Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 6th General Science Chapter 3-Notes, Solution, Videos, PDF
Notes
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
| Diversity in living organisms can be experienced everywhere on earth. The warm and humid regions of the earth are highly diverse and are called the region of mega biodiversity. |
Various types of living things have survived because of their ability to adjust themselves to the conditions in their surroundings.
- Plants are classified on the basis of their height and the shape of stems, period of life cycle and habitat.
- Animals are classified on the basis of the cell structure, vertebral column, method of reproduction and habitat.
[/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Autotrophic plants : Plants make their own food in sunlight. Such plants are called autotrophic plants.
Example, the hibiscus, pomegranate, periwinkle, etc.
Heterotrophic plants: Some plants use other plants for food and are said to be heterotrophic plants.
Example: funguses, loranthus, dodder.
Insectivorous plants : Plants consume insects are insectivorous plants.
Example the pitcher plant.
The structure of a plant :
Plant structure divided into two parts :
Stem- grows above the ground. The height, shape and size of a plant depends upon the stem.
The stem carries out the functions of production, conduction and storage of food.
In some plants, it has the function of reproduction. It gives support to other parts of the plant.
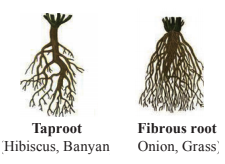
Root- grows below the ground surface. Roots hold the soil firmly and anchor the plant.
The main functions of the root are to absorb and transport water and nutrients from the soil.
The roots of the carrot and radish also store food.
There are two types of roots : taproot and fibrous root.
Parts of plants: The root, stem and leaves are the main parts of plants.
The leaf : The leaf is flat. It plays an important role in the production of food.
Leaves are of two types : simple and compound leaves.
The flower : This is the most attractive part of a plant. It is connected to the stem by a stalk which may be long or short.
A flower has a typical colour and shape.
The flower is an important means of reproduction.
Flowers are transformed into fruits. Fruits have seeds. Seeds give rise to new plants. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Classification of plants : While studying the diversity in plants, they are classified for the sake of convenience on the basis of the similarities and differences in their structure, their organs and their other characteristics.
It is necessary to classify plants because
- Classification is a tool which helps us to deal with a great diversity. Classification allows us to understand diversity better.
- It helps in the identification of living organisms as well as in understanding the diversity of living organisms.
- Classification helps us to learn about different kinds of plants, their features, similarities and differences.
- It enables us to understand how complex structure evolve from simpler.
- To understand and study the features, similarities and differences between different Plants, they are grouped under different categories of living forms.
It is easy to classify the plants on the basis of shape and height of the plants.
According to the size and height of their stems, plants can be classified into three types: trees, shrubs and herbs.
Trees : Plants which grow tall, having hard and strong stem, or trunk. They have branches at some height above the ground. They bear flowers and fruit for many years. Such plants are called trees.
Trees are perennial, i.e. they live for many years.
Shrubs : Some plants grow and give out branches close to the ground. They are shorter and smaller than trees, but having a thick and hard stem.
Example : oleander, hibiscus, lantana, koranti and rose are shrubs
Herbs : Herbs grow 1 to 1.5 metres tall. The stems of herbs are green and quite flexible as compared to those of trees and bushes. Herbs may live for a few months or up to two years.
Vine : Vine a plant whose stem requires support and which climbs by tendrils or twining or creeps along the ground
Some vines need vertical support for growing, while some others spread on the ground.
Example pumpkin, the railroad creeper, kavali, watermelon, grapevine.
Climbers like the money plant have aerial roots.
The stem of a creeper is very flexible, soft and green. It grows rapidly with the help
of a support. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Q. what are the similarities between the hibiscus oleander and lantana plants
Ans. The oleander, hibiscus, lantana, koranti and rose are shrubs that may grow
up to two to three metres.they all are flowering plants and renowned for their large, beautiful coloured showy flowers, These plants are widely cultivated as ornamental plants.
Because of lots of similar characteristics of three plants, people use these as showy displays in homes and in the offices.

[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
According to the period of their lifecycle, plants are classified as annuals, biennials, perennials.
Annuals : Plants which completed lifecycle in one year. These plants are called annuals.
Example jowar, sunflower
Biennials: The lifecycle of plants is of two years, they are called biennials.
Example carrot, beetroot
Perennials: Plants which live for several years and bear flowers and fruit. They are called perennials.
Example :Shrubs like the hibiscus and oleander and trees like mango and gulmohur.
Plants that bear flowers are called flowering plants,
Plants that never bear flowers are called non-flowering plants. Non-flowering plants may not have organs like roots, stems, leaves. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Q. What type of plants are toadstools and mushrooms ?
Ans. Toadstool and mushrooms belong to the fungus family. From a scientific perspective, there's no difference between a toadstool and a mushroom. In common speech, people tend to use the word toadstool to refer to fungi that are toxic, poisonous, or simply inedible. While the word mushroom is used to describe tasty and edible mushrooms.
Q. What type of plant is the fig ?
Ans. Fig is plant of the mulberry family and its edible fruit. The fig plant is a bush or small tree, from 1 metre to 12 metres high, with broad, rough, deciduous leaves that are deeply lobed, it is cultivated in warm climates.
fig is so widely used, both fresh and dried, that it is called “the poor man’s food.” The fruit contains significant amounts of calcium, potassium, phosphorus, and iron
Q. Do ferns, algae, money plant bear flowers ?
Ans. ferns, algae, money plant do not produce flowers.
Plants can be classified according to their habitat or the place where they grow.
Land, water, marshy areas, deserts and even a big tree are the various habitats of plants.
Q. Where does the pomegranate shrub grow ?
The pomegranate originated in the region extending from Iran to northern India and throughout the Mediterranean region.
it is widely cultivated throughout the Middle East and Caucasus region, north and tropical Africa, the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, the drier parts of Southeast Asia, and parts of the Mediterranean Basin.

