Chemical Reactions and Equations
Based on Class 10-Science & Technology Part-1-Chapter-3- Maharashtra Board
Solution
Question 1:
Choose the correct option from the bracket and explain the statement giving reason.
(Oxidation, displacement, electrolysis, reduction, zinc, copper, double displacement, decomposition)
a. To prevent rusting, a layer of ........ metal is applied on iron sheets.
a. To prevent rusting, a layer of zinc metal is applied on iron sheets. The rusting of iron is an oxidation process. Due to corrosion of an iron a deposit of reddish substance (Fe203.H2O) is formed on it. This substance is called rust. To prevent corrosion, a layer of zinc metal (galvanisation) is applied on iron sheets.
b. The conversion of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is ........ reaction.
b. The conversion of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is oxidation reaction. When ferric ion is formed from ferrous ion, the positive charge is increased by one unit. While this happens the ferrous ion loses one electron. A process in which a metal or its ion loses one or more electrons is called an oxidation. 2FeSO4 —-> Fe2(SO4)3 Fe2+ +SO42- —> 2Fe3+ + 3S042- Net reaction : Fe2+ --> Fe3+ +e- Ferrous Ferric
c. When electric current is passed through acidulated water ........ of water takes place.
c. When electric current is passed through acidulated water of electrolysis water takes place. This decomposition takes place with the help of an electric current, it is also called electrolytic decomposition. 2H2O(l) \( \underrightarrow {\text{Electric Current}}\) 2H2 ↑+ O2 ↑
d. Addition of an aqueous solution of ZnSO4 to an aqueous solution of BaCl2 is an example of ....... reaction.
d. Addition of an aqueous solution of ZnSO4 to an aqueous solution of BaCl2 is an example of double displacement reaction. Barium chloride reacts with zinc sulphate to form a white precipitate of barium sulphate. White precipitate is formed by exchange of ions Ba++ and SO4-- between the reactants.
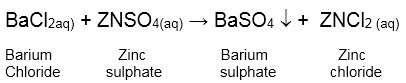
Question 2:
Write answers to the following.
a. What is the reaction called when oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously? Explain with one example.
The process in which oxidation and reduction occurs simutaneously is called as redox reaction. For example: If we add stannous chloride solution to the yellow solution of ferric chloride then light green ferrous chloride solution and stannic chloride solution are produced. 2FeCl3(aq) + SnCl2(aq) → 2FeCl2(aq) + SnCl4(aq) Before the reaction, 3Cl atoms were attached to each iron atom. After the reaction, only two chlorine atoms are attached. That is one negative chlorine atom is released. Therefore, reduction of FeCl3 happened or this reactor on the other hand, before reaction two chlorine atoms where attached with each atom of tin (stannum). Due to the above reaction the number of chlorine attached to tin atom increases to four. That is, oxidation of SnCl2 has taken place. Therefore, in this reaction oxidation of one substance and reduction of another substance take place simultaneously. This is called redox reaction.
b. How can the rate of the chemical reaction, namely, decomposition of hydrogen peroxide be increased?
At room temprature, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen takes place slowly.However the same reaction occures at a faster rate on adding manganese dioxide (MnO2) powder in it.
c. Explain the term reactant and product giving examples.
Reactant: The substance which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
Product: the substance which forms as a result of chemical reaction is called products.
The new substance produced as a result of chemical reaction is called products.
Example: When two sodium atoms react with two chlorine atoms(reactants), they give a completely new compound (product) i.e. sodium chloride (two atoms).
2Na+Cl2→2NaCl
d. Explain the types of reaction with reference to oxygen and hydrogen. Illustrate with examples.
There are main three types of chemical reactions with reference to oxygen and hydrogen: 3. Oxidation and reduction reaction: In the above reaction, copper oxide is changing to Cu. That is, oxygen is being removed from copper oxide. So, copper oxide is being reduced to copper.
1. Combination Reaction :
When two atoms react to form a compound, it is know as combination reaction.
Example: H2 + O2→ 2H2O
2. Decomposition Reaction :
When a compound breaks into simple molecular substances from which it is made up of, it is know as decomposition reaction.
Example: 2H2O→ 2H2 + O2
Oxidation:
(i) The addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation.
(ii) The removal of hydrogen to a substance is called oxidation.
Reduction:
(i) The addition of hydrogen to a substance is called reduction.
(ii) The removal of oxygen to a substance is called reduction.
Example: CuO+H2→Cu+ H2O
In the above reaction, H2 is changing into H2O. That is oxygen is being added to hydrogen. So, hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
e. Explain the similarity and difference in two events, namely adding NaOH to water and adding CaO to water.
Chemical equations involved: 2)CaO(s) +H2O(l) → Ca(OH)₂(aq) + Δ(HEAT) Similarities:
1) NaOH(s) + H2O(l) →Na⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq) + Δ(HEAT)
1) Both of the equations are exothermic. It means a lot of heat is evolved during the reaction.
2) Both reaction form strong basic solution.
Differences :
1) Sodium Hydroxide is strong base dissociates to form Na⁺ and OH⁻ ion. While Calcium oxide added water to form Calcium Hydroxide which further dissociates.
