Sources of History
Maharashtra Board-Class 6th-History-Chapter-2
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
Sources of History : All those artifacts, structures and written records as well as folk tales and folk arts that help us to understand history are called the sources of history.
- A number of objects used by our ancestors still exist. Some inscriptions from past have been recovered. These sources help us to understand history.
- The customs and traditions, artifacts, structures, folk arts and folk literature and historical documents help us to understand history
- All these are known as the sources of history.
Sources of History are : (i) Material sources, (ii) Written sources and (iii) Oral sources.
Material sources : The artefacts, articles, monuments or their ruins are called material sources of history.

Written sources : The Stone Age people have recorded many events and expressed their emotions in paintings on rocks. It was only after thousands of years that man learnt the art of writing.
Oral sources : Literature preserved by oral tradition is the oral source of history
Sources of ancient Indian history : The ancient period of Indian history extends from the Stone Age to the eighth century CE.
- Since scripts had not developed at that time, no written sources are available. However, information about the ancient period from 1500 BCE onwards can be derived from Vedic literature.
- We have a large number of material, written and oral sources of ancient Indian history.
- Material sources are artefacts and structural remains.
- The written sources include the stone inscriptions, copper plates, Harappan seals,
- Vedic literature, Jain and Buddhist religious texts, travelogues of the foreigners, literary and non-literary works.
- Vedic, Jain and Buddhist literature which was earlier in oral form is now available in written form. However, the tradition of memorization continues.
Precautions to be taken while writing history : It is necessary to take precautions while using these sources to write history. These precautions are :
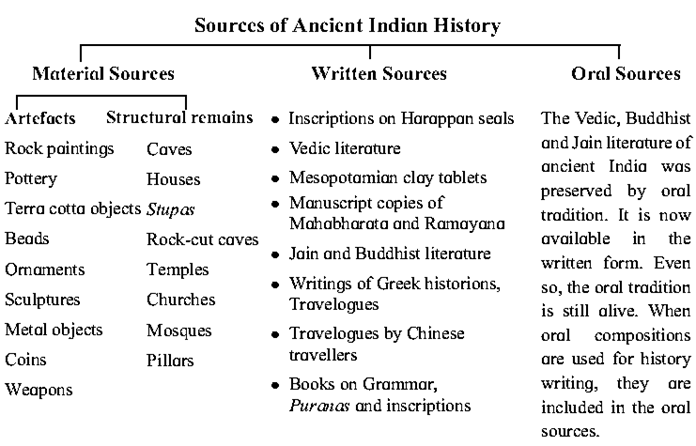
Q. Why are the Vedic literature, the Jain and Buddhist scriptures regarded as the oral sources?
Therefore Vedic literature, the Jain and the Buddhist scriptures are regarded as oral sources.
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – History - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-1: The Indian Subcontinent and History - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-3-The Harappan Civilization - Online Notes |