Microorganisms: Friend & Foe
NCERT Class 8- Science - Chapter 2-Notes-Solution-Video-PDF
NCERT-Class 8-Science-Chapter-2-Microorganisms: Friend & Foe-Notes
Topics to be learn :
- Microorganisms
- Where do Microorganisms Live?
- Microorganisms and Us
- Harmful Microorganisms
- Food Preservation
- Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen cycle
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Microorganisms :
There are four major types of microorganisms:
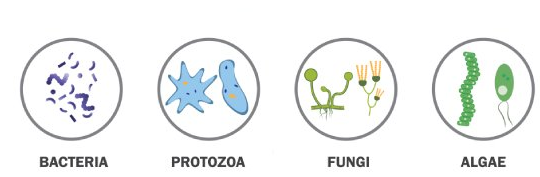
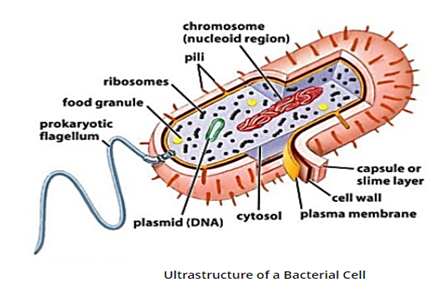
Bacteria: These are single-celled organisms with a rigid cell wall. They can only be seen under a microscope which enlarges images from 100 to 1000 times.
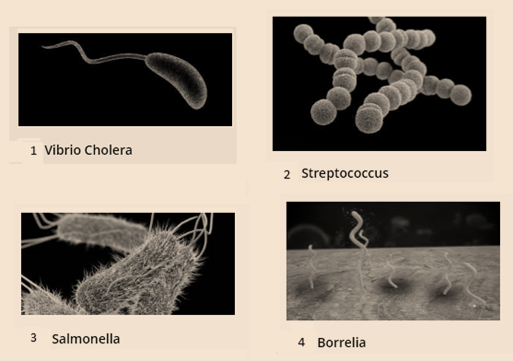
Shapes & Types of Bacteria and their Examples
- Comma-shaped Bacteria : Example -Vibrio Cholerae
- Spherical-shaped Bacteria (Cocci) –Example -Staphylococcus and Streptococcus
- Rod-shaped Bacteria (Bacilli) –Example-coli and Salmonella
- Spiral-shaped Bacteria (Spirilla) –Example-Treponema and Borrelia
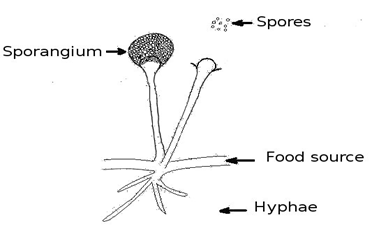
Fungi: These are non-green plants and hence, cannot make their own food.
They either live as parasites (deriving nutrition from host organisms, for example, Puccinia (which causes wheat leaf rust) or grow on the organic matter (such as bread mould).
Fungi, like mushrooms, moulds, mildews, and years, are eukaryotic. It means that they have a true nucleus.
The main components of fungi are:
- Hyphae: They are thread-like filaments which penetrate into substrates, secrete enzymes to break down nutrients into smaller molecules, and absorb them.
- Spores are a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction. They can adapt for dispersal and survival for extended periods of time in unfavourable conditions.
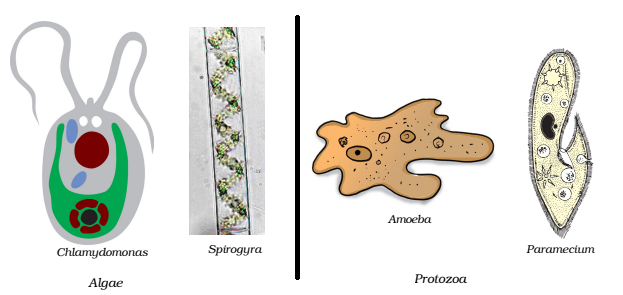
Algae : These are simple plant- like organisms which are usually aquatic in nature. They contain a cell wall and chlorophyll and can make their own food by photosynthesis.Algae can be unicellular or multicellular. Some of the common examples are diatoms,Chlamydomonas, and seaweed.
