District Administration
Maharashtra Board-Class 6th-Civic-Chapter-5
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
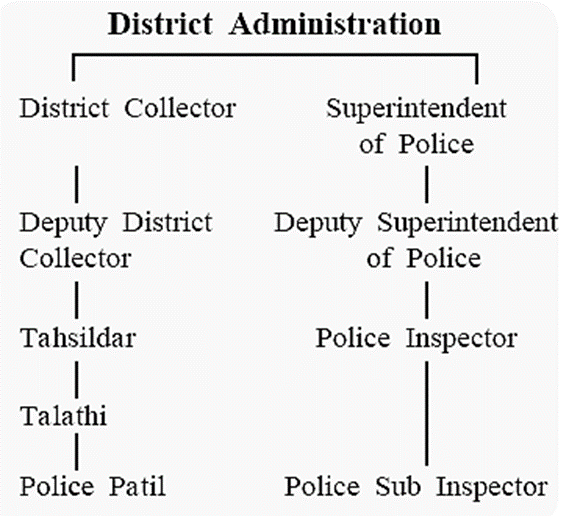
The District Collector
- The District Collector is the administrative head of the district.
- The State Government appoints him.
- He is the principal revenue officer in the district.
- He is also entrusted with the duty of upholding law and order, and thus social harmony.
- He serves as the district election officer and the Chief coordinator of disaster management.
Functions of the District Collector :
(i) Functions of the District Collector related to Agriculture :
- The District Collector is the official responsible for collection of land revenue in the district.
- He implements laws related to agriculture.
- In times of famines, he orders famine relief measures, including fodder for the animals.
(ii) Functions of the District Collector related to law and order :
- The District Collector is also the District Magistrate and maintains law and order in the district.
- He takes preventive measures such as ordering curfew and preventive detention to check occurrence of unpleasant incidents, especially during the times of festivals.
- He strives to maintain social harmony in the District.
(iii) Role of the District Collector as District Election Officer :
- As there is no separate machinery to conduct elections, the District Collector is assigned the responsibility of peaceful conduct of elections.
- He is empowered to take decisions in the context of conduct of elections.
- He supervises updating of the list of voters from time to time.
(iv) Role of the District Collector in disaster management :
- Being the head of the district administration, the District Collector heads the disaster management machinery.
- He takes on-the-spot decision to control the extent of damage caused by the disasters.
- He issues orders to the disaster management machinery regarding action to be taken.
- He supervises steps taken for the rehabilitation of the disaster-affected people.
Know This : Importance social harmony :
- The differences of opinion, disputes and conflicts in the society must be resolved by peaceful means.
- However, when this does not happen it gives rise to tensions.
- If this leads to violent incidents, it disturbs social harmony.
- It acts as an obstacle to our progress.
- Public property is damaged.
- The District Collector makes efforts to prevent such occurrences but it is the duty of the citizens also to help maintain social harmony.
Tahsildar :
- There is a Tahsildar for each taluka or tehsil, and as a Judicial Officer, he gives decisions to resolve local conflicts.
- The Tahsildar has the responsibility of maintaining peace and order in the taluka.
The Chief of the District Police
- In Maharashtra, there is a Superintendent of Police at every district headquarters.
- He is the chief Police Officer of the district.
- He helps the District Collector to maintain peace and order in the district.
- In the city, the Police Commissioner has the responsibility of maintaining law and order
District Courts :
- The Court at the district level is known as the District Court.
- The district court has a chief District Judge and some other Judges.
- Their main function is to hear the various cases in the district and deliver the final judgment.
- One can appeal against the judgment of the taluka court in the District Court.
Structure :
- The District Court is divided into criminal wing and civil wing.
- The criminal court at the district level is known as the District Sessions court, consisting of the District Magistrate, Magistrate Class I and Magistrate Class II.
- The District Judge presides over the civil court of the district and is assisted by Civil Judge Class I and Civil Judge Class II.
Disaster Management :
- Disaster Management is the systematic and scientific method to deal with disasters.
- Disaster Management is necessary as the people have to face natural calamities like earthquakes, floods and cyclones.
- The other man-made disasters such as bomb explosions and fire breaking out are also dealt under Disaster Management.
- Rehabilitation of the people affected by disasters is an important component of Disaster Management.
- With the advances made in technology it is possible to give prior intimation to me people of such anticipated calamities as floods and cyclones.
- The entire district administrative machinery works for Disaster Management.
Remember :
- It is important to remain alert during a time of crisis.
- To face a disaster one needs the help of people as well as different systems and organizations.
- In order to be able to contact them urgently, one should display the contact numbers of the police, fire brigade, hospitals, blood banks at a prominent place in the house.
Know This :
(1) Lakhina Pattern :
Shri Anilkumar Lakhina brought many reforms when he was District Collector of Ahmadnagar District. These are known as the ‘Lakhina Pattern’.
- Standardization of work procedures, stating rules in simple language which could be understood by the people, etc. were the administrative changes he introduced.
- He also started the ‘Single Window’ system, so that jobs that people came to do could be completed under one roof.
(2) Dalvi Pattern :
The administrative reforms implemented by Shri Chandrakant Dalvi when he was District Collector of Pune District, are known as the ‘Dalvi Pattern’.
- This pattern is also known as ‘Zero Pendancy Pattern’
- The objective of the reform was to speed up the decision making by ensuring that files were not allowed to stack up and that they were dealt with on the same day that they were received.
- It helped in bringing efficiency and speed into administrative work.
(3) Chahande Pattern :
When Dr Sanjay Chahande was the Divisional Commissioner of Nashik he implemented certain reforms which are now known as the ‘Chahande Pattern’.
- In order to reduce the gap between the people and the administration, to increase the accountability of the administration towards the people and to prioritize the development work through people’s pariticipation, he implemented the ‘Gramastha Din’ (Villagers’ Day) scheme.
- This is the appointed day when the administrative officials and staff visit a village and establish a dialogue with the people to understand their problems and help to solve them.
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – History & Civics - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-4-Urban Local Government Bodies - Online Notes |
