Ecosystems
Maharashtra Board Class 8- General Science - Chapter-18
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction : In our surroundings there are abiotic and biotic factors.
- The biotic factors are animals and plants in the surroundings.
- The invisible bacteria and fungi also have important role in the ecosystem as decomposers.
- Important abiotic factors are air, Water, land, sunlight, etc.
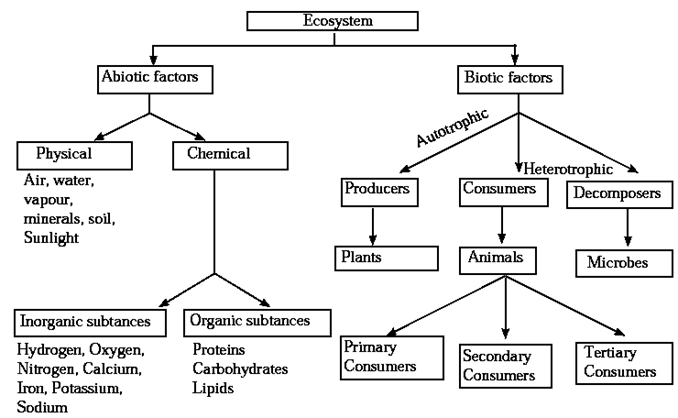
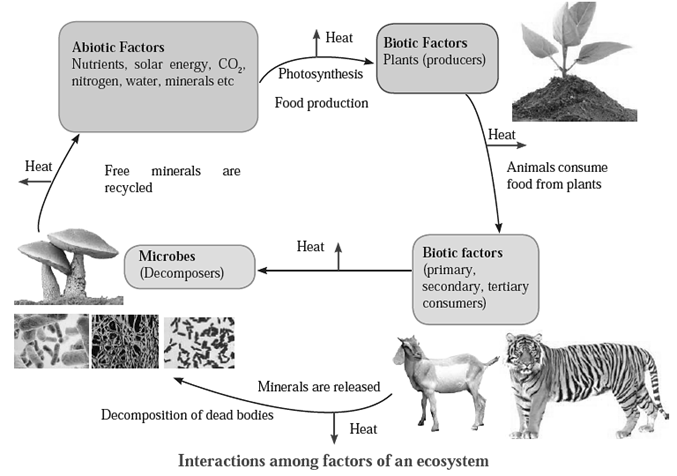
Ecosystem : Living beings means biotic factors and non-living things are abiotic factors. The interactions between the Biotic and abiotic factors, form an ecosystem. The structure which is formed due to these reciprocal relationships is called an ecosystem.
Decomposers : Decomposition is the process in which the organic compounds are broken down to their inorganic constituents. The carbohydrates, proteins and lipids which are organic substances are converted back into inorganic substances such as hydrogen, oxygen, calcium, iron, sodium, potassium, etc. by decomposers. Decomposers are microorganisms that act on the dead bodies of animals and plants and bring about this natural degradation.
- Microbes play the role of decomposers in the above interactions.
- Producers obtain solar energy from sunlight. The other nutrients are obtained from soil, water and air.
- Consumers get their food from producers and other consumers.
Structure of an ecosystem : Every living organism needs some abiotic factors for survival. Each one thus adapts to the surrounding abiotic factors in their own way. The abiotic factors are : Air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature, humidity, etc.
Niche :
- Niche is the role played by the living organism in its own ecosystem.
- The position of the organism and role played by it in response to other organisms together form the niche.
- E.g. A sunflower plant produces oxygen during the process of photosynthesis and also provides food and shelter for insects.
Types of ecosystem : Earth is a vast boundless ecosystem. On the Earth there are various types of ecosystems.
Biomes :
- Biome is a general term given to an aggregation of many small ecosystems.
- The living organisms in any biome have similarities with each other.
- The abiotic factors and climate is specific for each biome.
- There are two main types of biomes : 1. Land biomes. 2. Aquatic biomes.
Land Biomes : The biomes that are present only on the land are called land biomes. Land biomes are subdivided into subtypes according to the distribution of abiotic factors therein.
- E.g. : Grasslands, Evergreen forests, Desert, Tundra/ Polar ecosystems, Ecosystems in Taiga, Tropical rainforests.
Grassland Ecosystem :
Evergreen forests : About seven per cent of the Earth’s surface is occupied by evergreen forests. More than half of the earth’s terrestrial plants and animals are seen in evergreen forests.
Dudhwa Forest : In Dudhwa forest around 150 years ago the one-horned Rhino were in good number. But due to uncontrolled poaching and hunting, the one-horned Rhino became extinct in twentieth century. However, on 1st April 1984 the rhinos were restored here with special efforts. Now Dudhwa has become sanctuary for single-horned Rhino.
Sanctuaries : In India there are about 520 wildlife sanctuaries and National Parks in which ecosystem conservation is taken care of.
Aquatic Ecosystems : 71% of the earth’s surface is covered over with water. Only 29% of the earth has land. According to area, aquatic ecosystems are largest on the earth.
Aquatic ecosystems are subdivided into : At the bottom of water body there are many decomposing bacteria. The characteristics of fresh water and marine ecosystems are almost the same. But the marine waters are saline having many dissolved salts in it. The fresh water does not contain dissolved salts in that proportion. Algae and phytoplankton are the producers of aquatic ecosystem. The small fish feeding on this phytoplankton are the primary consumers. Larger fish» which are secondary consumers, feed on such small fish. Such food chains are seen in aquatic ecosystems. Dead algae and animals are decomposed by microbes at the bottom of the water.
Destruction of ecosystem due to human interference : There is destruction of every ecosystem due to man-made activities. The natural functioning of the ecosystems is disturbed due to many actions such as mining, deforestation, pollution. Some of such actions can even cause complete destruction of the ecosystem. Some animals too are exterminated.
Human activities responsible for destruction of the ecosystems : Increasing use of resources due to increased population : Human beings occupy the top consumer’s position in any ecosystem. Urbanization : Industrialization and transport : Tourism : When large number of people visit a particular place, there is pressure on the resources therein. The amenities provided to the tourists, cause destruction of the local ecosystems. Large Dams (Mega projects) : Huge mega projects like dams can cause vast land surface to be submerged. The surrounding vegetation and grasslands can go under water. The forests nearby are completely destroyed. The water currents in the lower area are lessened. Moreover, many human settlements are destroyed. The people are displaced. Wars : Differences and competition over land, water, mineral resources or some economic and political reasons lead to war among human races. Due to natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods or droughts and also due to man-made changes, some natural ecosystems are either changed or completely destroyed. It is very essential to protect and conserve natural ecosystems because they help to maintain the balance in the biosphere.
Click on link to get PDF from store
MSBSHSE-Class 8-Science-Chapter-18-Ecosystems -Notes
MSBSHSE-Class 8-Science-Chapter-18-Ecosystems-Solutions
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 17-Man-Made Materials - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 19-Life Cycle of Stars -online Notes |
It’s best , brilliant, great and superb
I always use this only for writing 👍🏻👍🏻👍🏻