Protozoa: Protozoa are unicellular are organisms. Some of them live independently while others live as parasites. Many of the parasitic protozoans cause diseases in plants, domestic animals, and human beings. Example of some protozoans are Amoeba, Plasmodium and Paramecium.
How are Viruses different from other microbes?
Viruses are microscopic organisms but they are different from other microbes because they reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism (which can be a plant, animal, or a bacterium).
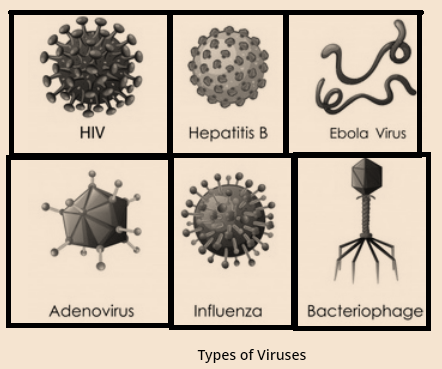
Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. A complete virus particle is known as Virion.
Virion consists of a nucleic acid surrounded by 'capsid'. Capsid is a protective coat made of protein. The sub units of this protein called 'Capsomeres'.
Viruses can be seen only by an electron microscope as they are ultra-microscopic in size.
Outside the body of a living organism, they do not show any reaction and hence, can be crystallized and stored like non-living things.
[/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Microbes can survive in all kinds of environments – from icy cold climates to hot springs; and deserts to marshy lands. Some live independently while others live as parasites – inside the bodies of other organisms (including animals and human beings).
Microorganisms and Us :
Some microorganisms are beneficial to us while others are harmful and cause diseases.
How are bacteria useful to us?
Bacteria are helpful because:
- It decomposes organic wastes (such as vegetable peels, animal remains, and faeces etc.).
- It is used in the preparation of medicines.
- It increases soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
- It is used in the setting of curd and making cheese, pickles, and other food items.
How is yeast useful to us?
- Yeast is used in the baking industry (to make bread, pastries, and cakes) because it helps in fermentation. It reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of the carbon-dioxide gas it produces fill the spaces in the dough and increases its volume.
- It is also used in the commercial production of alcohol and wine which is done by growing yeast on natural sugars present in fruit juices and grains like rice, wheat, and barley.
Antibiotics :
What are Antibiotics? What are their uses?
Antibiotics are medicines that can kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms.
Example: Penicillin.
Antibiotics are used to:
- Cure a variety of diseases (such as streptomycin, erythromycin, and tetracycline that are made from bacteria and fungi),
- Cure microbial infection in animals (by mixing antibiotics with the feed of livestock and poultry), and
- Control several plant diseases.
What precautions should be followed while taking antibiotics and why?
- Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of the doctor, and one must complete the course the doctor prescribes.
- Antibiotics taken in wrong doses may make the body resistant to the drug and it may not be effective in the future. Moreover, antibiotics may also kill the beneficial bacteria in the body.
- Please Note: Antibiotics cannot cure cold and flu caused by viruses.
Name some of the diseases which can be prevented by vaccines
Some of the diseases that can be prevented by vaccination are:
- Cholera,
- Hepatitis,
- Smallpox
- Tuberculosis.
How do microbes clean up the environment?
Microbes or microorganisms decompose organic waste and dead remains of plants and animals and convert them into simpler substances (which can again be used by other plants and animals) by the process of biodegradation. Thus, they help us in getting rid of harmful and smelly substances and clean up the environment. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Pathogens: Disease-causing microbes are called Pathogens.
Communicable Diseases: These are microbial diseases (diseases caused by microbes) that spread from one infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact, such as cholera, chicken pox, common cold and tuberculosis.
