Life Processes in Living Organisms-1
Based on Class 10 -Science & Technology-Part 2-Chapter 2- Maharashtra Board
Solution
Question 1: Fill in the blanks and explain the statements.
(a) After complete oxidation of a glucose molecules, ---- --- --- number of ATP molecules are formed.
After complete oxidation of a glucose molecules, 38 number of ATP molecules are formed.
(b) At the end of glycolysis, ---- --- -- molecules are obtained.
At the end of glycolysis pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water molecules are obtained.
(c) Genetic recombination occurs in -- -- -- phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
Genetic recombination occurs in pachytene phase of prophase of meiosis-I.
(d) All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in -- -- -- phase of mitosis.
All chromosomes are arranged parallel to equatorial plane of cell in metaphase phase of mitosis.
(e) For formation of plasma membrane, --- --- --- molecules are necessary.
For formation of plasma membrane, phospholipid molecules are necessary.
(f) Our muscle cells perform -- -- -- type of respiration during exercise.
Our muscle cells perform anerobic type of respiration during exercise.
Question 2: Write definitions.
(a) Nutrition
Nutrition: The process by which organisms take up nutrients and utilise these nutrients for various biological activities is called nutrition.
(b) Nutrients
The substances like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, lipids, etc. which are components of the food are called nutrients. Nutrient helps us to stay healthy.
(c) Proteins
Proteins are a type of biomolecules which are made up of of several amino acids which are linked together by peptide bonds.
(d) Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is a process in which respiratory substrates such as starch, glucose, fats and proteins are broken down to release energy. This energy is then trapped for the synthesis of ATP to release CO2.
(e) Aerobic respiration
Cellular respiration occurs by two processes i.e. aerobic and anaerobic respiration. The process by which the breakdown of carbohydrates occurs in the presence of oxygen resulting in the release of energy in the form of ATP is called aerobic respiration.
(f) Glycolysis
The process occurring in the cell where a molecule of glucose is oxidized in step by step process forming two molecules of each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water, is called glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step in respiration.
Question 3: Distinguish between
(a) Glycolysis and TCA cycle.
| Krebs Cycle/TCA cycle | Glycolysis |
| It is a cyclic pathway. | It is a linear pathway. |
| Substrate is acetyl-CoA. | Substrate is glucose. |
| Occurs in the matrix of mitochondria | Occurs in the cytoplasm |
| It produces oxaloacetic acid, NADH2, FADH2, ATP and CO2. | It produces pyruvic acid, NADH2 and ATP. |
| It does not consume ATP. | It consumes 2 ATP molecules. |
| It generates 2 GTP/ATP molecules from 2 acetyl-CoA molecules. | It generates 2 ATP molecules from 1 glucose molecule. |
| Occurs only in eukaryotes | Occurs in eukaryotes as well as in prokaryotes |
(b) Mitosis and meiosis.
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| In mitosis the chromosome number does not change. Diploid cells remain diploid, without change. | In meiosis, the chromosome number is reduced to half. The diploid cells become haploid. |
| One cell gives rise to two daughter cells in mitosis. | One cell gives rise to four daughter cells in meiosis |
| Karyokinesis of mitosis has four stages, viz. prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. | Meiosis has two major stages, viz. meiosis-I and meiosis-II. Each is further subdivided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. |
| The prophase stage is short. | Prophase of meiosis I is very lengthy. |
| Genetic recombination does not happen in mitosis as there is no crossing over. | Genetic recombination takes place in homologous chromosomes as there is crossing over during prophase-I. |
| It plays a significant role in cell growth, repair, and healing of wounds. | Meiosis is essential for formation of gametes in sexual reproduction. |
| Mitosis takes place both in somatic cells and germinal cells. | Meiosis takes place in only germinal cells. It does not take place in somatic cells. |
(c) Aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
| Anaerobic respiration | Aerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen is required for aerobic respiration. | Oxygen is not required for anaerobic respiration. |
| Aerobic respiration takes place in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm. | Anaerobic respiration occurs only in the cytoplasm. |
| At the end of aerobic respiration CO2 and H2O is formed. | At the end of anaerobic respiration CO2 and C2H5OH are formed. |
| Energy is produced in large amount in aerobic respiration. | Energy is produced in lesser amount in anaerobic respiration. |
| Glucose is completely oxidized in aerobic respiration. | Glucose is incompletely oxidized in anaerobic respiration. |
| 38 molecules of ATP are formed during aerobic respiration. | 2 molecules of ATP are formed during anaerobic respiration. |
| Chemical reaction :
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6H2O + 6CO2 + 686 Kcal |
Chemical reaction :
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 +50 Kcal |
Question 4: Give scientific reasons.
