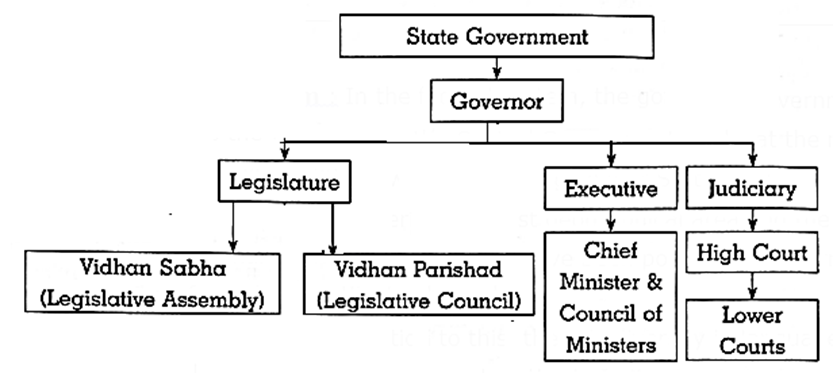
The State Government
Maharashtra Board Class 8- Civics - Chapter-5
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Background
Federal system : In the federal system, the government exists at two levels. Federal that is the Central Government works at the national level and the State government works at the regional or State level.
- Considering the vast geographical area and the multicultural population of India, it would not have been possible to govern the country from a centralised place.
- In addition to this, there is diversity in language, religion, ways of life, and regional characteristics in India.
- Therefore, the Constitution has adopted a federal setup for India.
- It was decided to form the states on the basis of languages.
- The nature of government machinery is the same in all states.
State Legislature : Legislature of Maharashtra
- Maharashtra has a bicameral legislature having Legislative Assembly (Vidhan Sabha) and Legislative Council (Vidhan Parishad).
- The Members of the State Legislatures are known as Members of Legislative Assembly (MLA) and Members of Legislative Council (MLC).
(1) Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) :
- This is the first House of the Maharashtra legislature and comprises of 288 members.
- Tenure of Vidhan Sabha is 5 years. However, in exceptional circumstances elections can be held before the completion of 5 years.
- Any citizen residing in Maharashtra and who has completed 25 years of age can contest the elections to the Vidhan Sabha.
- Governor nominates 1 member of Anglo-Indian community if required
- Some seats are reserved for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- Speaker and Dy. Speaker elected by the MLAs
Powers of Speaker :
- Supervises over the functioning of Vidhan Sabha
- Prepares order of business
- Conducts the proceedings in a disciplined manner
- Can suspend members for misbehaviour or misconduct
(2) Vidhan Parishad (Legislative Council) :
- It is the second House of the Maharashtra legislature.
- There are 78 members in the Vidhan Parishad of Maharashtra.
Election :
Members are indirectly elected from various sections of society by following ways.
- Some members who are distinguished personalities from the fields of literature, science and social service are nominated by the Governor;
- Remaining representatives are elected by the MLA, local government institutions, teacher-constituencies and graduate constituencies.
Tenure :
- Vidhan Parishad is a Permanent house. The Vidhan Parishad is never fully dissolved.
- Tenure of every member is 6 years.
- A specific number of members retire every 2 years and these vacant seats are filled again by conducting fresh elections for those seats.
- The proceedings of the Vidhan Parishad are conducted under the control and guidance of the Chairman. In absence of the Chairman, the Deputy Chairman takes over the responsibility.
Executive of Maharashtra :
The Governor, Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers together form the executive of Maharashtra.
Governor :
- The Governor is the titular/nominal head of the state.
- The government of the state is run in the name of the Governor.
- He is appointed by the President and holds the office during the pleasure of the President.
- He appoints the Chief Minister and the Council of Ministers.
- As the head of the state, he enjoys certain important Legislative and Executive powers.
Powers of Governor :
(i) Legislative Power :
- The Bills passed by Vidhan Sabha and Vidhan Parishad are converted into laws only after receiving his assent.
- He has the right to summon the session of the state legislature and to conclude it.
- He can issue an ordinance to make law, on important subject if required, when the Legislature is not in session.
(ii) Executive Power :
- He appoints the Chief Minister and the other Council of Ministers.
- He appoints one Anglo-Indian member to Vidhan Sabha if required.
- He appoints distinguished personalities from various fields to Vidhan Parishad.
Chief Minister and Council of Ministers :
- The leader of the majority party in Legislative Assembly becomes the Chief Minister.
- The Chief Minister includes his trustworthy colleagues in the Council of Ministers.
- Through the State Government is run in the name of the Governor, the actual administration is carried out by the Chief Minister.
Functions of the Chief Minister :
(i) Formation of Council of Ministers :
- To give representation to various regions and social groups.
- To maintain regional balance.
- To give representation to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Castes, etc.
- To give representation to women and minorities.
- To give a place to all constituent parties in the council in case of coalition government.
(ii) Distribution of portfolios : To distribute portfolios considering the political experience, administrative skills, public awareness, leadership, etc. of the ministers.
(iii) Coordination between Ministries/Department : To develop proper cooperation and coordination between Departments, resolve their conflicts and make them work effectively.
(iv) Leader of the State : To lead the state, frame proper policies and implement them effectively, intervene in issues of the state and solve them for the comfort of the people.
About Maharashtra State :
- Maharashtra is one of the progressive States in India.
- The State leads in sectors like education, industry, service sector, health and social security etc.
- Terror attacks and Naxalite (Left-wing extremist) movements active in certain regions are the two major challenges facing the State of Maharashtra.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th History & Civics - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 4-The Indian Judicial System -online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 6-Bureaucracy -online Notes |
