Urban Local Government Bodies
Maharashtra Board-Class 6th-Civic-Chapter-4
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
Urban local government bodies :
- The Nagar Panchayat. The Municipal Council and the Municipal Corporation are the urban local government bodies.
Facilities and Problems in cities :
Facilities in cities :
|
Problems in cities :
|
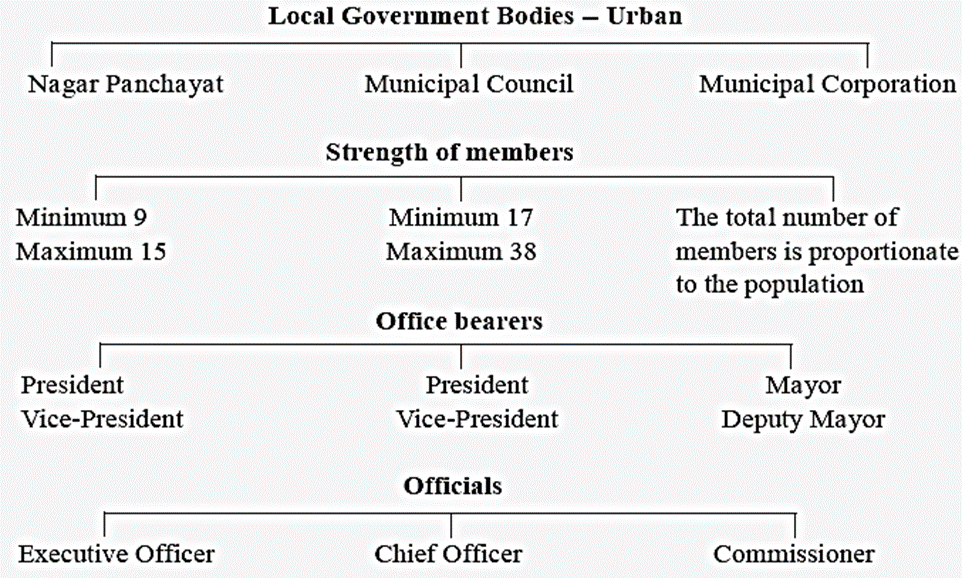
Urban local government structure :
Urban local government structure :
 [collapse]
[collapse]
(1) Nagar Panchayat :
- The villages that are in the process of becoming towns have a Nagar Panchayat.
- The areas which are neither fully rural nor fully urban in such areas, the local government body is the Nagar Panchayat.
- As with other local bodies, elections to a Nagar Panchayat are held every five years.
- Administrative head of Nagar Panchayat is the Executive Officer, appointed by the State Government.
- The councillors or ward members are chosen by direct election from electoral wards in the Nagar Panchayat.
- The elected members choose a President and a Vice-President from among themselves.
- Sources of Income : (i) Revenue from taxes. (ii) Grants from the State Government.
Functions of Nagar Panchayat :
- Essential services and facilities to the urban area.
- Sanitation program.
- Street lighting and providing roads in wards and main roads of town.
- Schools in urban areas.
- Program for adult literacy and run city libraries.
- Water supply to every ward of urban area.
(2) Municipal Council :
- The Municipal Council is the local government body for small cities.
- Elections to the Council are held every five years.
- The elected representatives function as Councillors.
- They choose a President from among themselves.
Administration :
- The President of the Municipal Council is the chairman of all its meetings.
- He controls the working of the Council and keeps a watch on the financial administration of the Council.
- In the absence of the President, the Vice-President looks after the work of the Council.
- For every Municipal Council, there is a Chief Officer. He implements the decisions taken by the Municipal Council. There are several officers who assist him.
Essential functions of a Municipal Council :
- Lighting public streets.
- Planning for social and economic development.
- Urban forestry and protection of the environment.
- Registration of births and deaths.
- Restore or demolish dilapidated (old and in very bad condition) buildings.
- Providing facilities for primary education.
- Providing public dispensaries.
- Making proper arrangements for crematoriums, burial grounds, etc.
- Providing drinking water.
- Making proper arrangements for sewage and drainage.
- Providing fire-fighting services.
Discretionary functions of the Municipal Council :
- Slum improvement and upgradation.
- Urban poverty alleviation.
- Providing facilities for secondary education.
- Providing facilities like libraries, museums and gymnasiums.
- Providing homes for the disabled and destitutes.
- Building and maintaining gardens and public parks; planting trees on both sides of the road.
Income sources of Municipal Council :
- The Municipal Council earns its revenue through a number of taxes levied on the people such as property tax, water tax, entertainment tax, etc.
- The State Government also provides it with grants.
- The Municipal Council can also raise a loan.
(3) Municipal Corporation :
- The local body that provides different services to the people in big cities is called ‘Municipal Corporation’.
- The first Municipal Corporation in Maharashtra was established at Mumbai.
- The total number of members of a Municipal Corporation is determined so as to be in proportion to the population of the city.
- The elections to the Corporation are held every five years.
- The elected members are known as Corporators.
- Corporators elect a Mayor and a Deputy Mayor from among themselves.
- The Mayor is considered to be the first citizen of the city.
- Mayor presides over all the meetings of the Corporation.
- Many important issues regarding the city are discussed, and decisions regarding the development of the city are made in the General Body meeting of the Corporation.
Administration :
- The Municipal Commissioner is the administrative head of the Municipal Corporation.
- He is appointed by the State Government.
- His main duty is to implement all the decisions taken by the Municipal Corporation.
- He prepares the annual budget of the Municipal Corporation.
- He attends all the General Body Meetings of the Corporation.
Obligatory functions of the Municipal Corporation :
- Regular supply of drinking water.
- Maintenance of roads and providing street lighting.
- Registration of births and deaths.
- Providing health-related services.
- Making proper arrangements for sewage disposal.
- Slum improvement and up-gradation.
- Maintaining a fire-brigade.
- Making arrangements for primary education.
- Restoring or demolishing dilapidated (old and in very bad condition] buildings.
Discretionary functions of the Municipal Corporation :
- Beautification of streets and crossroads.
- Felicitating individuals for their outstanding contribution to the city or state.
- Providing facilities for secondary and higher secondary education.
- Providing for a public transport system.
- Providing for public parks, gardens and playgrounds.
- Planting trees and maintaining them.
Sources of income of the Municipal Corporation :
- The Municipal Corporation collects various types of taxes such as property tax, water tax etc.
- The corporation also gets grants from the State Government for the fulfilment of its various development projects.
- The Municipal Corporation can also raise a loan to meet its financial demands.
PDF-Notes,Solution and Text Book
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – History & Civics - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-3-Rural Local Government Bodies - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-5-District Administration - Online Notes |