2) NaOH is a monoacidic base. and CaO is a Di-Acidic base.
3) NaOH, CaO should be added to water gradually with constant stirring. CaO on reacting with water produces basic solution called as Calcium hydroxide which is used for white washing and this reaction is more dangerous as compare to NaOH.
Question 3:
Explain the following terms with examples.
a. Endothermic reaction
Endothermic reaction : The reaction in which heat is absorbed is called an endothermic reaction. When KNO3(s) dissolves in water, there is absorption of heat during the reaction and the temperature of the solution falls. KNO3(s) + H2O(l) + Heat —-> KNO3(aq)
b. Combination reaction
Combination reaction:
Those reactions in which two or more substances combine to form single substance is called combination reaction
For example: Magnesium and oxygen combine, when heated, to form magnesium oxide.
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
c. Balanced equation
A balanced equation is an equation for a chemical reaction in which the number of atoms for each element in the reaction and the total charge are the same for both the reactants and the products. In other words, the mass and the charge are balanced on both sides of the reaction.
The balanced equation is:
2 Fe2O3 + 3 C → 4 Fe + 3 CO2
Both the left and right sides of the equation have 4 Fe, 6 O, and 3 C atoms.
d. Displacement reaction
Displacement reaction : The reaction in which the place of the ion of a less reactive element in a compound is taken by another more reactive element by formation of its own ions, is called displacement reaction. Examples of displacement reaction : (1) When zinc granules are added to the blue coloured copper sulphate solution, the zinc ions formed from zinc atoms take the place of Cu2+ ions in CuSO4 and copper atoms, formed from Cu2+ ions comes out i.e. the more reactive zinc displaces the less reactive Cu from copper sulphate. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s) + Heat (2) When iron powder is added to the blue coloured copper sulphate solution, the iron ions formed from iron atoms take the place of Cu2+ ions in CuSO4 and copper atoms, formed from Cu2+ ions comes out i.e. the more reactive iron displaces the less reactive Cu from copper sulphate.

Question 4:
Give scientific reasons. Limestone is made up of calcium carbonate. When calcium carbonate is heated Carbon dioxide is evolved. Lime water is made up of Calcium hydroxide.
a. When the gas formed on heating limestone is passed through freshly prepared lime water, the lime water turns milky.
When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, the Carbon dioxide reacts with calcium hydroxide to form Calcium carbonate which is a white precipitate, then lime water turns milky as there is formation of calcium carbonate.
CO2+ Ca(OH)2→CaCO3 + H2O
b. It takes time for pieces of Shahabad tile to disappear in HCl, but its powder disappears rapidly.
(1) The rate of a reaction depends upon the size of the particles of the reactants taking part in the reaction. Smaller the size of the reactants particles, the more will be their total surface area and faster will be the rate of reaction.
(2) In the reaction of dil. HCl with pieces of Shahabad tile, Co, effervescence is formed and the tile disappears slowly. On the other hand, CO2 effervescence forms at faster speed with Shahabad tile powder and it disappears rapidly.
c. While preparing dilute sulphuric acid from concentrated sulphuric acid in the laboratory, the concentrated sulphuric acid is added slowly to water with constant stirring. While preparing dilute sulphuric acid from concentrated sulphuric acid in the laboratory, the concentrated sulphuric acid is added slowly to water with constant stirring because sulphuric acid (H2SO4) reacts very vigorously with water, it is a highly exothermic reaction. If you add water to concentrated sulphuric acid, it can boil and bump out due to which you may get a nasty acid burn. Water is a good absorber of heat, so we add acid to the water, slowly and with constant stirring, In this way onlu a small amount of heat is libereted at a time and dilute sulphuric acid is prepared.
d. It is recommended to use air tight container for storing oil for long time.
It is recommended to use air tight container for storing oil for long time in order to avoid the problem of rancidity. Rancidity is the condition produced by aerial oxidation of fats and oils marked by unpleasant smell and taste.
Question 5:
Observe the following picture a write down the chemical reaction with explanation.
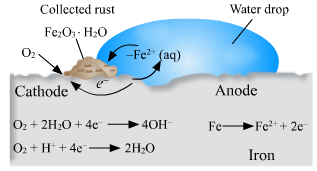
The rusting of iron is an oxidation process. The rust on iron does not form by a simple reaction between oxygen and iron surface. The rust is formed by an electrochemical reaction, Fe oxidises to Fe2O3.H2O on one part of iron surface while oxygen gets reduced to H2O in another part of surface, Different regions on the surface of iron become anode and cathode. (1) Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ in the anode region, Fe(s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e - (2)O2 is reduced to form water in the cathode region. O2(g)+4H+(aq)+4e- → 2H2O(l) When Fe2+ ions migrate from the anode region they react with water and further get oxidised to form Fe3+ ions. A reddish coloured hydrated oxide is formed from Fe3+ ions. It is called rust. It collect on the surface. 2Fe3+(aq) + 4H2O(l) → Fe2O.H2O(s)+6H+(aq)… Because of various components of atmosphere, oxidation of metals takes place, consequently resulting in their damage. This is called 'corrosion'. Iron rusts and a reddish coloured layer is collected on it. This is corrosion of iron.
