Exogenetic Processes Part-2
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-4
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn : Erosional, transportational and depositional work of agents :
|
Erosional, transportational and depositional work of agents :
- The agents like running water (river), glacier, wind, sea waves and groundwater do the work of erosion, transportation and deposition.
- Because of these agents, the earth’s surface keeps on changing and new landforms are formed.
Works of river and landforms : When many flows of water come together, a river is formed.The slope of the land, the type of rock, volume of water flowing in river, the length of flow, volume of sediments in the river, etc. are the factors on which the erosional, transportational and depositional work of the river depends.
- Erosional work of river: The riverbed and the river banks get eroded because of the fast flow of water, sand particles, pebbles and the various tributaries joining the main river. All these lead to the formation of gorges (canyons), V-shaped valleys and waterfall.
- Transportational and depositional work of river : At the foothills, the change in the slope causes deposition of coarse sediments leading to formation of alluvial fans. Due to decreased speed, the sediments of river get deposited in its bed and on its banks. This leads to formation of flood levees, flood plains and deltas.
Click here to View Figure-1
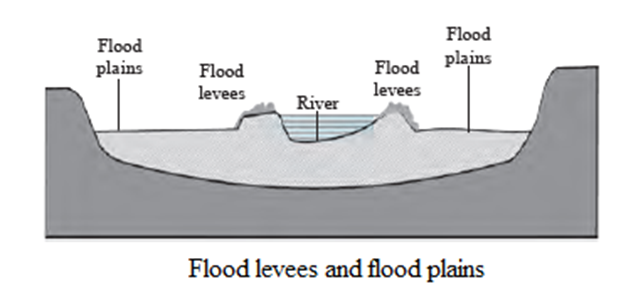
Works of glacier and landforms : In regions where the temperatures are generally below freezing points, precipitation is in the form of snowfall. Layers of snow accumulate on the earth’s surface because of snowfall. The heavy weight of these overlaying layers makes the snow move along the slope. At the base of the layer, the snow starts melting because of the friction and pressure from above. Thus, glacier starts moving slowly along the slope.
- Erosional work of glacier : Glacier erodes its own banks and its bed on a large scale. The erosional Work of glacier produces landforms like cirques, arétes, horns, U-shaped valleys, hanging valleys and roche moutonnées.
- Transportational and depositional work of glacier : Glacier carries sediments with it. The depositional work of glacier produces landforms like moraines, drumlins, eskers, etc.
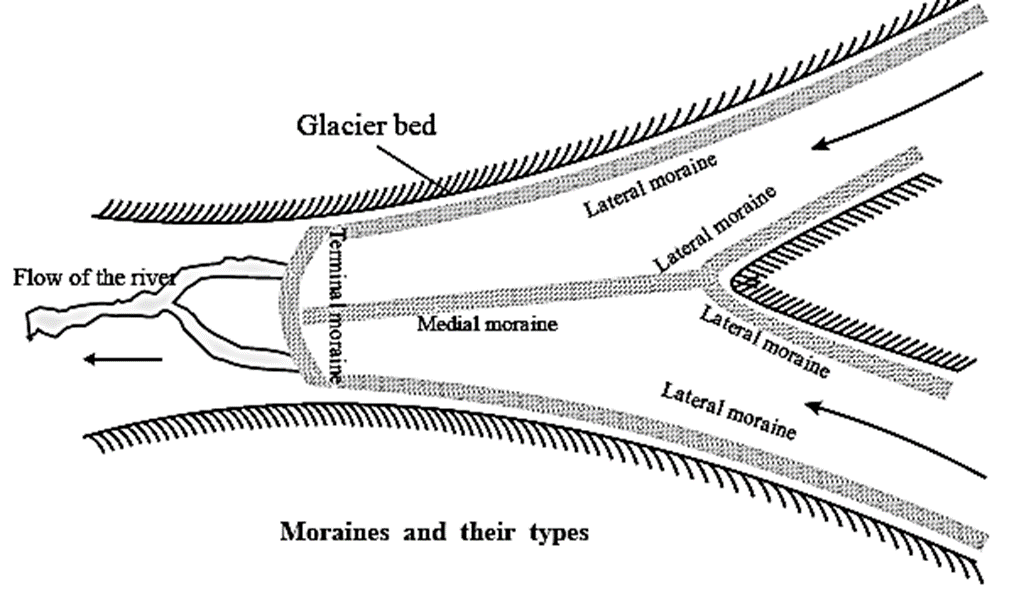
Moraines : The glaciers carry sediments with them. These sediments are called moraines. Depending on the location of the deposits, moraines can be divided into 4 types: Ground moraines, Lateral moraines, Medial moraines and Terminal moraines.
Click here to View Figure-2
Works of wind and landforms : The movement of air is called wind. The erosional, transportational and depositional work of wind is more prominent in deserts and semi-arid regions. Mechanical weathering occurs on a large scale in such regions. Powdered rock and sand particles are transported along the wind over long distances and get deposited where the speed of the wind reduces.
