The living world: Adaptations and Classifications
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 7th General Science Chapter 1
Adaptations
| Adaptations are the changes that take place in the various organs and life-processes of organisms, so as to enable them to live, feed, reproduce and protect themselves from their enemies in specific habitat and its geographical conditions . |
- Adaptations is long term gradual and continuous process.
- Adaptations helps them to adjust their surroundings.
- The structure and appearance of present day animals and animals of thousands of years ago are different from each other.
 Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who proposed the theory of biological evolution by natural selection.
Charles Darwin was a British naturalist who proposed the theory of biological evolution by natural selection.
Survival of the fittest : Only those organisms are likely to survive which can best adapt themselves to a changing environment.
Theory of natural selection : If an organism is born with new beneficial characteristic and is able to survive, this change is preserved in next generation.
[/responsivevoice]Adaptations in plant
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]In this lesson, we will talk about plant adaptations.
These are changes that help a plant species survive in its environment.
We will see how plants survive underwater, in the desert, and where the soil lacks nutrients.
Example, the seaweed is a plant adapted for its underwater environment.
Cacti are adapted for the desert environment.
Venus fly trap plant that is adapted for living in soil that doesn't provide enough nutrients.
Some plants even have their own self-defense system in place to ward off insects and other critters. The rose bush, for example, has thorns to keep away predators.[/responsivevoice]
| Aquatic plants are plants that have adapted to living in aquatic environments (saltwater or freshwater). |
First, the seaweed. This is an aquatic plant. It is adapted for underwater life.
This plant has its own air bubble in each leaf that provides the necessary space for the exchange of oxygen from the water to the plant.
It also helps keep the seaweed upright. T
he leaves of underwater aquatic plants are also softer then above ground plants. This softness allows the plant to move easily with the waves without breaking.
Adaptations in Aquatic plants:
- Firmly rooted in soil and submerged stems. Some plants entirely afloat with floating roots while some submerged in water.
- Stems and petioles are soft, flexible, leaves and flowers float on water.
- Some plants have thin ribbon shaped slender leaves. This is an adaptation to withstand fast currents of water.
- Leaves and stems coated with waxy layer and air spaces inside the stem and leaves, Adapted for floating.
[/responsivevoice]
 Pistia stratiotes, an example of a pleuston, a plant that floats freely on the water surface |
 Bud of Nelumbo nucifera, an aquatic plant. |
 Many liverworts grow either submerged or on land. |
 Ceratophyllum submersum, a free-floating plant that grows completely submerged |
 Water lilies grow rooted in the bottom with leaves that float on the water surface. |
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Plants and animals living in the desert need special adaptations to survive in the harsh environment.
 Deserts are the home to many living things. In fact, deserts are second only to tropical rain-forests in the variety of plant and animal species that live there.
Deserts are the home to many living things. In fact, deserts are second only to tropical rain-forests in the variety of plant and animal species that live there.
How do you think plants grow in a place that is very, very dry?
Many of the fascinating features of desert plants are adaptations -- characteristic that help the plant survive in its harsh environment.
Desert plants have two main adaptations:
Ability to collect and store water
Features that reduce water loss
- Roots of the desert plants penetrate deep in the soil in search of water.
- Thick layer of waxy substance on stems
- Leafless of leaves like small needles.
- Some leaves seen to be modified into thorns for conserving water. Very little water is lost by evaporation.
- The stems are fleshy as water and food is stored in them.
- Modified stems performed photosynthesis and hence are green.
Example -Cactus, Acacia [/responsivevoice]

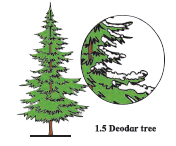
1.Conifers like deodar and pine are seen in snowy regions.
2. Tress are conical in shape with sloping branches.
3. Due to heavy snowfall and extreme cold weather, such adaptations are seen.
4. Conical shape prevents accumulation of snow on the tree.
5. Thick bark helps the tree to withstand the cold. [/responsivevoice]
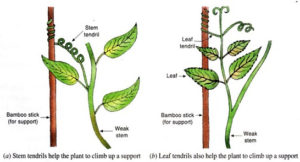
1.All the plants compete for sunlight. Tree goes tall to capture the sunlight, and climbers and vines grow with the support of trees.