Carriers: Insects and animals that carry disease-causing microbes and transfer them from one place to other are called carriers or vectors, such as house flies and mosquitoes.
How do houseflies transfer pathogens?
A housefly may sit on the garbage and animal excreta and the pathogens stick to their body. When they sit on uncovered food, these pathogens get transferred to the food. When someone eats this contaminated food, he or she may fall sick.
To avoid this, we must keep the food covered.
Name the carriers of:
Malaria :- Female Anopheles mosquito (carries the parasite of malaria called Plasmodium)
Dengue : emale Aedes mosquito (carries the dengue virus called Flavivirus)
Common Diseases and their Modes of Transmission
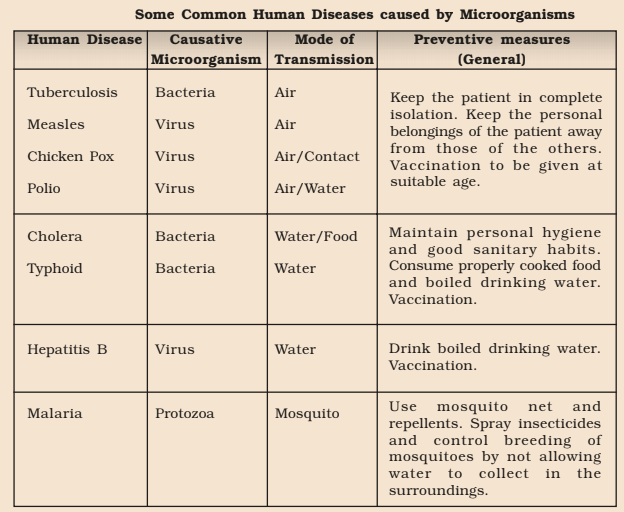
How to prevent diseases that spread through air or contact?
To prevent diseases that spread through the air, keep the patient in complete isolation and keep his or her personal belongings away from others. Vaccination at the suitable age can prevent the onset of tuberculosis, chicken pox, polio, and measles.
How to prevent diseases that spread through water or food?
To prevent the spread of polio, cholera, typhoid and hepatitis A, vaccination is effective. One should also maintain personal hygiene and good sanitary habits and drink boiled drinking water.
One should also eat properly cooked food to avoid diseases like cholera.
How to prevent diseases that spread through mosquitoes?
We can stop the spreading of diseases caused by mosquitoes (such as malaria and dengue) by not allowing the mosquitoes to breed. We should keep our surroundings clean and dry, and not let water collect anywhere - in coolers, tyres, and flower pots etc.
We should also spray insecticides and use mosquito repellents and mosquito nets to protect ourselves from mosquito bites.
Diseases Caused by Microorganisms in Animals :
Anthrax: A dangerous disease that affects human and cattle is caused by a bacterium called Bacillus Anthracis.
Foot and mouth disease in Cattle: It is caused by a virus called Foot-and-mouth-disease Virus (FMDV) or Picornavirus.
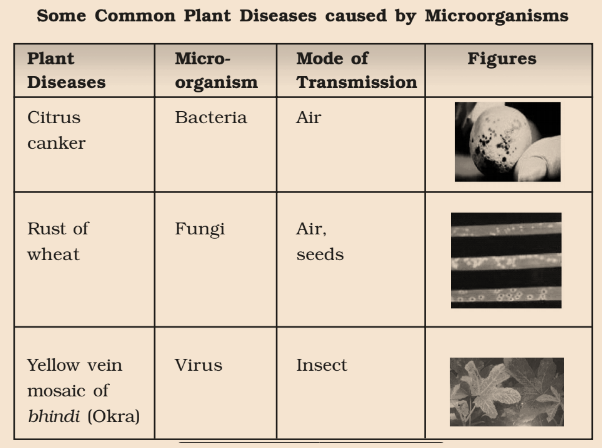
Diseases Caused by Microorganisms in Plants
Microorganisms can cause diseases in plants and reduce crop yield. The plants can be protected by using chemicals that kill these microbes.
