Chapter-14-Light and the Formation of Shadows
Maharashtra Board Class 6th General Science Chapter 14
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction : We cannot see anything in total darkness. We are able to see the objects around us due to the light
Sun, Electric bulb, illuminated candle etc. are the examples that is giving us the light.
Luminous objects or materials : The objects that emit light or those which themselves are a source of light are called luminous objects. The intensity of light depends on the extent to which they emit this light. Every luminous object is a source of light.
Non-luminous objects or materials: The objects that do not emit light and those which are not the sources of light are called non-luminous objects.
- Stars are luminous.
- Planets, satellites are non-luminous.
- Sunlight reflected from the surface of the moon reaches us. That is how we can see the moon. We call this light moonlight.
Artificial sources of light : The substances that cannot emit light on their own, but emit it due to man's effort are man-made sources or artificial sources of light.
Natural sources of light: Sun is the main natural source of all light. Other stars, fireflies, some bio-luminescent (i.e. able to produce light) animals like angler fish and honey mushroom are the natural sources of light.
The propagation of light : Light always travels in a straight line. This is known as linear propagation of light.
- Example : The rays of light are seen entering a room through a slit in a door or a small hole in the roof. These rays show dust particles within them. Due to these particles, the path of the light is clearly seen. As the rays move to the ground from the hole in the roof, they are seen to be in a straight line.
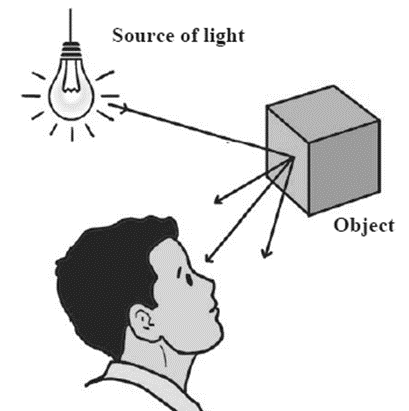
Reflection of light : When the light rays from any source fall on a surface, they are thrown back. This is called the reflection of light. When the reflected rays from an object reach our eyes, we are able to see this object.
- The reflection shows reverse characters of that of the object. The reflection of light rays falling on the surface causes this difference.
- We are able to see the reflection in mirror, in window glass pane and also in any shining, glossy object.
Images : The light reflected from our face falls into the mirror. When we stand in front of the mirror, this light is reflected back again and due to this reflection we are able to see our image in the mirror.
In a glass pane, we can see a faint and unclear image.
On the wooden surface, we will not be able to see our image
Images in the plane mirror :
- The left and right sides of the original object and that of the mirror image appears to be exchanged.
- The image looks as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
- The size of the image is same as that of the object.
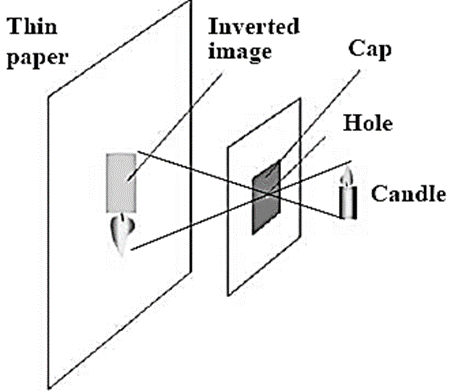
A pinhole camera : A pinhole camera is an apparatus with a single small aperture. All the sides of this box like pinhole camera are closed and has complete darkness inside it. The light rays try to enter through the small aperture and an image is formed on the diaphragm inside.
Working of pinhole camera :
Transparent, Opaque, Translucent : As per the material of object, the propagation of light takes place or does not take place.

Formation of a shadow : Light does not pass through an opaque object. As a result, the light is hindered from going to the wall or on any other surface on the other side of the object. This part remains dark which is called the shadow of the object.
- The shadows are produced only for the opaque objects, because light does not pass through these objects.
The kind and type of a shadow depends upon the following points :
- Relative distances between the sources of light,
- The type of object,
- The surface on which the shadow falls.
Shadows formed by the sunlight are longer in the early mornings and late evenings.
While in the afternoon they are short. This change in these shadows also depends upon the source of light, the type of object and the surface on which the shadow falls.
There are seven colours in the sunlight. Many small experiments can be performed to show this fact.
Newton's disc :
Click on below link to download pdf from store:
MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-14-Light and the Formation of Shadows-Notes
MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-14-Light and the Formation of Shadows-Solution
MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-14-Light and the Formation of Shadows-Book
Useful links of Class 6th General Science :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-13-Sound - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-15-Fun With Magnets - Online Notes |