2. A diverse variety of plants trees, herbs and shrubs seen in the forests.
3. Climbers have adopted by having spring like tendrils with which they seek support from host tree.[/responsivevoice]
 |
 |
1.Bushes and grasses of diverse types are seen in grasslands.
2. Vast meadows are found in plains and hilly areas
3. Soil erosion is prevented by fibrous roots of grasses.
4. Very tall grasses are seen in the equatorial region. Various types of large animals take shelter in these grasses.
5. Very short grass grow in cold regions. Smaller animals like rabbits are seen in these grasses. [/responsivevoice]

Grassland plants (grow from the bottom) are resistant to grazing and fire. Wind dispersal of seeds. Examples: Lush perennial grasses, few scattered trees.
1.Most of the plants are autotrophic.
2. Some plants are parasitic. e.g. Dodder(Cuscuta) which is leafless and thus can't perform photosynthesis.
3.There are haustorial roots for sucking and absorbing nutrients from the host plant. It grows on host plant.
4. Fungi can not perform photosynthesis as they lack chlorophyll and they obtain food from starchy foodstuffs. Root like fibres are present in them for absorption of food.
5. Plants like Drosera(sundew) , Venus flytrap, pitcher plant, etc. consumes insects to fulfill their need for nitrogen. The plants in nitrogen deficient are usually insectivorous plants. Such plants have structural adaptations to attract insects and hold them captive.[/responsivevoice]
Adaptations in animals
Aquatic animals have lots of adaptations for moving in the water, like a streamlined design, flippers, and a swim bladder, which acts like a ballast for the fish. Oxygen is transferred from water through organs called gills in fish, sharks, and rays.
1.The aquatic animals show modified structure of body
2.Tapering spindle shaped body with scales and fins for swimming.
3.Respiration by gills. Air bladders within the body for floating. [/responsivevoice]
The Amphibians term was initially used as a general adjective for animals that could live on land or in water.
Amphibious Animals. Animals that live both on land and water are called amphibious animals. Some other animals like water-snakes, crocodiles, tortoises,crabs also spend a part of their life in water and a part on land
Frog is an amphibian. It inhabits both land and water. Being a true amphibian, it can breath in water with the help of skin and when on land it breathes with nose and lungs.
Duck is a bird it cannot take oxygen dissolved in water. It breathes only with the help of lung.
Tortoise is a reptile that can not breath in water. It puts its nose out of water to get some air.
There are webbed toes in frog and duck oar-like legs. Both these helps in swimming.
Waxy coating on feathers help in quick draining of water in birds like duck and waterhen. [/responsivevoice]
Carnivorous Animals
1- Legs : Strong with sharp claws
2- Gait : Silent walker
3 - Eyes : Front of head. Keen eyesight to spot the pray from long distance.
4-Teeth : Pointed canines.
5- Ears : Small
Ex.: Wild dog, fox, tiger and lion
Herbivorous Animals
1- Legs : Log, tapering legs with strong hooves
2- Gait : Running and leaping fast
3 - Eyes : Below the forehead, on either side of head
4-Teeth : Strong molars
5- Ears : Long and freely moving
Ex.: Deer Antelope [/responsivevoice]
Staying in the shadow (shade) of plants or rocks, thus avoiding the direct rays of the Sun.
These animals also seek shelter by burrowing into the ground.
Another behavioral adaptation used by desert animals is to remain inactive during the hot daylight hours. They hunt at night when temperatures are cool and when there is less risk of losing precious body water.
Some animals get all of the water they need from the insects, bulbs, and seeds they eat. They will not drink water even when it is available.
Characteristics in camel: Long legs with flat and cushioned soles, folds of skin over the nostrils, long and thick eyelashes. Thick skin to conserve water in the body.