Common Diseases in Plants caused by Microbes
Citrus Canker is caused by Bacteria and spreads through Air.
Rust of Wheat is caused by Fungi and spreads through Air or Seeds.
Yellow Vein Mosaic of Okra (Bhindi) is caused by Virus and spreads through Insects. [/responsivevoice]
Some of the plants in which they cause diseases are:-
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Why do we need to preserve food?
We need to preserve food because microorganisms that grow on food can sometimes produce toxic substances which are poisonous to us. If we consume this spoilt food, we can become seriously ill or die. Hence, we need to preserve food from being spoilt.
Objectives of Food Preservation
Following are the important objectives of food preservation:
- To prevent microbial contamination.
- To kill pathogens.
- To minimise food spoilage and food poisoning.
Common Methods of preserving food are:
Chemical Method :
Salt and edible oils are two main preservatives which are used since ages to prevent microbial growth. This is why we add extra oil to pickles. Preservation by salt is known as salting. Salting helps to preserve fruits for a long term. Meats and fishes can also be preserved by salting.
Other synthetic preservatives include vinegar, sodium benzoate, sodium metabisulphite, etc.
Sugar :
Sugar is another common preservative used in jams and jellies. Sugar is a good moisture absorbent. By reducing moisture content, it restrains the microbial growth.
Heat and Cold Methods :
Boiling and refrigeration prevent around 70 percent of microbial growth. Boiling kills the microorganisms that cannot tolerate extreme temperatures. Thus, it helps in food preservation.
Refrigerators have very low temperatures. Since microbes do not get optimum temperature they need for growth, their growth is inhibited. Pasteurization developed by Louis Pasteur is used until today to preserve milk.
Smoking :
Smoking prevents dehydration in fish and meat and thus prevents spoilage. The wood smoke contains a large number of anti-microbial compounds that slow the rancidification of animal fats.
Canning :
The food contents are sealed in an airtight container at high temperatures. Meat, fish, fruits are preserved by canning.
Sterilization :
This method is carried out to remove microbes from food. For eg., milk sterilization at 100°C kills the microbes.
Dehydration :
It is the process of removal of water from food. It is the simplest method and prevents food spoilage by removing water.
Lyophilization :
This is the process of freezing and dehydration of the frozen product under vacuum.
Radiation :
This method is also known as cold sterilization. The UV rays, X rays, gamma rays kill all the unwanted microbes present in food. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Nitrogen constitutes 78% of our atmosphere.
In living organisms, it is found in:
- Proteins,
- Nucleic Acids,
- Chlorophyll
- Vitamins
Atmospheric nitrogen cannot be used directly by the plants and animals. It gets fixed by either lightning or natural nitrogen fixers.
Because the nitrogen gas present in the atmosphere can not be directly used by plants. There are certain bacteria and some natural phenomenon which help in Nitrogen fixation.
Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation
A species of bacteria called Rhizobium, help in nitrogen fixation. These bacteria live in the roots of leguminous plants (e.g., pea and beans plants) and using certain types of enzymes, they help in fixing nitrogen in the soil.
During this biological process, they convert the non-absorbable nitrogen form into a usable form. This form of the nitrogen gets dissolved in the soil, and plants absorb the modified nitrogen from the soil.
Nitrogen fixation by bacteria is an example of the symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium and the leguminous plants. While bacteria fix nitrogen in the soil, plants provide them food.
