Rural Local Government Bodies
Maharashtra Board-Class 6th-Civic-Chapter-3
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
Levels of governance :
The administration in our country is carried on at three levels.
- Central (Union Government) : Responsible for : Defence, Foreign affairs, Currency & coinage.
- State : Responsible for : Law and order, public health and education
- Local : (a) Rural (b) Urban : Responsible for : Local issues
Panchayati Raj :
The three units of Rural local government, viz. Gram Panchayat. Panchayat Samiti
and Zilla Parishad are collectively described as the Panchayati Raj.
Urban local government :
Nagar Panchayat, Municipal Council and Municipal Corporation, are three types of
Urban local government.
Panchayati Raj Institutions at a glance :
1) Grampanchayat : (ii) Grants from the Zilla Parishad and the State Government
Topics
Descriptions
1-Level at which functions
Gram Panchayat for villages having population of 500 and above. If the population of a village is less than 500, two or more such villages come under one Gram Panchayat.
2-Number of Members
7 to 17
3-Term (Duration)
5 years
4-Office Bearers
(i) Sarpanch (ii) Up-Sarpanch
5-Officials
Gram Sevak appointed by the CEO of Zilla Parishad
6-Source of Income
(i) Property tax, water tax, pilgrimage tax, market cess
7- Main Functions
The Gram Panchayat carries out the functions relating to
Gram Sabha : The assembly of all the voters of the village or rural area is the Gram Sabha. It is the most important organization of the people at the local level.
- Assembly of all registered voters in the village, which meet six times in a financial year.
- Meetings convened by the Sarpanch.
- Annual report and statement of account discussed at the first meeting every year.
- Gives approval to the village development schemes.
- Makes suggestions to the Gram Panchayat.
- Women’s participation important as they express their opinion on the various problems faced by the village.
- May pass resolution like ban on production and consumption of liquor in the village.
The same is sent to the State Government.
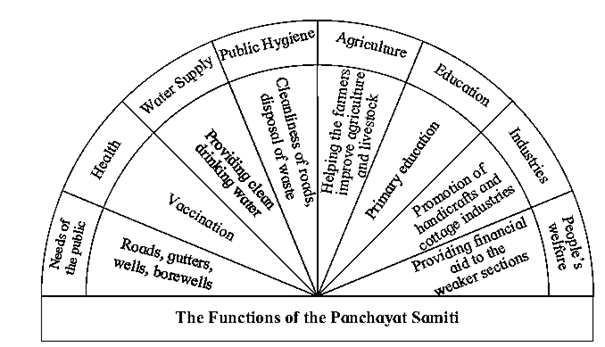
2) Panchayat Samiti : (ii) Grants from the state Government (ii) Public health (ii) Water supply (iv) Agriculture (v) Education (vi) Cottage and village industries (vii) Welfare activities
Topics
Descriptions
1-Level at which functions
Taluka
2-Number of Members
15-45
3-Term (Duration)
5 years
4-Office Bearers
(i) Chairman (ii) Deputy Chairman
5-Officials
Block Development Officer appointed by the State Government
6-Source of Income
(i)A portion of district fund
7- Main Functions
(i) Work for the development of block
3) Zila Parishad : (ii) Share of land revenue (iii) Grants from the State Government (ii) Agriculture (iii) Social welfare (iv) Public health (v) Education
Topics
Descriptions
1-Level at which functions
District
2-Number of Members
50-75
3-Term (Duration)
5 years
4-Office Bearers
(i) President (ii) Vice-President
5-Officials
Chief Executive Officer, appointed by the State Government
6-Source of Income
(i) Water tax, market cess, pilgrimage tax
7- Main Functions
(i) Work for the development of the district
In 1992 our Constitution was amended by the 73rd and 74th Amendment Act. These amendments have granted:
|
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – History & Civics - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-2-Diversity in Society - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-4-Urban Local Government Bodies - Online Notes |