(a) Oxygen is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
- When glucose is fully metabolized via aerobic cellular respiration. It generates 38 molecules of ATP.
- During cellular respiration, three processes occur: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain reactions.
- In the absence of oxygen, only glycolysis can continue, but the remaining two processes will not occur.
- If glycolysis happens in the absence of oxygen, it creates alcohol. Anaerobic glycolysis produces just two molecules of ATP. This leads in a lower supply of energy to the body.
- Therefore, oxygen is required for full oxidation of glucose.
(b) Fibers are one of the important nutrients.
Fibers are one of the important nutrients because they help in the digestion of foods although they themselves are not digestible. They help in the egestion of undigested substances which is also a reason why we are advised to have fiber rich food in case of constipation. Fibers are naturally present in leafy vegetables, fruits, cereals, etc.
(c) Cell division is one of the important properties of cells and organisms.
Cell division is very essential for all the living organisms.
- The growth and development is possible only due to cell division.
- The emaciated body can be restored only through the cell division which adds new cells.
- Offspring is produced only through the cell division that take place in parents.
- In asexual reproduction, mitosis helps to give rise to new generation.
- In sexual reproduction, meiosis helps to form haploid gametes.
All such functions show that cell division is one of the important properties of cells and organisms.
(d) Sometimes, higher plants and animals too perform anaerobic respiration.
- When there is deficiency of oxygen in the surrounding, the aerobic respiration is not possible. In such case, to survive, higher plants switch over to anaerobic respiration.
- In some animal tissues in case of oxygen deficiency cells perform anaerobic respiration and results in the production of lactic acid.
- Although the energy obtained through anaerobic respiration is less as compared to the energy released during aerobic respiration.
(e) Kreb's cycle is also known as citric acid cycle.
- Sir Hans Kreb proposed this cycle and hence it is called Krebs cycle.
- These are a sequence of cyclic chain reactions that start with oxaloacetic acid molecules reacting with acetyl-coenzyme-A molecules.
- Certain enzymes aid in the catalysis of the processes. Citric acid is the first molecule to produce in this process.
- Thus, the citric acid cycle is another name for the Krebs cycle.
Question 5: Answer in detail.
(a) Explain the glycolysis in detail.
Glycolysis was first given by Embden, Meyerhof and Parnas, and is referred to as EMP pathway. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms. For the discovery they had performed experiments on muscles.
The steps involved in the partial oxidation of glucose to form pyruvate are as follows:
Figure
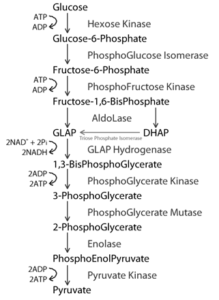
In this pathway, Carbohydrates are converted to glucose after the process of digestion is completed. The oxidation of glucose for releasing energy is called glycolysis which takes place in cytoplasm.
- Glycolysis can occur in presence of oxygen or without oxygen too. The first type of glycolysis takes place in aerobic respiration and the second type is in anaerobic respiration.
- In aerobic respiration, there is step-wise oxidation of glucose molecule forming two molecules each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2 and water.
- Later the pyruvic acid formed in this process is converted into molecules of Acetyl-Coenzyme-A along with two molecules of NADH2 and two molecules of CO2.
- During anaerobic respiration along with glycolysis there is fermentation too. This is incomplete oxidation of glucose and thus it results in formation of lesser energy.
(b) With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the mitosis in detail.
Mitosis is the process of equational cell division where daughter cells, so produced, contain an equal number of chromosomes as that in the parent cell.
- There are two stages of mitosis. These are Karyokinesis or nuclear division and Cytokinesis or cytoplasmic division.
- Karyokinesis takes place in further four phases, viz prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
Karyokinesis :
(i) Prophase: It is the first stage of mitosis that is marked by the initiation of the condensation of chromosomal material. Each chromosome is composed of two chromatids, which are attached by the centromere. At the end of prophase, the mitotic spindle begins to form from the centrioles. The nuclear membrane and the nucleolus disappear completely by the end of this stage.
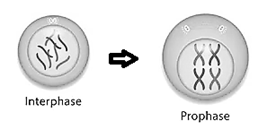
(ii) Metaphase: It is the second stage of mitosis in which the condensation of the chromosomal material and the spindle formation gets complete.
The spindle fibres get attached to the kinetochores of the chromosomes and the chromosomes get aligned along the metaphase plate in the middle of the nucleus.

(iii) Anaphase: It is the stage of mitosis where the centromere of the chromosomes split and the chromatids get separated. The contraction of the spindle fibres moves the sister chromatid apart, towards the two opposite poles.