Nitrogen Cycle :
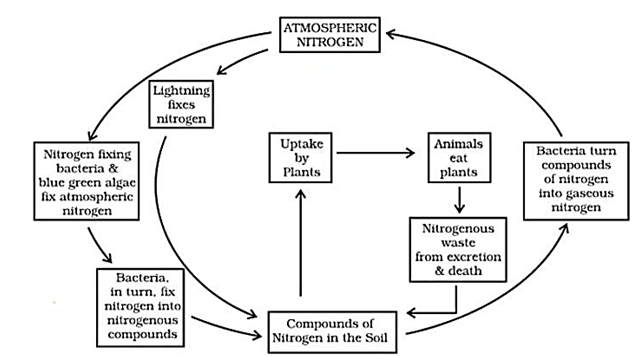
A step-by-step explanation :
Nitrogen Fixation: Atmospheric nitrogen is converted by lightning or certain bacteria like Rhizobium, Azotobacter and blue-green algae (present in soil) into compounds usable by plants.
- Nitrification: Ammonia conversion into nitrites by Nitrosomonasand further conversion of nitrites into nitrates by Nitrobacter. Plants take up nitrogen in form of ammonia or nitrates.
- Assimilation: Roots of plants absorb these nitrogenous compounds from soils and plants use them to synthesize proteins and other compounds.
- Animals feeding on plants get these proteins and nitrogen compounds.
- Ammonification: When plants and animals die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert the nitrogenous wastes into compounds that can be used by plants again.
- Denitrification: Nitrates can be converted into nitrogen gas which is released back in the atmosphere by certain bacteria. Eg. Pseudomonas Due to this, atmospheric nitrogen remains constant. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
- Microorganisms are too small and are not visible to the unaided eye.
- They can live in all kinds of environment, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands.
- Microorganisms are found in air, water and in the bodies of plants and animals.
- They may be unicellular or multicellular.
- Microorganisms include bacteria, fungi,protozoa and some algae.
- Viruses, though different from the above mentioned living organisms, are considered microbes.
- Viruses are quite different from other microorganisms. They reproduce only inside the host organism; bacterium, plant or animal cell.
- Some microorganisms are useful for commercial production of medicines and alcohol.Some microorganisms decompose the organic waste and dead plants and animals into simple substances and clean up the environment.
- Protozoans cause serious diseases like dysentery and malaria.
- Some of the microorganisms grow on our food and cause food poisoning.
- Some microorganisms reside in the root nodules of leguminous plants. They can fix nitrogen from air into soil and increase the soil fertility.
- Some bacteria and blue green algae present in the soil fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and convert into nitrogenous compounds.
- Certain bacteria convert compounds of nitrogen present in the soil into nitrogen gas which is released to the atmosphere. [/responsivevoice]
NCERT-Class 8 -Chapter 2 : MICROORGANISMS : FRIEND AND FOE -Exercise-Solution
Question1.
Fill in the blanks.
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a________________.
(b) Blue-green algae fix ______________ directly from air to enhance fertility of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of __________.
(d) Cholera is caused by ____________.
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a microscope. (b) Blue-green algae fix nitrogen directly from air to enhance fertility of soil. (c) Alcohol is produced with the help of yeast. (d) Cholera is caused by a bacteria.
Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) Sugar (ii) alcohol (iii) hydrochloric acid (iv) oxygen
(a) (ii) alcohol.
(b) The following is an antibiotic.
(i) Sodium bicarbonate (ii) Streptomycin (iii) Alcohol (iv) Yeast
(b) (ii) Streptomycin
(c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
(i) Female Anopheles mosquito (ii) cockroach (iii) housefly (iv) butterfly
(c) (i) female anopheles mosquito
(d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant (ii) housefly (iii) dragonfly (iv) spider
(d) (ii) housefly
(e) The bread or idli dough rises because of
(i) heat (ii) grinding (iii) growth of yeast cells (iv) kneading
(e) (iii) growth of yeast cells
(f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen fixation (ii) moulding (iii) fermentation (iv) infection.
(f) (iii) fermentation.
Question 3.