Ex. Rats, snakes, spiders, lizards in deserts [/responsivevoice]
White and silver colour body helps it blend in with the white background
Thick skin and thick hair on the skin protect it from cold
They huddle together in groups to keep themselves warm
They have webbed feet and they streamline their body while swimming which makes them good swimmers
Ex.: Yak, Polar bear, White fox, Silver fox, Mountain goat, Siberian husky dog and snow leopard [/responsivevoice]
Spindle shaped body minimizes the resistance of air while flying.
Feathers covering the body
Forelegs modified into wings.
Air sacs in the body to increase buoyancy.
Hollow bones making body light in weight and adapted for flying. [/responsivevoice]
Here are some adaptations insects can have:
Light weight and tapering body.
Two pairs of wings for flight
Six stick-like walking legs.
Insects can be camouflaged. Insects that look like their environment won’t be seen by predators such as birds and lizards.
Some insects look like sticks, leaves, and thorns. This type of adaptation helps insect survive by blending in with their surroundings so they aren’t eaten or so that prey doesn’t see them hiding. [/responsivevoice]
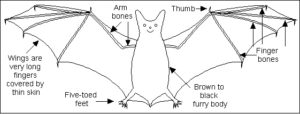
Bats are the only mammals that are able to fly.
Thin fold of skin between their forelegs and hind legs called patagium, that enable them to fly effectively.
Light weight and ability to hang.
Bats are nocturnal animals, normally sleeping during the day in shelters such as caves or empty buildings. This behavioral adaptation enables them to hide from predators. [/responsivevoice]
Reptiles use their muscles for creeping
Ex. House Lizard, Garden lizard, Crocodile
Snakes use scales on their skin for creeping.
Body colour shows camouflage to hide with surroundings [/responsivevoice]
Animals are either herbivores and carnivores, Few are omnivores.
According to their feeding there are some special adaptations. [/responsivevoice]
Many animals use camouflage, which means they are able to blend in with the color, pattern, or texture of their surroundings so they are not detected by a predator.
An animal may be camouflaged all the time, or it may change its coat or skin depending on the surroundings. [/responsivevoice]
Classification of plants and animals
It is necessary to classify the living things because it is difficult to study and remember all the diverse organisms in this world.
Different scientists used different criteria and gave the methods of classification.
All living organisms are classified into groups based on very basic, shared characteristics.
Organisms within each group are then further divided into smaller groups. These smaller groups are based on more detailed similarities within each larger group.
The classification of living things includes 7 levels: kingdom, phylum, classes, order, families, genus, and species . This is known as hierarchy of classification. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
The main purpose of classifying plants is to ensure that the right plants are correctly named grouped and are identified regardless of where it is on earth.
Plants are classified into:
- The evergreens are plants that retain leaves at all times (all year round).
- Woody plants can also be grouped as deciduous or evergreen.
- Deciduous plants are seasonal plants which shed its leaves at the end of the growing season, either during the winter season in the temperate climate or during the dry season in the tropical climate.
Apart from the above features, there are some plant species which can be classified based on their height, shape of stems, period of life cycles, their habitat, flowering, non-flowering plants. [/responsivevoice]
Animals are classified according to cell structure, body plan, vertebral column, method of reproduction and habitat.
- With the help of classification, characters of animals with which they adapt to the given environment can be known.
- There are millions of organisms and it is difficult to study each of them. The study of selected animals of a particular group can give us an idea about the remaining animals of that group.
- The knowledge about relationships of different animals with other animal species comes from classification. [/responsivevoice]
Carolus Linnaeus, Father of Taxonomy developed the Binomial System of nomenclature
which is the current scientific system of naming the species.
He described about 5,900 species of plants in ‘Species Plantarum’ and 4200 species of animals in “Systema Naturae”.
Every organism has given uniform name throughout the world. This is called scientific name.
Scientific name consists of two parts 1. Genus 2. Species.
As per the international code of nomenclature every organisms has a binomial name
Only organism belonging to the same species can produce an offspring.
