Mass Media and History
Maharashtra Board- Class 10-History-Chapter-5
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
Introduction to Mass Media : Mass media is a field of mass communication
Mass media can be used to send information to a far away destination through a medium of communication.
Means of Communication in earlier times :
- According to the orders of the king, a crier would run in the streets beating drums to convey news.
- Then, the news would spread among people by word of mouth.
British Period :
- People started receiving printed news through newspapers after the arrival of the British.
- Newspaper became a medium of circulating news, information and knowledge.
History of Mass Media :
Newspaper : A community needs news, for the same reason that a man needs eyes. News is information from all over the land. The medium which prints this information is newspaper. England Gazette was the first newspaper started in England in 1966. James Augustus Hickey started the Bengal Gazette and laid the foundation of newspapers in India. In the later period, many newspapers were printed in English and regional languages.
- Newspaper is a publication which mainly prints news, editorials, people's Opinions and other contents. It is distributed regularly at a definite time.
- Newspaper provides various local, national and international news,
- Newspapers are called the fourth column (pillar) of democracy.
- They are historical documents which record current events.
- In recent times, many newspapers have introduced e-newspapers.
Precursors of Newspapers :
Different means to convey King's order to the people :
- Egypt and Emperor Ashoka : Custom of placing inscriptions, with royal decrees, at public places.
- Roman Empire : Decrees written on papers with various information were distributed in all regions.
- Julius Caesar : Newspapers named Acta-Diurnas used to be placed at public places in Home to convey royal commands.
- In the 7th century C.E : China royal dictates were distributed among people at public places.
- England : Handouts were distributed giving information on important events or war.
- The ambassadors of a king posted at various places would send back important news to the royal court.
In the later period, many newspapers were printed in English and regional languages.
Newspapers in India :
1) Bengal Gazette : Started by : Irish gentleman James Hickey
- The first English newspaper was started in Calcutta on 29th January, 1780.
- It was called ‘Calcutta General Advertiser’ or 'Bengal Gazette.’
2) Darpan (1832) : Editor/ Started by : Balshastri Jambhekar
- First newspaper in Marathi.
- It was started on 6th Ianuary 1832 in Mumbai hence, the day is celebrated as 'Patrakar Din‘ (Journalists' Day).
- The political, economic, social and cultural events of these times can be viewed through Darpan.
Events reported in Darpan are :
- Expenditure of East India company was reported.
- The danger of Russian attack on India.
- Remarriage of Hindu widows.
- Achievements of Raja Ram Mohan Roy.
- Committee appointed for cleanliness in city and other such news were printed in Darpan, throwing light on various situations of those days.
3) Prabhakar : Editor/ Started by : Bhau Mahajan
- We get to read thorough history of French Revolution.
- The letters by Lokhitvadi (Gopal Hari Deshmukh) were published in Prabhakar.
- It aimed at creating social awareness.
4) Dnyanoday :
- Printed Maps of Asia in 1842 and Europe in 1851.
- Illustrations were printed for the first time.
- Installation of telegraph was reported in this paper.
- Printed 'Chakya Mhasoba', i.e. the news about beginning of railway services in India.
- Printed the news of the lndian War of Independence of 1857.
5) Induprakash :
- Work for the cause of social awakening.
- Supported the cause of widow remarriage.
6) Deenbandhu : Started by : Krishnarao Bhalekar, close associate of Mahatma Phule
- Mouthpiece oi Bahujansamaj.
- Throws light on the conditions of Bahujan Samqj in those times.
7) Kesari and Maratha (1881) : Started by : Gopal Ganesh Agarkar and Lokmanya Tilak
- Published articles about prevalent Social and Political problems.
- Described the condition in the country which led to social awakening.
- Propagated various texts and books in Indian languages.
- Created awareness among the people about political systems in foreign countries.
- Created discontent among the masses against British rule.
Important role of newspaper in the freedom struggle :
- The press was the chief instrument for carrying out the political tasks and propagation of nationalist ideology.
- Both English and Vernacular press started by prominent leaders like Gopal Ganesh Agarkar and Lokmanya Tilak acted as catalyst to the freedom struggle. They started 'Kesari' and 'Maratha' in 1881.
- Newspapers played a great role in building up an increasingly strong national sentiment and consciousness among people. It was an instrument to arouse, train, mobilise and consolidate nationalist public opinion.
