Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-13
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction : There are two methods of classification of changes : Physical change and chemical change.
- In physical change, the composition of substance does not change. No new substance is formed. Examples: Melting of ice, boiling of water, dissolution of salt in water.
- In chemical change, the composition of compounds change and new compounds are formed. Examples: Ripening of mango, ripening of banana, fragrance of ripening fruit, darkening of a cut potato, bursting of an inflated balloon, sound of bursting firecracker, foul smell from spoiled food.
Chemical change and word equation : In a chemical change the chemical composition of the original matter changes and new substances having different properties and different chemical composition are formed.
A chemical equation can be written for a chemical change, if the exact change in chemical composition is known.
The word equation can be Written for a chemical reaction, baking soda with lemon juice as follows :
Citric acid + Sodium bicarbonate → Carbon dioxide + Sodium citrate
Acid + Alkali → CO2 + Salt
How to write chemical equations :
- First step of writing a chemical equation is to write a word equation by using the names of the concerned substances.
- When the chemical formula is written in place of each of the names, it becomes a chemical equation.
- While writing a chemical equation, original substances are written on the left side and newly formed substances are written on right side and an arrow is drawn in between.
- Arrow head points towards the substances formed. Arrow indicates the direction of the reaction.
- Substances written on the left side of the arrow are original substances that take part in the reaction. They are called reactants.
- New substances formed as a result of the reaction are called products. Place for the products of a reaction is on the right side of the arrow.
Chemical changes in everyday life :
Natural chemical changes :
(a) Respiration : Respiration is a continuously occurring biological process. In this process air is inhaled, oxygen present in this inhaled air reacts with glucose present in the cells of the body forming carbon dioxide and water. The word equation and the chemical equation of this chemical reaction are as follows: (Here, the chemical equation is not balanced.) Word equation : Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water Chemical equation : C6H12O6 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
(b) Photosynthesis : Green plants perform photosynthesis in sunlight. A word equation and a Chemical equation (unbalanced) is written for this natural chemical change as follows : Word equation : Carbon dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen Chemical equation : CO2 + H2O → C6H12O6 + O2
Man-made chemical changes : Man bring about many chemical changes for their use in everyday life. Some of them are given below.
(a) Combustion of fuels : Wood, coal, petrol or cooking gas are burnt for producing energy. Carbon is the common substance that burns in all these fuels. The product carbon dioxide is formed when carbon combines with oxygen in the air during the combustion process. A common equation for all these combustion processes is as follows : Word equation : Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide Chemical equation : C + O2 → CO2 Combustion of fuel is a fast and irreversible chemical change.
Cleaning Shahabad tile with dilute hydrochloric acid : The main chemical constituent of Shahabad tile is calcium carbonate. During it’s cleaning with hydrochloric acid the upper layer of the tile reacts with hydrochloric acid and three products are formed. One of them is calcium chloride, which being soluble in water, gets washed away with water. The second product is carbon dioxide; its bubbles mix up in air. The third product, water mixes with water. The following equation is a chemical change. Word equation : . Calcium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid → Calcium chloride + Carbon dioxide + Water
Softening of hard water : Water in some wells or tube wells is hard water. * ' It is brackish to taste and does not form lather with soap. This is because hard water contains the chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium in dissolved state. Hard water is softened by adding solution of washing soda to it. This results in the formation of a precipitate of insoluble salts of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate. As the dissolved salts of calcium and magnesium go out in the form of precipitate of the carbonate salts, the water is softened. The following equation . is written for this chemical change. Word equation : . Calcium chloride + Sodium carbonate → Calcium carbonate + Sodium chloride Chemical equation (unbalanced) : CaCl2 + Na2CO3 —> CaCO3 + NaCl
Distinguish between Physical change and Chemical change : 2) In this case, physical properties such as state, colour, density, etc. are changed. 3) This change is temporary. 4) In this case, the original substance can be recovered by simple means or by merely reversing the process. 2) In this case, physical and chemical properties are entirely changed. 3) This change is permanent. 4) In this case, the original substance cannot be recovered by easy means or by reversing the process.
Physical change
Chemical change
1) In this change, the composition of the substance does not change. No new substance is formed.
1) In this change, the composition of the compounds change and new compounds are formed. -
Chemical bond : Noble gases do not form any chemical bond as their electron octet/duplet is complete while the atoms with incomplete electron octet/duplet form chemical bonds. During the formation of a chemical bond an atom uses its valence electrons. Moreover on forming chemical bonds equal to its valency the atom attains the electronic configuration of complete octet/duplet.
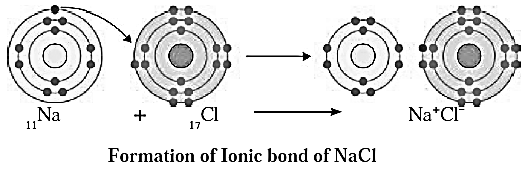
Ionic bond : The chemical bond formed due to an electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged cation and anion is called an ionic bond or an electrovalent bond.
The compound formed by means of one or more ionic bonds is called ionic compound.
One ionic bond is formed due to the electrical charge +1 or -1 on an ion. The valency of an ion 1 is equal to the magnitude of Positive or negative charge on 1t. An ion forms the same number of ionic bonds as its valency.
Examples : Sodium chloride (NaCl), Magnesium chloride are ionic compounds.
Formation of Sodium chloride (NaCl) :
Covalent bond : The chemical bond formed by sharing of valence electrons of two atoms with each other is called a covalent bond. One covalent bond is formed by sharing of two valence electrons.
Examples : Hydrogen, oxygen, water are covalent compounds.
Ionic bond and Covalent bond : (2) Atoms of metals and nonmetals combine to form ionic bonds. (3) Molecules of the compounds formed due to ionic bond split up into ions in aqueous solution. (2) Atoms of -nonmetals combine to form covalent bonds. (3) Molecules of the compounds formed due to covalent bond so not split up into ions in a solution.
Ionic bond
Covalent bond
(1) Ionic bond is formed due to the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
(1) Covalent bond is formed due to the sharing of electrons between two or more atoms.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 12-Introduction to Acid and Base - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 14-Measurement and Effects of Heat -online Notes |
