Fun with Magnets
Maharashtra Board Class 6th General Science Chapter 15
Solution
Question 1:
How will you do this ?
(a) Determine whether a material is magnetic or non-magnetic.
The material should be taken near to the magnet. If a material sticks to a magnet, then it is a magnetic material otherwise it is a non-magnetic material.
(b) Explain that a magnet has a certain magnetic field.
A magnet has a certain magnetic field which can be demonstrated using the below activity. Paper. The iron filings will get attracted to the magnet only till a particular region. Beyond this region, the iron filings will not get attracted. The region where iron filings are attracted is the magnetic field, whereas the region from where the iron filings are not attracted, will be the region with no magnetic field. This experiment can give some idea about the extent of magnetic field of a magnet.
Keep a magnet in the centre of a paper. Spread iron filings uniformly on the fiat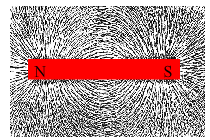
(c) Find the north pole of a magnet.
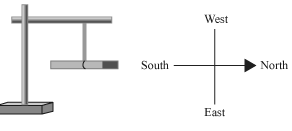
Tie a thread to the centre of a magnet and hang it from a stand as shown. Wait till the magnet settles itself. The north pole of the magnet will point to the north direction while the south pole of the magnet will point to the south direction. If the directions are not known, then we can use mariner's compass. Take a magnet near the mariner’s compass. The pole which shows repulsion if taken near the north pole of a mariner’s compass, will be the north pole of this magnet.
Question 2.
Which magnet will you use ?
(a) Iron is to be separated from trash.
Electromagnet can be used to separate iron from trash.
(b) You are lost in a forest.
If the directions are not known, then we can use mariner's compass.
(c) A window shutter opens and shuts continuously in the wind.
Permanent magnet can be used to stop the continuous shuttering of the window in the wind.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate word.
(a) If a bar magnet is hung by a thread tied at its centre, its north pole becomes steady in the direction of the ……………. Pole of the earth.
(South, north, east, west)
If a bar magnet is hung by a thread tied at its centre, its north pole becomes steady in the direction of the north Pole of the earth.
(b) If a bar magnet is cut into equal pieces by cutting it at right angles to its axis at two places, ........... bar magnets are formed, and a total of ................ poles are formed.
(6,3,2)
If a bar magnet is cut into equal pieces by cutting it at right angles to its axis at two places, 3 bar magnets are formed, and a total of 6 poles are formed.
(c) There is repulsion between the ………. poles of a magnet, and attraction between its ………… poles.
(opposite, like.)
There is repulsion between the like poles of a magnet, and attraction between its opposite poles.
(d) When magnetic material is taken close to a magnet, the material acquires …………… .
(permanent magnetism, induced magnetism)
When magnetic material is taken close to a magnet, the material acquires induced magnetism.
(e) If a magnet attracts a piece of metal, that piece must be made of ............
(any other metal but iron, magnetic material or iron, non-magnetic material)
If a magnet attracts a piece of metal, that piece must be made of magnetic material or iron.
(f) A magnet remains steady in a ………….. direction.
(east-west, north-south)
(f) A magnet remains steady in a north-south direction.
Question 4.
Write the answers in your words.
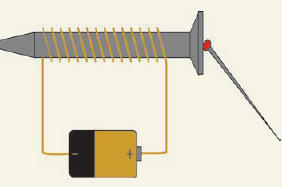
(a) How is an electromagnet made ?
For the construction of an electromagnet, we require an iron nail, a long insulated copper wire, a battery and a switch. When an article of iron is wound by a copper wire and the electric current is sent through the wire, the magnetism is produced in this iron article. As soon as the current stops flowing in the circuit, the article of iron loses magnetism. This is how temporarily magnetism can be produced by creating electromagnetism.
(b) Write the properties of a magnet.
(b) Properties of a magnet are following:
(c) What are the practical uses of a magnet ?
Magnets have very wide range of uses:
Click on below link to download pdf from store:
MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-15-Fun with Magnets-Notes
MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Chapter-15-Fun with Magnets-Solution
Useful links of Class 6th General Science :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 6th Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Videos : MSBSHSE-Class-6-Science-Videos- All Chapter videos Previous Chapter : Chapter-14-Light and the Formation of Shadows - Online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter-16-The Universe - Online Solution |