- The newspapers were an effective tool in the hands of social reformers. They exposed social evils such as child marriage, ban on remarriage of the widows, inhuman institution as untouchability, caste letters, etc. It became a weapon in their hands to educate masses.
- A comparative study was presented in newspaper on western education, knowledge and national education.
- Newspapers also discussed political institutions in India and the west. The main aim of these newspapers was not to gain profit but to serve the people.
Magazines and Journals (Periodicals) :
Meaning and Type: Magazines which are published at regular intervals are called ‘Periodicals’.
- Magazines and Journals are two types of periodicals.
- They are categorised as weekly, biweekly, monthly, bimonthly, quarterly, six monthly, annual, etc. depending on the duration at which they are published.
- There may be some chronicles which are published at no fixed time.
Early Magazines :
- Balshastri Jambhekar started the first monthly magazine in Marathi known as 'Digdarshan'.
- 'Pragati', now a defunct journal, was started in 1929 and edited by Tryambak
- Shankar Shejwalkar.
- Marathi journals like 'Bharatiya Itihas ani Sanskruti' and 'Marathwada Itihas Parishad Patrika' are periodicals devoted to Indian history in the present times.
Periodicals : Magazines and journals which are published at regular intervals are known as Periodicals.
Types :
- They are categorised as weekly, biweekly, monthly, bimonthly, quarterly, six monthly and annual.
- There are some chronicles which are published at no fixed time.
Classification : Periodicals can be classified as popular and scholarly.
- It a periodical aims at specialists and researchers, it is a 'journal'. Articles are generally written by experts in the subject.
- Popular periodicals are magazines published with variety of content. They can be on fashion, sports, entertainment and films.
- Bharatiya Itihas ani Sanskruti and Marathwada Itihas Parishad Patrika are periodicals of present times. Periodicals are an important source to study history.
Electronic or Digital Journalism :
- In the modem times, the computer and internet have become indispensable parts of printing and publishing process. Computer technology, Internate has led to the widespread practice of digital journalism.
- Websites run by newspapers are basically extensions of newspapers themselves. Modem periodicals are part of electronic or digital journalism.
- People get access to news through social media like Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube qnd from web news portals, web channels. This information is available in English and many other languages.
- Journalists working in this area today have to have many more skills than in the past when writing was the only requirement. Information available on these mediums should be reviewed critically and used with utmost care.
- Web news portal, social media, web channels, YouTube provide historical content for readers.
Digital Newspaper (e-newspaper) : In recent times, e-newspaper has got prominent place in Mass Media. A digital newspaper is a newspaper created digitally and available online via the Internet.
- In e-newspaper, news comes in sequence and not in accordance with importance like in a printed newspaper.
- We have to click on the news headline that we want to read and then it appears on the screen in detail.
- There is a place provided to express the opinion of the reader.
- ‘The Hindu‘ and 'Kesari' became the first English and Marathi e-newspapers respectively.
- Presently, almost all newspapers have their digital edition, i.e. e-newspapers.
- Digital newspapers include pre-press digital files used for production of hard copy newspapers;
- Differences between these editions and the corresponding printed version of the newspaper are generally, continuous stream of content and updates.
- They may be accessed through apps on mobile devices.
Radio (Akashvani) : ‘Indian Broadcasting Company’ (IBC), a private radio company was the first one to broadcast daily programmes.
Development of AIR :
- A private radio company, Indian Broadcasting Company (IBC) broadcasted daily programmes, which was later taken over by the British Government.
- It was later named as Indian State Broadcasting Services (ISBS).
- On 8th June 1936, it was named as All India Radio (AIR).
- After Independence, AIR became an integral part of the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India).
- A famous poet, Pandit Narendra Sharma suggested the name 'Akashvani'.
Akashvani :
Alexander Graham Bell invented telephone in 1876. Words were communicated / travelled from one place to other using wires. Telegram (wireless communication) was invented by Italian scientist Guglielmo Marconi in 1896.
The first radio centre was started by British Broadcasting Company which was established in 1922 and expanded all over the world.
In India, the first radio station was started by Bombay Presidency Club in 1923. In India, it was called 'Nabhovani'. It was later named Akashvani. ‘Bahujan Hitay, Bahujan Sukhay' is the tagline of 'Akashvani'.
Format of Akashvani's programmes :
- Initially, Akashvani gave iniormation about government's programmes and projects.
- Later on, programmes related to entertainment, social awareness and literacy were broadcast.