All the organisms belonging to the same species may have difference in colour, height, habitats and habits but still they can reproduce among themselves and form offspring like themselves.
Advantages of using scientific names for an organism
- The scientific name remains the same world wide and hence is easily recognizable.
- The possibility of confusion due multiple name s given to the same organism in different parts of the world is eliminated by scientifically naming the organism.
- A relationship between different species of organisms in a particular genus can be deduced by scientific names.
- It also helps in recognizing or identifying any new organisms discovered.
- Any incorrect name to a particular organism can be corrected.
- The scientific names provided are often descriptive and also indicate some important characteristics of the org [/responsivevoice]
Scientists use a two-name system called a Binomial Naming System.
Scientists name animals and plants using the system that describes the genus and species of the organism.
The first word is the genus and the second is the species. [/responsivevoice]
Scientific names of plants.
| Common Name | Scientific Names |
| Sunflower | Helianthus annuus |
| Mango | Magnifera indica |
| Neem | Azadicta indica |
| Rose | Rosa |
| Tulsi | Ocimum tenuiflorum |
Scientific names of animals
| Common Name | Scientific Names |
| Dog | Canis lupus |
| Housefly | Musca domestica |
| Tiger | Panthera tigris |
| Lepoard | Panther pardus |
| Lion | Panthera leo |
| Bear | Ursidae carnivora |
| Crow | Corvus splendens |
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
World Frog Protection Day is observed on 29th April.
This is for creating awareness about conservation of frog .
According to wild life protection act killing or harming frog is prohibited. [/responsivevoice]
Video
Click on below link to watch video of this chapter
1- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="Sfy93k2oORw&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-1"]
Solution
Question 1:
Find my match!
| 'A' Group | 'B' Group | ||
| (1) | Lotus | (a) | Flower and leaves attract insects |
| (2) | Aloe | (b) | Haustorial roots for absorption of food |
| (3) | Cuscuta | (c) | Adapted to live in deserts |
| (4) | Venus flytrap | (d) | Adapted to live in water |
‘A’ Group
‘B’ Group
(1)
Lotus
(d)
Adapted to live in water
(2)
Aloe
(c)
Adapted to live in deserts
(3)
Cuscuta
(b)
Haustorial roots for absorption of food
(4)
Venus flytrap
(a)
Flower and leaves attract insects
Question 2:
Read the paragraph and answer the following questions.
I am a penguin. I live in polar region covered by snow. My abdomen is white. My skin is thick with a layer of fat underneath. My body is spindle-shaped. My wings are small. My toes are webbed. We live in flocks.
(a) Why is my skin white and thick and why is there a thick layer of fat underneath?
Having black and white skin is a type of adaptation known as camouflaging. It is called counter-shading and makes it harder for both the predators and the prey to see penguins from all sorts of angles. The white chest of penguin protects them in the water by camouflaging them from being seen from below against the lighter sky coming through the waters surface. Their black backs help them blend in with the darker, deeper ocean waters below them, thus protecting them from their predators. They have thick layer of fat because it keeps them warm under such extreme cold conditions.
(b) Why do we live in flocks sticking close to each other?
We know that penguins live in the coldest regions of earth and in order to find warmth and solace they remain in flocks with each other. In order to escape the extreme cold conditions, they nestle together to keep each other warm.
(c) Which geographical region do I inhabit? Why?
Penguins are found in regions of Antarctica, South America, Africa and Australia. Many species can also be found in New Zealand and the sub-Antarctic islands.
(d) Which adaptations should you have to enable you to live permanently in the polar region? Why?
The following adaptations are required to survive in polar regions:
Question 3:
Who is lying?
(a) Cockroach – I have five legs.
(b) Hen – My toes are webbed.
(c) Cactus – My fleshy, green part is a leaf.
The cockroach is lying beacuse it has six legs and not five.
The cactus is also lying because its fleshy, green part is a stem and not a leaf.
Question 4:
Read each of the following statements. Write a paragraph about adaptation with reference to each statement.
(a) There is extreme heat in deserts.