Question 6:
Identify from the following reaction the reactants that undergo oxidation and reduction.
a. Fe + S → FeS
Fe + S → FeS
In a reaction, Fe is changing to FeS. That means, iron loses electrons to form FeS. Loss of electron from a substance is called oxidation, so iron undergoes oxidation.
b. 2Ag2O → 4 Ag + O2 ↑
2Ag2O → 4 Ag +O2↑
In a reaction, silver oxide is changing to silver. That is, oxygen is being removed from silver oxide. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so silver oxide undergoes reduction.
c. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In a reaction, magnesium is changing to magnesium oxide. That means, oxygen is being added to magnesium. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation, so magnesium undergoes oxidation.
d. NiO + H2 → Ni + H2O
NiO + H2 → Ni + H2O
In a reaction, Nickle oxide is changing to nickle. That is, oxygen is being removed from nickle oxide. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so nickle oxide undergoes reduction.In a reaction, hydrogen is changing to H2O. That is,oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation, so hydrogen undergoes oxidation.
Question 7:
Balance the following equation stepwise.
a. H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → H2SO4(l)
Step1. Count the number of each atom in reactant side:
H= 4
S=2
O=8
Step2. Count the number of each atom in product side:
H= 2
S=1
O=4
Step3. Then balance the number of each atom in an equation by multiplying reactant and product side with numeral value:
If we multiply product side by 2, then number of atoms in product and reactant side gets balance.
H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
b. SO2(g) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + H2O(l)
SO2(g) + H2S(aq) → S(s) + H2O(l)
Step1. Count the number of each atom in reactant side:
H= 2
S=2
O=2
Step2. Count the number of each atom in product side:
H= 2
S=1
O=2
Step3. Then balance the number of each atom in an equation by multiplying reactant and product side with numeral value:
If we multiply H2S by 2 in the reactant side and S by 3 and H2O by 2 in the product side, then number of atoms in product and reactant side gets balance.
SO2(g) + 2H2S(aq) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l)
c. Ag(s) + HCl(aq) → AgCl ↓+ H2 ↑
Ag(s) + HCl(aq) → AgCl ↓+ H2 ↑
Step1. Count the number of each atom in reactant side:
H= 1
Ag=1
Cl=1
Step2. Count the number of each atom in product side:
H= 2
Ag=1
Cl=1
Step3. Then balance the number of each atom in an equation by multiplying reactant and product side with numeral value:
If we multiply Ag by 2 and HCl by 2 in the reactant side and AgCl by 2 in the product side, then number of atoms in product and reactant side gets balance.
2Ag(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2AgCl ↓+ H2 ↑
d. NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
Step1. Count the number of each atom in reactant side:
Na= 1
H=3
O=5
S=1
Step2. Count the number of each atom in product side:
Na= 2
H=2
O=5
S=1
Step3.Then balance the number of each atom in an equation by multiplying reactant and product side with numeral value:
If we multiply NaOH by 2 in the reactant side and H2O by 2 in the product side, then number of atoms in product and reactant side gets balance.
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) +2H2O(l)
Question 8:
Identify the endothermic and exothermic reaction.
a. HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat
HCl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O + heat
Heat is released in the product side, as it mentioned in the above reaction. So, It is an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved in exothermic reaction.
b. 2KClO3(s) \( \underrightarrow {Δ}\) 2KCl(s)+3O2↑
2KClO3(s) \( \underrightarrow {Δ}\) 2KCl(s)+3O2↑
Heat is given in the product side to break the compound into simpler substances, as it mentioned in the above reaction. So, It is an endothermic reaction because heat is supplied in exothermic reaction.
c. CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat
Heat is released in the product side, as it mentioned in the above reaction. So, It is an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved in exothermic reaction.
d. CaCO3(s) \( \underrightarrow {Δ}\) CaO(s)+CO2↑
CaCO3(s) \( \underrightarrow {Δ}\) CaO(s)+CO2↑ Heat is provided in the product side to break the compound into simpler substances, as it mentioned in the above reaction. So, It is an endothermic reaction because heat is supplied in exothermic reaction.
Question 9:
| Reactants | Products | Type of chemical reaction |
| BaCl2(aq) + ZnSO4(aq) | H2CO3(aq) | Displacement |
| 2AgCl(s) | FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) | Combination |
| CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s) | BaSO4↓ + ZnCl2(aq) | Decomposition |
| H2O(l) + CO2(g) | 2Ag(s) + Cl2(g) | Double displacement |
Reactants
Products
Type of chemical reaction
BaCl2(aq) + ZnSO4(aq)
BaSO4↓ + ZnCl2(aq)
Double displacement
2AgCl(s)
2Ag(s) + Cl2(g)
Decomposition
CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Displacement
H2O(l) + CO2(g)
H2CO3(aq)
Combination
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : MSBSHSE -Class 10th Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Previous Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech.-1-Chapter-2-Periodic Classification of Element - Online Solution Next Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech.-1-Chapter-4-Effects of electric current - Online Solution |
