Natural Resources Air Water and Land
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 6th General Science Chapter 1
Notes
|
Topics to be learned :
|
Natural resources :
- Natural resources are substances which are found in nature and can be caused by human beings to fulfill basic necessities.
- Earth consists of three main spheres: hydrosphere (water), lithosphere (land), and air (atmosphere).
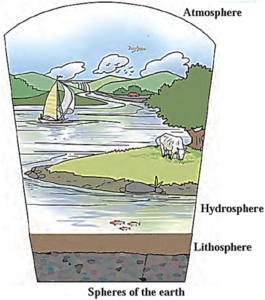
- These spheres contain living organisms, forming the biosphere.
- 71% of the earth's surface is formed of hydrosphere while 29% is that of the lithosphere.
- Air, water, and land are the important natural resources, fulfilling all basic needs of the living world, making them essential for life sustenance.
- Layers of the atmosphere : The troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, ionosphere and exosphere are the five layers of the atmosphere.
Air :
- The earth is surrounded by atmosphere which is made up of air.
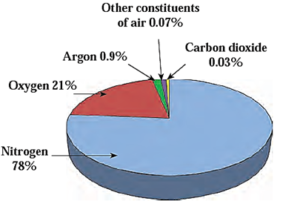
- Air is a mixture of gases.
- The constituents of air are : Nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, six types of inert gases, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, water vapour and dust particles.
- Gases concentration is highest near Earth's surface.
- As altitudes rise, gas proportion decreases.
- Air is rarer at high altitudes.
The proportion of gases in different spheres of the earth :
- Troposphere -> 80% of the total mass of gases in the air.
- Stratosphere -> 19% of the total mass of gases in the air.
- Mesosphere -> proportion of the gases is less
- Ionosphere -> proportion of gases is still lesser
- Exosphere -> No gases found
Some uses of gases in air :
- Nitrogen – Helps living things to build the necessary proteins. It is useful in the production of ammonia and in airtight packaging of foodstuffs.
- Oxygen – Necessary for respiration in living things and for combustion.
- Carbon dioxide – Plants use it for producing their food. Used in fire extinguishers.
- Argon – Used in electric bulbs.
- Helium – Used for obtaining low temperature and also for generating lift in airships.
- Neon – Used in decorative lights and for street lighting.
- Krypton – Used in fluorescent tubes.
- Xenon – Used in flash photography.
Earth's Life Support and Atmosphere Function :
- Balance between gases and air constituents sustains earth's life.
- Atmosphere acts as a filter, allowing sun's light and heat to reach earth.
- Prevents harmful elements from reaching earth.
- Atmosphere produces fog, clouds, snow, and rain.
Air pollution :
- When harmful substances produced through the combustion are released into the air, it causes air pollution.
- Caused by incomplete combustion of fuels in vehicles, industries, and other sources.
- Pollutants like smoke disrupt air's constituent balance, causing hazardous effects on living beings.
- Common harmful air pollutants include nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and soot.
Ozone layer :
- The lower stratosphere has an ozone layer (O3).
The ozone layer shields the earth's surface from damaging UV radiation from the sun. - Chemicals like carbon tetrachloride and chlorofluorocarbons can deplete the ozone layer.
- These gases are employed in air conditioning and refrigeration.
- Every year, on September 16th, the world celebrates 'Ozone Protection Day'. This is to make people aware of the importance of the ozone layer.
Water :
- Water is essential for the survival of every living organism, with daily requirements varying based on body size. For smooth functioning of our body we need 3 to 4 litres of water daily.
- It can be formed by burning hydrogen gas in air
- Water is available in three different states: colorless, tasteless, and odourless.
- Water is also a universal solvent, as it dissolves many substances.
- Animals and plants contain a high proportion of water in their blood and sap of plants.
- Water is considered life-giving as no living thing can survive without it.
- Though 71% of the earth's surface is covered with the water, most of this water is not usable and potable.
- 97% of this water is salty water of the sea. This water cannot be used for agriculture or for drinking, cooking, etc.
- Some fresh water is in frozen state.
- Only a small amount of water remains on the earth for drinking purposes.