There is extreme heat in deserts and dry conditions prevail in this region. The animals and plants which are found in this region have special modifications which help them to survive in such environment. For example, cactus and acacia plants withstand hot and dry environment of the desert with the help of various modifications. They have thick cuticle on their leaf surface and their stomata are arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss by transpiration. They have special photosynthetic pathway, CAM in which stomata remains closed during day time. Their leaves are reduced to spines to minimise water loss, and photosynthetic functions are performed by flattened stems.
Similarly desert animals have adaptive features like- thick skin to prevent the loss of water, long legs with flat and cushioned soles, long and thick eyelashes and nostrils which are protected by folds of skin.
(b) Grasslands are lush green.
Grasslands are lush green due to the presence of diverse types of bushes and grasses. Grasses are tall so that animals like tiger, lion, elephant can remain hidden in them. Animals which are found in grasslands have adaptations like strong legs to run fast and capture their prey, claws, sharp and pointed canine. The herbivores which are found in this region have eyes below the forehead which gives them wide angle vision which protects them from predators.
(c) Insects are found in large numbers.
Insects are found in large numbers because they have developed mechanisms which help them to survive even in harshest of environment. They are found in extreme conditions of deserts and Antartic region due to these modifications. For example grasshopper have long, strong hind legs that help them jump, house flies have sponging mouthparts to slurp up food, stinky bugs and walking sticks have the ability to camouflage.
(d) We hide.
There are certain species which are able to hide themselves by blending their colour with that of the surrounding. This adaptive mechanism is termed as camouflage and is a method to protect oneself from the predators and prey. For example, grasshopper, lizards, butterflies, chameleon, frogs etc.
(e) We have long ears.
Animals with long ears are found in grasslands. It is an adaptive mechanism which enables them to receive sounds from long distances and from different directions. Another important function of long ears is that they act as a cooling system. The large ears have thin skin and contain an extensive network of blood vessels that provide a large surface area for heat exchange. These vessels swell when the animal is hot to allow the blood to cool and contract when temperatures drop to conserve heat.
Question 5:
Answer the following.
(a) Why is the camel called the 'Ship of the desert'?
Camel is called the “Ship of Desert” because it is the only means of transport found in deserts. The body of a camel has undergone various modifications that help it to survive in the hot and dry conditions of the deserts.
(b) How can the plants like cactus and acacia live in deserts with scarce water?
Cactus and acacia plants withstand hot and dry environment of the desert with the help of various modifications. They have thick cuticle on their leaf surface and their stomata are arranged in deep pits to minimise water loss by transpiration. They have special photosynthetic pathway, CAM in which stomata remains closed during day time. Their leaves are reduced to spines to minimise water loss and photosynthetic functions are performed by flattened stems.
(c) What is the inter-relationship between adaptations of organisms and their surroundings?
Adaptation is defined as the modification or change in the organism’s body or behaviour that helps it to survive in a particular environment. The environment in which an animal survives consists of many different things and it must learn to adapt to each of these factors in order to survive. These factors can be in the form of climate, the kinds of food plants that grow in it, other animals that may be predators or competitors etc. This fact is evident from the following examples:
(d) How are organisms classified?
The hierarchy of classification was developed by Carolus Linnaeus. It refers to the organisation or classification of organisms in the order of rank or importance. According to this system, kingdom is the highest rank. It is divided into phyla or divisions, which are further subdivided into classes. Further divisions include order, family, genus and species, in that order. Thus, species is the basic unit of classification.
Test
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 7 Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Next Chapter : Chapter 2 : Plants : Structure and Function - Notes |

In which habitat we survive ? and why ?
Unlike animals, we humans are able to adapt to different habitats quickly because we can bundle up in jumpers and blankets if it’s cold, or sit in a paddling pool with an ice lolly if it’s hot. We are also able to adapt habitats to suit ourselves by building shelter in a hot place or digging a well for water in a dry place. This means that there are many habitats that humans can live in, as long as our basic needs for food and water are met.
ok
where are ans
View in solution