- It also broadcast special programmes for women, labourers, youngsters and farmers.
- The ‘Vividh Bharati’ programmes are broadcasted in 24 regional languages as well as 146 dialects of Indian languages.
- Recently, private radio stations like Radio Mirchi and many other FM stations are providing radio services.
Television (Doordarshan) :
- The first President of India, Dr. Rajendra Prasad, inaugurated Delhi Doordarshan Centre.
- Mumbai Doordarshan was started on 2nd October, 1972.
- Colour television started on 15th August, 1982 and private channels started their telecast in 1991.
Why do we need Mass Media?
- We need mass media to facilitate free flow of information to all strata of the society.
- To avail a platform to readers to express their views and opinions.
- To make democracy stronger.
- To create social awareness and educate the masses.
- As television shows visuals and images it overcomes the limitations of newspapers.
Critical Understanding of the information received through Mass Media :
- Information received through mass media should be reviewed critically.
- The news or information printed in newspapers or shown on television may not represent the exact truth.
- Handwritten diaries of Adolf Hitler were published by a magazine in Hamburg city of Germany. Those diaries were later proved to be forged.
Mass Media and Professional Opportunities :
There are many professional opportunities available in printed, electronic and digital media.
- Newspaper : Writers, columnists, editors are required to write articles, columns and editorials in newspapers. Newspapers also require reporters to gather news and technicians to work in the press. Newspapers require photographer, writer, technician, computer operator, office staff.
- There is requirement of actors and technicians in electronic media.
- Akashvani : Require Office staff, centre head, Interviewer, news editor, technicians working in studio, manager, etc.
- Doordarshan : Artists are required to present programmes on television, in the same way news presenters, anchors are required. If the articles, columns and programmes are based on history, an expert in history is required. Journalist, news editor, cameraman, art director, lightman, technical director, interviewer, artists, make-up man, etc. are also required for television.
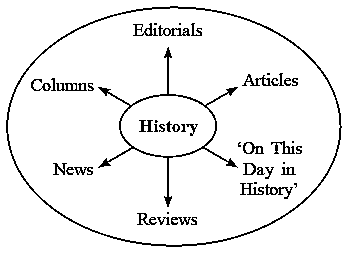
History Applied in Mass Media :
Newspapers :
- To unfold the background of an event in the news.
- If past references are required while reviewing the news.
- To make the columns like '50 years ago or 100 years ago' informative.
- In order to review the economical, social and political events knowledge of similar events in the past is very essential.
- While writing columns to commemorate the 100th year of an event having historical significance.
Akashvani :
- While presenting programmes, celebrating Independence Day or Republic Day references of speeches made by previous Prime Ministers and Presidents are given.
- Knowledge of history is essential while planning radio programmes.
- On occasions such as birth or death anniversaries of national leaders,
- Centennial Year or Golden Jubilee year, special programmes are presented giving information about their work.
- For presenting programmes like ‘On This Day in History‘ one needs to have knowledge of history.
- Knowledge of history is helpful while presenting programmes on historical events, leaders or conducting discussions on the same.
Television :
- While producing historical or mythological serials, maintaining accuracy with regard to the presentation of environment, outfits, weaponry, lifestyle, lingual expression, etc. is essential.
- We should have a deep understanding of history of the specific period.
- In order to present programmes on lives of players, soldiers, heroics of men and women achievers, empires, forts, heritage, etc. knowledge of history is necessary.
Important events and the year :
- 29-January-1780 — The first English newspaper ‘Bengal Gazette‘ started in India.
- 6-January-1832 — The first newspaper in Marathi ‘Darpan‘ started in Mumbai-
- 1852 — Telegraph services started in India.
- July-1924 — A private Radio Station started in Madras
- 23-July-1927 - The Frst English news bulletin was broadcast.
- 1929 — 'Pragati' a periodical was published.
- 1936 — Indian State Broadcasting Service (ISBS) started.
- 15 August, 1959 — The first Doordarshan Centre — Delhi Doordarshan was inaugurated by President Dr. Rajendra Prasad.
- 2 October, 1972 — Doordarshan Centre in Mumbai began its telecast.
- 15 August, 1982 — Colour Television was introduced.
- 1991 — Indian government granted permission for private, national, international channels to telecast in India.
Bharat Ek Khoj :
|
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 - History & Political Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter 4 -History of Indian Arts - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 6 - Entertainment and History - Online Notes |
