Crop Production and Management
Based on NCERT Class 8- Science Chapter 1
NCERT-Class 8- Chapter-1-Crop Production and Management -Notes
Topics in Crop Production and Management.
- Agricultural Practices.
- Basic Practices of Crop Production.
- Preparation of Soil, Sowing.
- Adding Manure and Fertilisers.
- Irrigation, Protection from Weeds.
- Harvesting,Storage.
- Food from Animals
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Introduction : When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop.
Crops are of different types- Cereals, Vegetables and Fruits.
These can be classified on the basis of the season in which they grow.
(i) Kharif Crops : The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops.
The rainy season in India is generally from June to September.
Examples : Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc., are kharif crops.
(ii) Rabi Crops : The crops grown in the winter season are called rabi crops.
Their time period is generally from October to March.
Examples : wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Besides these, pulses and vegetables are grown during summer at many places. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time these are.
(i) Preparation of soil.
(ii) Sowing.
(iii) Adding manure and fertilisers.
(iv) Irrigation.
(v) Protecting from weeds.
(vi) Harvesting.
(vii) Storage.
(i) Preparation of soil : It is the first method in crop management. Preparation of soil is done by loosening the soil by ploughing or tilling it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep in the soil and to breath easily even when they are deep. This will allow the seeds in growth and also for the growth of various bacteria and microorganism., which helps in the crop growth. This ploughing or tilling will help in being in the nutrient rich soil to the top, so that the seeds can derive nutrition for their growth.
Sometimes, manure is added to the soil before tilling. This helps in proper mixing of manure with soil. The soil is watered before sowing.
The main tools used for this purpose are the plough, hoe and cultivator.
- Plough : This is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc. This implement is made of wood and is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals
- Hoe : It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron.
- Cultivator : Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
(ii) Sowing: Sowing is another important step after soil preparation. The process of putting seeds into the soil is called sowing. Best quality of seeds are used to sow for better crop yield. Seeds are sown with the help of a traditional tool or a seed drill. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Nowadays a seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth.
(iii) Adding manure and fertilisers : The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure and fertilisers.
Fertiliser: Fertilisers are commercially available plant nutrients. They can be organic or inorganic in nature. They ensure healthy growth and development of plants by providing them with nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. The addition of fertilisers to the soil requires special guidelines such as dose time, post addition precautions, etc., to be followed. A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. Its excessive use causes water pollution. It cannot replenish organic matter of soil.
Manure : Manure is a natural substance prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant wastes. Manure is known to have a large quantity of organic materials and very little amount of plant nutrients. They help in enriching the soil with organic matter and nutrients. The addition of manure does not require any special guidelines. Manure provides humus to the soil and increases soil fertility. It protects the environment and helps in recycling farm waste. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
(iv) Irrigation : The artificial method of watering the plants for assisting in their growth is called irrigation. Irrigation is the process in which water is supplied to the crops in the field at various intervals. The intervals vary from crop to crop, season to season and it also depends on the soil type and amount of rainfall. The irrigation sources are lakes, ponds, rivers, canals and dams.
Main sources of irrigation are wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers.
Two methods of irrigation which help us to conserve water are:
(a) Sprinkler irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top. It is more useful in the uneven and sandy land where sufficient water is not available.
(b) Drip irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
(v) Protecting from weeds : The undesirable and unwanted plants which grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. The growth of weeds can be controlled by adopting many ways. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in the uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides. Weedicides are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Some important weeding methods are:
a. Weeds can be controlled using weedicides. It is a chemical, which is sprayed in the fields to kill all available weeds. Weedicides are not harmful to crops.
b. Tilling before sowing of crops also helps in removing weeds. Tilling uproots the weeds. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
c. The manual method of removing weeds is with the help of a khurpi. It involves regular uprooting or cutting of weeds close to the ground.
(vi) Harvesting : The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting. Harvesting is either done manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester. In the harvested crop, the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. Threshing is the last step in which the grains are separated from the chaff. It is done after the crop harvesting. There is a machine called “Combine” which carry out this work. Combine is combined harvester and thresher. It harvests crops and also separates the grains.
(vii) Storage : Proper storage of grains is necessary to protect them from pests and microorganisms. The fresh crop has
more moisture. Hence, before storing them, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This
prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria and fungi. Farmers store grains in jute bags or metallic bins.However, large scale storage of grainsis done in silos and granaries to protect them from pests like rats and insects
For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Food is also obtained from animals for which animals are reared. This is called animal husbandry.
Animal husbandry includes taking care of animals, breeding them, and domesticating them for different purposes such as meat, wool, milk, eggs, honey etc.
Types of animal husbandry popular in India include:
- Beekeeping or Apiculture
- Cattle farming
- Dairy farming
- Fish Farming or Aquaculture
- Poultry farming
- Sheep farming
Breeding means mating animals with superior characters to create a new breed (or offspring that is more useful to us than its parents). Breeding can be of two types:
- Inbreeding
- Outbreeding [/responsivevoice]
NCERT-Class 8- Chapter-1-Crop Production and Management -Solution
Question 1:
Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____
(b) The first step before growing crops is _______ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential.