Water cycle and uses of water :
- All the water on earth is regulated through the water cycle.
- Sun's heat evaporates water from the oceans. These water vapours condense after reaching the sky and fall back on the earth in the form of rains. Rainwater creates fresh water sources on the earth.
- Natural sources of water : Streams, rivers, ponds, springs and lakes, etc.
- Man-made sources of water : Wells, bore-wells, bunds, and dams on the rivers.
- Uncontrolled use of water : Increasing population, industry and farming all are responsible for excessive use of water. Water scarcity is thus a grave problem.
Important facts about Water Usage :
- Water should be used sparingly.
- Blocking water allows percolation in the ground.
- Rainwater harvesting and storage are key to addressing water scarcity.
- Stored water should be reused to prevent staleness.
Land :
- Land is made up of soil, stones, and big rocks.
- It is uneven, hilly in some areas and flat in other areas.
- All terrestrial living things are given shelter by land. Some animals dig burrows in the land.
- Man uses land for farming, for constructing shelters and roads.
- We make use of plants and animals which are found on forest land.
- Land is an important resource as from here we obtain minerals, crude oil and
- natural gas.
Layers of soil : The sequence with which the layers of soil are present from top to bottom are as follows : Humus, immature soil, layer of soil and small rocks and bedrock.
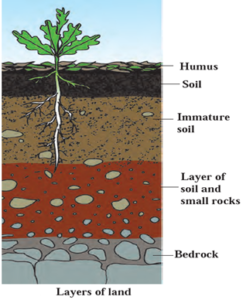
- Humus : The topmost layer of soil is formed by the decomposition of the remains of plants and animals. This is known as humus.
- Immature soil : The layer of land which is full of sand, soil, small stones, worms and insects is called immature soil.
- Bedrock : Below immature soil this there is bedrock. The main minerals of the soil are found in the bedrock.
The type of soil is different in different regions. This is dependent on the colour and texture of the constituents therein.
Know This : Humus, formed from the decomposition of dead plants and animals by microbes, is a crucial layer on soil that supplies nutrients, aerates the soil, and holds water. Its proportion in the upper layer of fertile soil ranges from 33% to 50%.
The process of soil formation :
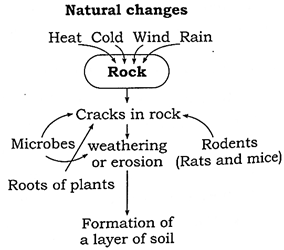
- Soil is formed by the natural process.
- Heat, cold and the rainwater cause weathering of the bedrock.
- This weathering process forms stones, sand and soil from the original rock.
- This supplies the abiotic components of the soil.
- Microbes, worms, insects and rodents further adds to the process of soil formation.
- The roots of big trees that grow on land also are weathering agents.
- All these factors cause soil formation in a very slow and continuous way. 5 cm thick layer of mature soil takes thousands of years to form.
Human activities and natural calamities like floods and storm cause destruction of soil. For the conservation of soil and for prevention of soil erosion, the green cover of the land should be increased.
Fossil fuels :
- The forests on the land were buried underground due to upheavals caused in the earth's crust in past. This happened many millions of years ago.
- From the remains of the living things the fossil fuels were created naturally due to pressure and heat.
- Petrol, diesel, kerosene, paraffin, tar and wax can be obtained from these fossil fuels.
Utilization of resources:
- All living things utilize the natural resources for their survival but the availability of natural resources in the environment is limited. For example – Oxygen – 21% Fresh water – 0.3% Land – 29%
- These resources although available in fewer quantities are sufficient to fulfill the needs of living organisms, provided these are used wisely and not wasted.
Indian Meteorological Department:
- In order to study the weather of Indian subcontinent, Indian Meteorological Department was established in 1875.
- This institute observes the weather and makes the weather and rain forecasts, conducts research related to the changes in the weather, and studies the developments related to global warming.
Click on below link to download pdf from store:
PDF : MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-1-Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land-Notes
PDF : MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-1-Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land-Solution
PDF : MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-1-Natural Resources – Air, Water and Land-Book
Useful links of Class 6th General Science :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter-2- The Living World- Online Notes |
Air points give