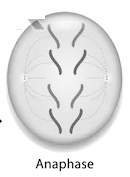
(iv) Telophase: It is the last stage of mitosis. In this stage, chromosomes finally reach their respective poles. The spindle fibres disappear and the nuclear envelope reappears around the chromosome cluster. Also, the nucleolus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, and other cell organelles re-appear.

Cytokinesis : In animal cells a notch develops in the middle of the cell. This notch goes on deepening down and later the cytoplasm divides into two. In plant cells, cell plate formation takes place and then cytokinesis takes place.
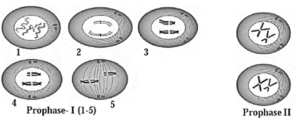
(c) With the help of suitable diagrams, explain the five stages of prophase-I of meiosis.
Prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis and is further sub divided into 5 phases:
- Leptotene− Condensation makes chromosomes become distinct and compact.
- Zygotene − Homologous chromosomes start pairing together by a process called synapsis to form a complex structure called synaptonemal complex. Two synapsed homologous chromosomes form a complex called bivalent or tetrad.
- Pachytene − Longest phase of prophase IRecombination nodules appear in this stage at the sites where crossing over has to take place between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
- Diplotene − Synaptonemal complex dissolves and recombinants separate from each other except at crossover sites to form X-shaped structure called chiasmata.
- Diakinesis− Chiasmata terminalises and chromosomes condense. Meiotic spindle assembles and nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear.
(d) How all the life processes contribute to the growth and development of the body?
Life processes are processes which are required to maintain body functions and are necessary for survival. The important life processes are nutrition, transportation, metabolism, reproduction, respiration, and excretion. All these processes work together and result in the growth and development of the body.
For example,
- The digested and absorbed nutrients of the food are transported to various cells with the help of circulatory system due to pumping of the heart. Simultaneously, the oxygen absorbed in the blood by lungs is also transported to each cell by RBCs.
- Mitochondria in every cell brings about Oxidation of nutrients and produce energy required for all of these functions.
- The control is exercised by the nervous system on all these actions. This keeps the organism alive and helps in growth and development of the same.
(e) Explain the Kreb's cycle with reaction.
Krebs cycle was proposed by Sir Hans Kreb. This cycle is named after him. It is also called tricarboxylic acid cycle or citric acid cycle.
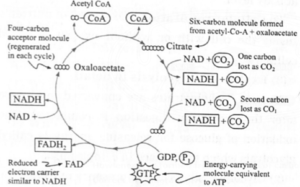
- Krebs cycle is a cyclic process that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix, in the presence of oxygen.
- The acetyl-coenzyme-A molecules enter the mitochondria located in the cytoplasm.
- They participate in the chemical reactions taking place in Krebs cycle.
- In the cyclic chemical reactions, acetyl-coenzyme-A is completely oxidised
- It yields molecules of CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 and ATP upon complete oxidation.
Question 6:
How energy is formed from oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins? Correct the diagram given below.

- First, the digestive system uses a variety of enzymes to break down and transform dietary carbs into glucose. In a similar way, fats are broken down into glycerol (alcohol) and fatty aid, and proteins into amino acids.
- Carbohydrates are oxidized during the process of cellular respiration. During aerobic respiration, glucose is oxidized in three steps: the electron transfer chain, the Krebs cycle, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and glycolysis.
- During glycolysis, two molecules of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH2, and water are created from one glucose molecule. The pyruvic acid produced in this step is transformed into Acetyl-Coenzyme-A and two molecules of CO2 and NADH2 are released simultaneously.
- In the next step, i.e. in TCA cycle molecules of Acetyl-CO-A enter the mitochondria and a cyclic chain of reactions take place. Acetyl part of Acetyl-CO-A is Completely oxidized through this cyclical process. The molecules CO2, H2O, NADH2, FADH2 are released in this process.
- In third step, i.e. in ETC reaction, NADH2 and FADH2 formed during first two steps are used for obtaining ATP molecules. 3 molecules of ATP are obtained from each NADH2 molecule and 2 molecules of ATP from each FADH2.
- Thus, one molecule of glucose upon complete oxidation in presence of oxygen yields 38 molecules of ATP. This is how from carbohydrates, energy is obtained.
-
If carbohydrates are insufficient in diet, then proteins or lipids are used for energy production. Fatty acids derived from fats and amino acids derived from proteins are converted into Acetyl-CO-A. Acetyl-CO-A once again can yield energy through TCA cycle.

Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter 1. Heredity and Evolution - Online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 3. Life Processes in living organisms Part -2 - Online Solution |