Match the organisms in Column I with their action in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Bacteria | (a) | Fixing nitrogen |
| (ii) | Rhizobium | (b) | Setting of curd |
| (iii) | Lactobacillus | (c) | Baking of bread |
| (iv) | Yeast | (d) | Causing malaria |
| (v) | A protozoan | (e) | Causing cholera |
| (vi) | A virus | (f) | Causing AIDS |
| (g) | Producing antibodies | ||
Column I
Column II
(i)
Bacteria
(e)
Causing cholera
(ii)
Rhizobium
(a)
Fixing nitrogen
(iii)
Lactobacillus
(b)
Setting of curd
(iv)
Yeast
(c)
Baking of bread
(v)
A protozoan
(d)
Causing malaria
(vi)
A virus
(f)
Causing AIDS
Question 4.
Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eyes? If not, how can they be seen?
Microorganisms are too small so they cannot be seen with naked eye. They can be seen with the help of a magnifying glass or microscope.
Question 5:
What are the major groups of microorganisms?
The major groups of microorganisms are: Bacteria: They are single celled disease causing microorganisms. They can be spiral or rodshaped. Fungi: They are mostly multicellular disease causing microbes. Bread moulds are common examples of fungi. Protozoa: They mainly include organisms such as Amoeba, Plasmodium,etc. They can be unicellular or multicellular. Virus: Viruses are disease causing microbes that reproduce only inside the host organism. Algae: They include multicellular, photosynthetic organisms such as Spirogyra, Chlamydomonas, etc.
Question 6.
Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
The microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen are Rhizobium, Azatobactor, Blue green algae etc.
Question 7.
Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
The usefulness of microorganisms are as follows: Lactobacillus is used to form curd from milk. Rhizobium present in the roots of pulse plants fix nitrogen from air and supply nitrogen compounds to the pulse plants. Microorganisms are also used in winemaking, baking, pickling, and other food making processes. Alcoholic fermentation by yeast is widely used in the preparation of wine and bread. Microbes are used to reduce pollution. For example, decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down dead bodies and excreta to form inorganic compounds, which can be absorbed by plants. Microbes also play an important role in the preparation of medicines. Antibiotics are chemicals produced by microorganisms to kill bacteria. Penicillin is an antibiotic made from Penicilium. Bacteria present in our intestine helps in proper digestion and release Vitamin B which is absorbed by intestine. Many vaccines are prepared from microorganisms. These vaccines are given to children to protect them from disease. Certain microbes are also used in the biological treatment of sewage and industrial effluents. Yeast is used in making idlis, bread, pastries and cakes.
Question 8.
Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms?
Microorganisms cause diseases in animals. For example, in humans, bacteria cause diseases such as tuberculosis, cholera, typhoid, etc. In cattle, the foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus. Also, several microbes cause diseases in plants. For example, the productivity of wheat, orange, apple, etc. is reduced due to microbial diseases in plants. Certain microbes, on entering into our body, produce toxic substances. This leads to food poisoning. Some microorganisms such as fungus spoil our food. For example, bread when left unused under moist conditions gets spoil by fungus, producing a white cotton like growth on the bread.
Question 9.
What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
The medicines that kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganism are called antibiotic. Streptomycin, tetracycline, erythromycin etc. are common antibiotics. They are manufactured by growing specific micro-organisms and are used to cure a variety of diseases. Following precautions must be taken in using antibiotics- These medicines should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. One must finish the course prescribed by the doctor. If anybody takes antibiotics when not needed, his or her body may develop resistance against that antibiotic.
NCERT-Class 8-Science-Chapter-2-Microorganisms: Friend & Foe-Videos
Click on link to open video
1- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="0TdQeTM0xec&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Introduction to Bacteria | Microorganisms "]
2- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="VVuYGkk_I8s&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Introduction to Fungus"]
3- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="B1CFVuQVG2U&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Introduction to Protozoa"]
4- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="18vbNJuzhx8&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Food Poisoning | Food Preservation"]
5- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="sK6Us18yEAE&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Microbial Habitat"]
6- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="tCrgTV20BD4&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Nitrogen Fixation | Nitrogen Cycle"]
