Sound: Production of Sound
Maharashtra Board-Class 7th-General Science-Chapter-18
Notes
Topics to be Learn:
|
Production of sound : Sound is generated by the rhythmic vibrations of an object.
When vibrations are produced in the objects, all these vibrations are imparted to the molecules in the air and get transferred from one molecule to the other. In this way, the vibrations reach our ears and the sound is heard.
Pitch of a sound : In Indian music, the musical notes, Sa, Re, Ga, Ma Pa Dha Ni are of increasingly higher pitch; i.e. of increasingly higher frequency. In scientific terms frequency is a measure of pitch.
Periodic motion : The object moves to one side of the central position and comes back to the central position while vibrating. This motion of an object is repeated again and again at fixed intervals of time. Such motion of an object is called periodic motion.
Vibrations, that produce sound, can be studied with the help of a simple ‘oscillator’.
Motion of a swing : A swing is an oscillator. The motion of a swing is an oscillatory motion.
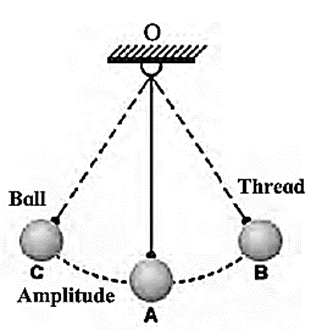
Simple oscillator or simple pendulum : The object moving from one end to the other end of its central position, again and again in fixed intervals of time is called a simple oscillator or simple pendulum.
Oscillatory Motion of Oscillator : The back and forth motion of an oscillator on either side of central position is called oscillatory motion.
Oscillation of Oscillator: When an oscillator moves from one end to the other a returns to its starting point, it is said to have completed one oscillation.
Amplitude : The maximum distance Covered by an Object on any one side of its central position while undergoing vibrations, is called amplitude of vibration.
Pendulum : An oscillator which is made up of a small iron or wooden ball tied to a half a meter long strong thread and the other end of the thread is tied to a fixed support such that the ball is freely suspended in the air. Such an oscillator is called a pendulum
Elasticity : A stretched rubber comes back to its original state on releasing. This property is called elasticity.
- When a stretched rubber band vibrates, elasticity works on the stretched rubber band.
- While the pendulum oscillates, earth’s gravitation works on it.
Time Period of Oscillation : The time taken by an oscillator to complete one oscillation is called the time period of the oscillator.
- Time period is denoted by letter ‘T’.
- Time period is measured in seconds.
Frequency of Oscillation : The number of oscillations completed by an oscillator in one second is called the frequency of oscillation.
- Example : Consider, an oscillator completes 30 oscillations in one second, then the frequency of that oscillator is 30 Hertz.
Unit of frequency : Hertz is a unit of frequency
- e.g. Frequency of 1 Hz means one oscillation in one second. Frequency of 100 Hz means there are hundred oscillations in one second.
- Frequency is denoted by letter ‘η’
- Frequency (η) = \(\frac{1}{\text{Time period of oscillation (T)}} = \frac 1T\)
Interrelation between length of the pendulum, its period of oscillation and frequency :
High and Low Pitch of Sound :
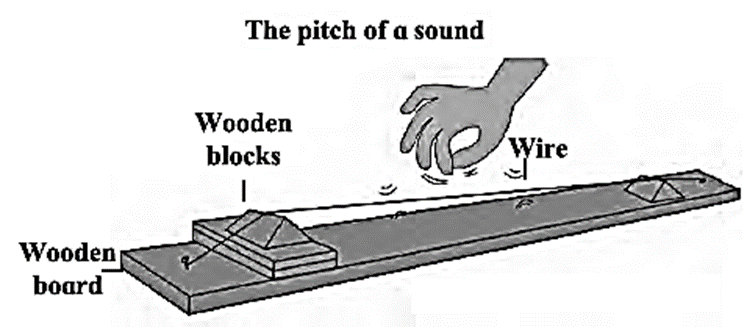
- When the tension in the wire is increased, the frequency increases and if the tension in the wire is decreased, the frequency decreases.
- When the tension in the wire is increased, the sound produced by the vibrating wire is shriller. On the other hand, when the tension is reduced, the sound is less shrill. This is called the high and low Pitch of Sound.
Intensity of sound and sound level :
Sound levels of some common sounds :
Hearing gets temporarily affected by sounds of frequency greater than 1000 Hz and levels of sound higher than 100 dB. This can result in temporary deafness This is experienced by the workers who work near aeroplane engines.
Audible sound : The human beings can hear the sounds having frequency between 20 Hz to 20000 Hz. Therefore, the sounds with frequency 20 Hz to 20000 Hz is called audible sounds.
Infrasonic sound : A sound having frequency less than 20 Hz is not audible to the human being. Therefore, the sound having frequency less than 20 Hz is called infrasonic sound.
- Sounds having a frequency less than 20 Hz are produced and can be heard by whales, elephants, hippopotamous and rhinoceros.
Ultrasonic sound : A sound having a frequency higher than 20000 Hz is called ultrasonic sound.
- Ultrasonic sounds cannot be heard by human beings.
- Some animals like dog, cat, dolphin, sea lion and bat can hear such sounds.
Uses of ultrasonic sound : Humans have used ultrasonic sounds in different equipments and technologies.
Pitch of sound and frequency of sound : 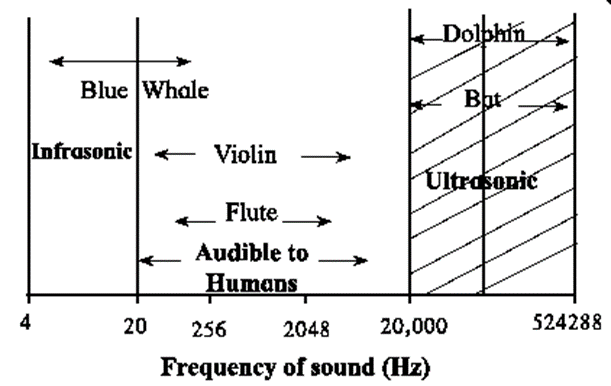
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 17 : Effects of Light - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-19- Properties of a Magnetic Field-Online Notes |
