Life Processes in Living Organisms-1
Based on Class 10 -Science & Technology-Part 2-Chapter 2- Maharashtra Board
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Lets’ recall :
Functions of Food stuffs and their Nutrients :
Body needs continuous source of energy for various functions. Food stuff and oxygen is man source of energy.
- The food stuffs are digested and converted into soluble nutrients.
- These nutrients are carried by blood to every cell of the body.
- The oxygen inhaled at the time of respiration is also carried to every cell.
- In the body cells, this oxygen carries out oxidation of nutrients and thus energy is produced.
- The energy helps the body to carry out all its functions. The nutrients help in the growth and development of the body.
Importance of balanced diet for body :
- Balanced diet has carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals in the right proportion.
- Each nutrient carries a specific important function.
- In balanced diet all these nutrients are in right proportion.
- Since balanced diet is required for energy and nutrition, it is very important to maintain our health.
Functions of muscles in body :
There are three types of muscles in our body,
- The voluntary muscles bring about all the movements according to our will.
- Involuntary muscles bring about all vital activities of the body. The visceral organs are under the control of involuntary muscles.
- The cardiac muscles control the movements of heart.
- Carbohydrates and proteins are stored in muscles.
Importance of digestive juices in digestive system :
- Digestive juice contains different enzymes.
- Enzymes act as catalysts and bring about the chemical reactions at faster pace.
- The digestive juices of stomach make pH of digestive tract acidic while that of intestinal juice make it alkaline.
Excretory system : Excretory system helps in the removal of nitrogenous waste materials produced in the human body.
Circulatory system :
- Due to circulatory system, glucose from digestive system and oxygen from respiratory system is transported to every cell.
- Red blood cells carry the oxygen as the blood is pumped by the heart.
- In every cell with the help of oxygen, glucose molecules yield the energy by the process of oxidation.
Q. How are the various processes occurring in the human body controlled? In how many ways?
Ans. The nervous system and the endocrine system brings about control by nervous and chemical coordination in the body. Due to such coordination different functions of the body are carried out in sequential and controlled manner.
Living organisms and Life processes :
- Different systems work in co-ordination with each other in the body of the living organisms. In human body the homoeostasis is very advanced.
- Digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, excretory system, nervous system and all the external and internal organs in the body work independently but in coordination with each other.
- The digested and absorbed nutrients of the food are transported to various cells with the help of circulatory system.
- Carbohydrates, fats and lipids are the main sources of this energy. The mitochondria present in cytoplasm of the cell synthesise the energy by utilizing these nutrients.
- Only foodstuff is not sufficient for energy production but oxygen is also necessary.
- Food stuffs and oxygen are transported up to the cell via circulatory system.
- Each cell is thus supplied with oxygen and nutrients to produce the energy.
- The control is exercised by the nervous system on all these actions. This keeps the organism alive and helps in growth and development of the same.
- Plants are autotrophic, they synthesise their own food by photosynthesis. After utilizing some for their own needs, the remaining food is stored in fruits, roots, stem-tubers, leaves, etc.
- Human and animals consume various plant materials and obtain different nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, etc.
Carbohydrates :
- Source : Milk, fruits, jaggary, cane sugar, cereals, vegetables, potatoes, sweet potatoes, sweet meats.
- Functions: Carbohydrates provide 4 Kcal energy per gram.
Respiration :
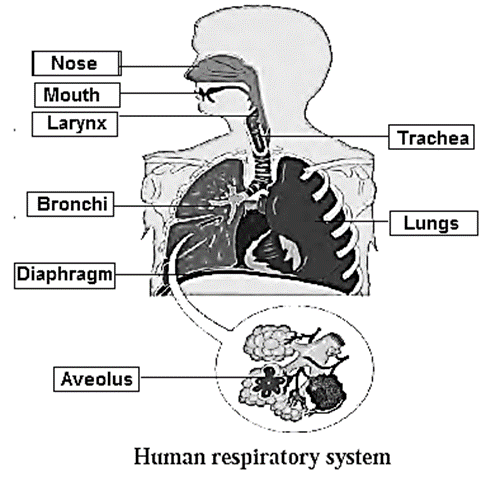
- Release of energy from the assimilated food is called respiration.
- Inhalation and exhalation is called breathing.
- When inhalation is done, air enters the lungs. The oxygen from this air enters the blood while carbon dioxide from the blood exits from the blood.
- Through exhalation, CO2 is given out. This gaseous exchange occurs through alveolar membrane. This is called external respiration.
- The RBCs carry oxygen to every cell. Here inside the mitochondria tissue respiration or internal respiration takes place. The oxygen is used for production of energy. By oxidation of food nutrients energy is released in the form of ATP
Living organism and Energy production :
In living organisms, respiration occurs at two levels as body and cellular level.
- Body level respiration : Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged between body and surrounding
- Cellular level respiration : In this process, foodstuffs are oxidized either with or without help of oxygen inside the cell.
Cellular level respiration :
- Dietary carbohydrates are utilized for production of energy in the form of ATP. Oxidation of glucose is carried out step by step in the cells during a process of cellular respiration.
- Cellular respiration is done by following two methods, viz. aerobic respiration (In presence of oxygen) and anaerobic respiration (In absence of oxygen).