Q. Where do bulrushes, the railroad creeper grow ?
Bulrushes grow in wet locations, including ponds, marshes, and lakes. Their stems are often used to weave strong mats, baskets, and chair seats.
Railroad creeper is most commonly grown in gardens, on trellises and railway platforms in India The plant is a common one in western peninsular India, and it grows on open, disturbed sites, in thickets and hedges, along streams, and also in fallow agricultural fields. Railway Creeper has some useful medicinal properties and usages
Q. Where does the lotus grow ?
Lotus is found throughout India The Lotus plant is an aquatic perennial, grows in the southern Asia and Australia region and most commonly cultivated in water gardens. The plant has its roots firmly in the mud and sends out long stems to which their leaves are attached.
Q. Where does the dodder plant grow ?
The dodder can grow and attach itself to multiple plants. In tropical areas it can grow continuously, and may reach high into the canopy of shrubs and trees. In temperate climates it is an annual plant, Dodder is parasitic on a very wide variety of plants.
Q. Why does the water hyacinth float on water ?
Air-filled tissues in various parts of the plant provide the buoyancy that allows them to float. A similar but invisible air-filled tissue is found in the swollen leaf stalks of the water hyacinth.
In many aquatic plants, parenchyma cells have large air cavities to give buoyancy to the plant and enable them to float in water. Such, parenchyma cells are called as aerenchyma. Water hyacinth possess such cells, which make them enable to float in water.

Q. Why is the stem of the cactus fleshy ?
Cacti have a thick, hard-walled, succulent stem. The stems are photosynthetic, green, and fleshy. When it rains, water is stored in the stem. A thick, waxy coating keeps the water inside the cactus from evaporating. Many cacti have very long, fibrous roots, which absorb moisture from the soil.
Q. What different criteria are used to classify plants ?
Ans. A plant. Classification is based on the following criteria:
- Similarities and differences in their structure, their organs
- Plant body: Presence or absence of Root, Stem and Leaves.
- Vascular system: Presence or absence of a vascular system for the transportation of water and other substances.
- Seed formation: Presence or absence of flowers and seeds.
- Habitat or the place where they grow
- Period of their lifecycle. [/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Diversity and classification in animals :
Different animals have developed different shapes to survive in the environment. There is a great variety in the body structure of animals.
Since animals depend on others for their food, they are found in places where food is available. Different animals have different methods of obtaining and eating food. This leads to differences in their body structure.
Animals are a unicellular or multicellular animals.
Animals form two groups. Animals with a vertebral column is vertebrates
Example Snakes, birds, fish and kangaroos as also humans are vertebrate animals.
Animals without vertebral column are called invertebrates.
Example: snails, cockroaches, earthworms do not have a vertebral column, therefore they are invertebrate animals.
According to the mode of reproduction, animals are classified into two types,
Oviparous animals which lay eggs.
Viviparous animals which give birth to their young ones.
According to their habitat, animals are usually classified into Terrestrial, Aquatic and Amphibious animals.
Terrestrial animals are animals that live predominantly or entirely on land e.g., cats, ants, spiders
Aquatic animals, which live predominantly or entirely in the water
e.g., fish, lobsters, octopuses
Amphibians, which rely on a combination of aquatic and terrestrial habitats e.g., frogs, salamander, toad live in both places, namely, land and water.
A kite, an eagle, a crow, a butterfly, a honeybee all fly in the air, though they live in different places. These animals are said to have an aerial mode of life. [/responsivevoice]
Video
Click on link to view :
1- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="TWAF-cZ1Lzs&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-1"]
2- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="WVn4dmfAX4U&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-2"]
3- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="9AwoM1uGsjw&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-3"]
4- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="Fw6qKBbY0VM&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-4"]
5- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="T9Yn5iE3-II&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-5"]
6- [video_lightbox_youtube video_id="tEhXvZg-KBg&rel=0" width="640" height="520" start="10" anchor="Video-6"]
Click on link to Download PDF:
Class 6th-General Science-Chapter-3-Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification - Notes
Class 6th-General Science-Chapter-3-Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification - Solution
Class 6th-General Science-Chapter-3-Diversity in Living Things and Their Classification -Books
Useful links of Class 6th General Science :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 6th Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Previous Chapter : Chapter 2 : The Living World - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-4-Disaster Management - Online Notes |

This is a good website