carbon 14, Radium 226 in our blood or bones
C-14 radio activity is present in our body
This is very useful
Thank you so much it was so helpful 👻❤️👌🏻
Thanku
How to get all pdf’s notes from your website? (Class 10 science part 2)
Visit : https://test.kitabcd.org/shop/
Achhi notes hai…
Helpful
Thank
C-14 radioactivity in human body
Thank for your notes important factor for study
Exlent. This very very good and very helpful.
The best notes I have ever reed
Best notes it will help me for better understanding
thank you so much from KitabCdAcademy
Very helpful 👌🏻👌🏻
It is very helpful for me to understand. Thankyou for making such beautiful notes 🙏🏻