Rocks and Rock Types
Class 6th-Geography-Chapter-7
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
Rocks :
- Rocks are a mixture of different minerals formed by natural processes in the lithosphere.
- The earth’s crust is made of rocks and soil.
- Silica, aluminium, magnesium and iron are the major rock forming minerals. There are other minerals, too, in different rocks.
- Properties of rocks depend on the constituent minerals and their proportion as well as on the formation process.
Types of rocks :
There are the following three types of rocks according to their formation process :
- Igneous rocks/ Primary rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks.
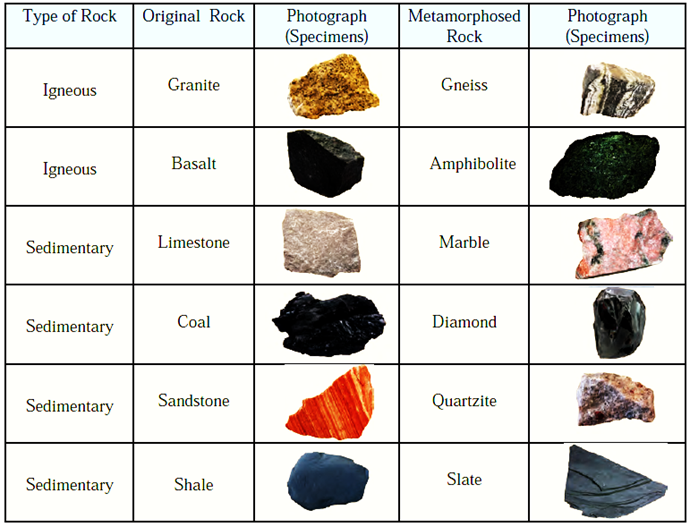
(i) Igneous rocks :
- When molten material cools, known as magma within the crust and lava on the surface, it solidifies, giving rise to igneous rocks.
- These are also referred to as primary rocks. We do not get fossils in these rocks.
- Basalt is a major example of igneous rock.
(ii) Sedimentary rocks :
- The rocks disintegrate/decompose as a result of heat, rivers, glaciers, wind, and so on. These rock particles are transported to low-lying places and deposited there. Layers of sediment are deposited one after the other in this manner.
- The top layers exert significant pressure on the lower layers, resulting in material compaction and the formation of sedimentary rocks.
- These rocks may include fossils. These rocks are typically fragile and light.
- Sedimentary rocks include sandstone, limestone, shale, corals, and others.
Metamorphic rocks :
- Igneous or sedimentary rocks are subjected to huge pressure and heat as a result of volcanic activity and other earth movements. As a result, the crystals in the original rocks re-crystallize/metamorphose, resulting in the production of metamorphic rocks, corals, and other sedimentary rocks.
- These rocks do not contain fossils. These rocks are heavy and hard.
- Gneiss, Marble, Diamond, Slate, etc. are metamorphic rocks.
Examples :
| Know This :
• Pumice is an example of igneous rock. This is formed out of volcanic froth. It is a porous rock. As its density is quite low, it can float on water. • The interior of the earth has very high temperature. As a result, the material in this part is in the molten state. Sometimes this material gets released through the fissures in the crust. This is called a volcano. Lava, gases, dust, ashes, etc. are thrown out during volcanic eruptions. |
Fossils :
- The impressions of buried remains of dead animals or plants become putrefied in the rocks as a result of high pressure. These are known as fossils.
- The study of fossils provides information about the life in that period.
Maharashtra's major rock distribution :
- Basalt rock formed out of volcanic eruption has spread over a vast region of
- Granite rock is found mainly in the eastern parts and in South Konkan.
- Laterite is found in South Konkan in the districts of Sindhudurg and Ratnagiri.
- Sedimentary rock is found in Nandurbar, Dhule, Jalgaon, Buldhana, Akola and Amravati districts of Maharashtra.
Mineral wealth of Maharashtra :
- Because of the thick and extensive layers of Basalt, Maharashtra does not have large reserves of mineral wealth
- In Maharashtra, mining activity is concentrated in South Konkan and in Eastern Maharashtra.
Click on below link to get pdf from store:
Chapter-7-Rocks and Rock Types-Notes
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-6-Importance of Oceans - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-8-Natural Resources - Online Notes |
Notes are good. want it