Substances In The Surroundings
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 6th General Science Chapter 5
Notes
Three States of the matter : Solid, liquid and gas (vapour).
- Every substance is found in either solid, liquid or gaseous state. If it is heated or cooled, it changes its state.
- When a substance changes from one state to another, this process is known as ‘change of state of the substance’.
- The characteristic properties of a substance depend on its physical state and the arrangement of particles in it, is shown by the scientist J. Willard Gibbs.
The differences between the states of substances :
Solid :
- Shape: Solid has a shape of its own which is retained.
- Volume : Has a definite volume. Forms a heap if emptied on a flat surface.
- Examples : metals pieces sugar, salt
Liquid :
- Shape: Liquid has no shape of its own, takes shape of the container in which the liquid is kept.
- Volume : Has a specific volume. If kept in a container it occupies certain space but if spread on a flat surface, it starts flowing.
- Examples : water, oil, milk.
Gas :
- Shape: Gaseous Occupies all the available space as it does not have a shape of its own.
- Volume : It does not have fixed volume. If kept under pressure, in a closed container its volume also changes.
- Examples : air, vapour
Change in the state :
Solid (If heated) —> Liquid (If heated) —> a Gas
Gas (If cooled) -—> Liquid (If cooled) —> Solid
Heat and change of physical state :
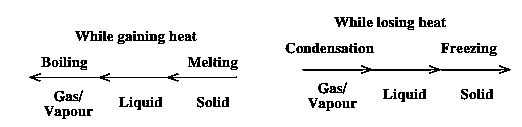
Change in physical state of the substance is an effect of the amount of heat in it. Solids on heating change their state into liquid. Liquids on heating, change into gas. Similarly, the gases when cooled convert into liquid and liquids when cooled further, can change into solids. Heating means gaining heat while cooling is losing heat.
The temperature and a thermometer : The temperature of a substance, (how hot or cold it is), can be measured with the help of a thermometer.
A thermometer is used to measure the temperature of a substance. Degrees Celsius (°C) is the unit for measuring the temperature. Nowadays digital thermometer is in use.
Boiling :
Condensation :
Freezing :
Melting :
|
Uses of changes of the state of substance :
Sublimation ; If upon heating a solid does not turn into liquid but changes directly into gaseous state, then this process is known as sublimation. e.g. Iodine crystals, naphthalene balls, camphor are substances that show sublimation.
Properties of substances :
| Diamond is the hardest naturally occurring substance found on Earth. But it is not the hardest substance. Wurtzite boron nitride (man-made substance) and lonsdaleite (which comes from meteorites) are both harder than diamond. |
Properties of metals :
- Malleability : The property of metals to be converted into sheets is called malleability.
- Ductility : The property of metals by which they can be stretched and drawn into wires is called ductility.
| Ornaments are made from gold or silver. Nowadays platinum is also used for making ornaments. All these metals have characteristic of ductility. Hence they can be stretched and pulled in the form of wires. Making ornaments from these metals thus becomes easier. Diamonds are also studded in ornaments. Diamond is the hardest substance and has shine. |
- Electrical conductivity : The property to carry electricity is called electrical conductivity. All metals are good conductors of electricity showing that electricity flows through metals.
| Electric cables are either of copper or aluminium. Copper is a good conductor of ‘electricity. Therefore, most of the electric cables are made from copper. |
- Thermal conductivity : The property to carry heat is called thermal conductivity. All metals are good conductors of heat showing that heat flows through metals.
| Pots and pans are made from different metals. Aluminium, stainless steel and brass are the common choices. Cooking food becomes easier in them.
All the metals have characteristic of thermal conductivity. In pots of stainless steel, the chemical reactions with the food do not take place. Therefore, it becomes convenient to use such materials. |
- Sonority : The ability to produce ringing sound is called sonority. Example- Electric bell.
- Characteristic colour and lustre. All the metals have a characteristic colour and lustre which is specific for each metal. Example : Gold and silver have lustre which makes ornaments shine.
Q. Why are the electric boards fitted on the wall made of plastic or wood ?
In the plastic and wooden material there is no electrical conductivity. When we are touching electric boards we should not get electric shock. Therefore, the electric boards fitted on the wall are made of plastic or Wood.
Q. The handle of pressure cooker is made of plastic. Why ?
Pressure Cooker is made from mixed metals such as hindalium or aluminium. When it is on cooking fire, it becomes hot. If we lift it up in a hurry, we may get burnt. To avoid this the handle of cooker is made from plastic. Plastic is not thermal conductive material. Therefore, we may not feel the heat of the cooker while lifting it up.
Useful links of Class 6th General Science :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-4- Disaster Management- Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-6- Substances in daily use- Online Notes |