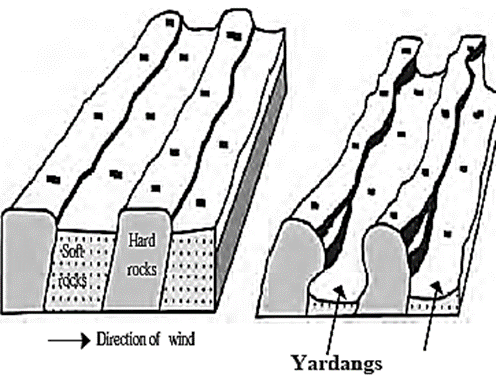
- Erosional work of wind : Due to friction, sand particles and small pebbles erode rocks coming in the way of wind. This leads to formation of mushroom rocks, deflation hollows, yardang, etc.
Click here to View Figure-3
- Transportational and depositional work of wind : The fine particles are carried over larger distances by wind. The larger particles get transported to shorter distances only. These sand particles get deposited in deserts and semi-arid regions. This leads to formation of sand dunes, barchans, seifs, ripple marks, loess plains, etc.
Works of sea waves and landforms : Sea waves carry out erosional, transportational and depositional work in the coastal areas. Winds and tides cause movements of sea water and as a result, waves come to the coast. Because of their hitting, the rocks at the coasts are eroded. In coastal areas having wide beaches, waves carry depositional work.
Click here to View Figure-4
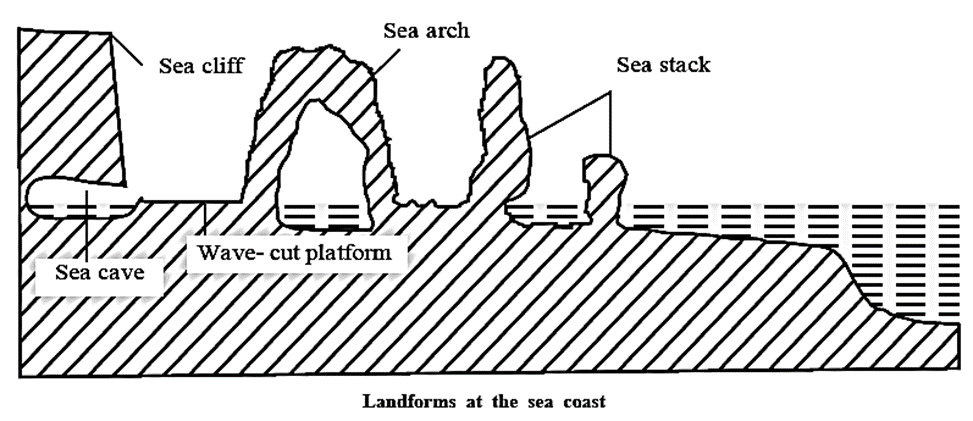
- Erosional Work of sea waves : When the waves break at the coast, they bring with them water, transported stones, pebbles, sand particles, etc. These materials erode the coast. This leads to formation of landforms like wave-cut platforms, sea caves, sea aches, sea cliffs, etc.
- Transportational and depositional work of sea waves : The eroded materials in sea bed keeps on moving towards the coast and away from the coast. It gets deposited where the effects of waves is less. This leads to formation of beaches, sand bars, lagoons, etc.
Works of groundwater and landforms : The rainwater seeps below the earth's surface through porous rocks or cracks in the rocks This water accumulates in the non-porous layer of the rock. This accumulated water is called groundwater.
- Erosional work of groundwater : The soluble minerals in the water get dissolved and flow with the groundwater. This erosional work leads to formation of sinkholes and limestone caves.
- Transportational and depositional work of groundwater : When the groundwater evaporates or the volume of soluble minerals is more than the solubility of the groundwater, the deposition of dissolved materials starts. This leads to formation of landforms like stalactites and stalagmites.
Groundwater table:
The upper surface of the water accumulated below the ground is called the water table. Factors like seasons, porosity of rocks, amount of rainfall, etc. affect the level of water table. The water table is closer to the ground during rainy seasons while it is deeper in the summers.
| Know This :
Eskers ; Narrow, long and winding ridges produced through deposition of moraines are called ‘eskars’. Drumlines : Egg-shaped hills that are formed due to deposition of moraines are called drumlines. Precipitation : Precipitation is a process of solidification of a previously dissolved substance from a solution. The stalactites and stalagmites formed in limestone landscape are a result of precipitation. Caves ; Open hollow spaces formed beneath the ground are called caves. Caves are naturally formed. Similarly they can be man-made. |
Click on link to get PDF from store
Chapter-3-Exogenetic Processes Part-2-Notes
Chapter-3-Exogenetic Processes Part-2-Solutions
Class 9 Geography PDF Set :
All Chapters Notes (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Solutions (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Notes+Solutions (24-PDF) Rs.80-Buy
Class 9 Social Science PDF Set :
All Notes- Social Science Notes(Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Notes+Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (56-PDF) Rs.175-Buy
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 3: Exogenetic Processes Part-1 - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 5: Precipitation - online Notes |