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
Question 2:
Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (e) Paddy and maize |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iv) Organic manure | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
Question 3:
Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
(a) Kharif crop → Paddy, maize
(b) Rabi crop → Wheat, gram
Question 3:
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
It is the first method in crop management. Preparation of soil is done by loosening the soil by ploughing or tilling it. This will allow the seeds in growth and also for the growth of various bacteria and microorganism., which helps in the crop growth. This ploughing or tilling will help in being in the nutrient rich soil to the top, so that the seeds can derive nutrition for their growth.
(b) Sowing
Sowing: Sowing is another important step after soil preparation. Best quality of seeds are used to sow for better crop yield. The process of putting seeds into the soil is called sowing. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Nowadays a seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth.
(c) Weeding
Weeding: Some undesirable plants grow along with crop and these unwanted plants are called weeds. The process of removing these unwanted plants is called weeding. Weeds compete with the plants in light and space and take up the nutrients given to the plant from the soil. Xanthium, Parthenium, etc. are some common weeds that affect the productivity of plant. Weeds can be controlled by using weedicide (a chemical which only kills the weeds not the crops).
(d) Threshing
Threshing: The process of separating the grain seeds from the chaff is called threshing. Threshing is the last step in which the grains are separated from the chaff. It is done after the crop harvesting. There is a machine called “Combine” which carry out this work. Combine is combined harvester and thresher. It harvests crops and also separates the grains.
Question 5.
Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| (i) A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | (i) Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| (ii) A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | (ii) Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| (iii) A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | (iii) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| (iv) Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | (iv) Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6.
What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Irrigation is the process in which water is supplied to the crops in the field at various intervals. The intervals vary from crop to crop, season to season and it also depends on the soil type and amount of rainfall. The irrigation sources are lakes, ponds, rivers, canals and dams.
Two methods which help us to conserve water are:
(i) Sprinkler irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top. It is more useful in the uneven and sandy land where sufficient water is not available.
(ii) Drip irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
Question 7.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Wheat crop is sown from November/December to March/April. It is grown in winter and requires less water. If wheat is sown in the kharif season (from June to October), then the whole crop might get destroyed because of many factors such as lack of optimum temperature, adaptability, availability of pests, etc. Kharif season includes the rainy season, which is not favourable for the growth of wheat crop. Therefore, wheat crop should not be sown during this season.
Question 8.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Continuous plantation of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients as the crops take up nutrients from the soil. The soil becomes infertile. It does not get enough time to replenish the nutrients. Continuous plantation of soil leads to the depletion of the soil minerals like potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen and various other nutrients. These ions are necessary for all the plants to grow. If continuous plantation is done these minerals won’t get time to replenish and the crop yield decreases immediately.
Question 9.
What are the weeds? How can we control them?
The undesirable and unwanted plants which grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. The growth of weeds can be controlled by adopting many ways.
Some important weeding methods are:
i. Weeds can be controlled using weedicides. It is a chemical, which is sprayed in the fields to kill all available weeds. Weedicides are not harmful to crops.
ii. Tilling before sowing of crops also helps in removing weeds. Tilling uproots the weeds. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
iii. The manual method of removing weeds is with the help of a khurpi. It involves regular uprooting or cutting of weeds close to the ground.
Question 10.
Arrange the following boxes in the proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.

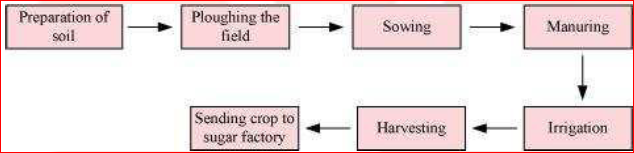
Question 11.
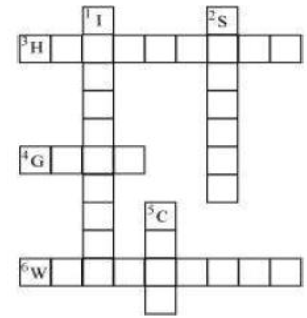
Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.

NCERT-Class 8- Chapter-1-Crop Production and Management -Videos
Click on below topic link to open video.
1- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="MYdb3NTE4nQ&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-1"]
2- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="NCp93xbSwWM&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Introduction to Agriculture"]
3- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="8ulpy_GFLDk&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Agricultural Practices | Soil Preparation "]
4- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="5RQU2V1CCAk&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Traditional Methods of Irrigation"]
5- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="T5KhzfBAbzg&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="What are the Cropping Patterns"]
6- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="Bc1UJZTcHkc&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Animal Husbandry and Cattle Farming"]
7- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="HXM7Z-7kG3w&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Exercise"]
I want to this chapter answers
will be available soon…