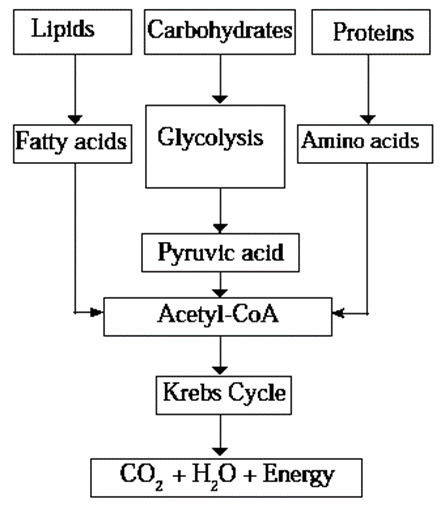
Aerobic respiration : Oxidation of glucose occurs in three steps during the aerobic respiration. These are glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle and electron transfer chain reaction.
(1) Glycolysis :
- In glycolysis glucose molecule is oxidized step-wise into two molecules of each of pyruvic acid, ATP, NADH, and water .
- This process takes place in cytoplasm. Pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is converted into a molecule of Acetyl-Coenzyme-A and two molecules each of NADH2 and CO2.
(2) Tricarboxylic acid cycle :
- When Acetyl-Co-A molecules enter the mitochondria, the tricarboxylic acid cyclic chain reactions take place in mitochondria.
- Acetyl part of Acetyl-Co-A is completely oxidized releasing molecules of CO2 H2O, NADH2, FADH2.

(3) Electron transfer chain reaction :
- The electron transfer chain reaction takes place only in mitochondria.
- Molecules of NADH2 and FADH2 formed during all above processes participate in electron transfer chain reaction.
- From NaDH2 molecule, 3 molecules of ATP and from FADH2 molecule 2 molecules of ATP are produced during these cyclic reactions.
- Along with ATP, water molecules are also formed during chain reactions.
Thus one molecule of glucose gives CO2 and H2O along with energy after complete oxidation in the presence of oxygen.
The two coenzymes that help in cellular respiration :
- NADH2 - Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide.
- FADH2 - Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide. These co-enzymes are formed in the cell and they take part in cellular respiration.
In case of less stores of carbohydrates in body :
- Then lipids and proteins are utilized for producing energy.
- Lipids are converted into fatty acids and proteins are broken down to amino acids in such condition. Both, fatty acids and amino acids are converted into Acetyl-Co-A for obtaining energy.
- Molecule of Acetyl-Co-A undergoes complete oxidation by the process of Krebs cycle in mitochondria for releasing the energy.
ATP:
- ATP or Adenosine triphosphate is energy-rich molecule and energy is stored in the bonds by which phosphate groups are attached to each other.
- These molecules are stored in the cells as per need.
- Chemically, ATP is triphosphate molecule formed from adenosine ribonucleoside.
- It contains a nitrogenous compound-adenine, pentose sugar- ribose and three phosphate groups.
- As per the need, energy is derived by breaking the phosphate bond of ATP; hence ATP is called as ‘energy currency’ of the cell.

| Recall :
Glucose molecule :
|
The cellular process and their researchers :
- Process of glycolysis was discovered by three scientists Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jacob Parnas along with their colleagues. For this purpose, they performed experiments on muscles. Hence, glycolysis is also called as Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway (EMP pathway).
- The cyclical reactions of tricarboxylic acid cycle were discovered by Sir Hans Krebs. Hence, this cyclical process is also called as Krebs cycle.
Process of energy production through aerobic respiration of carbohydrates, proteins and fats : Anaerobic respiration in living organisms/ cells :
Energy Production in Microorganisms through Anaerobic Respiration :
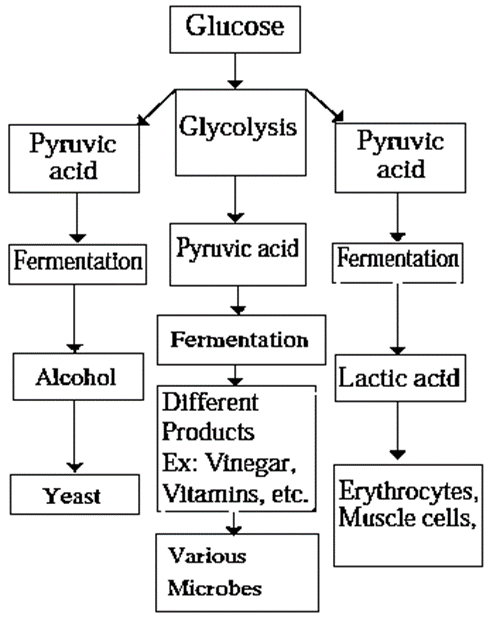
- Some bacteria and lower organisms do not live in presence of oxygen. They perform anaerobic respiration for energy production.
- Anaerobic respiration has two steps : Glycolysis and fermentation. In glycolysis glucose is incompletely oxidized releasing less amount of energy.
- Pyruvic acid produced through glycolysis is converted into other organic acids or alcohol (C2H5OH) in process which is called fermentation. This process is aided by some enzymes.
- If there is deficiency of oxygen level in the surrounding, some higher plants, animals and aerobic microorganisms also perform anaerobic respiration.
- E.g. If the soil is submerged under water during germination, seeds perform anaerobic respiration. Similarly, human muscle cells while performing the exercise may also switch to anaerobic respiration. This makes the person feel tired due to less amount of release of energy and due to lactic acid accumulation.
Q. Which type of cellular respiration performs complete oxidation of glucose?
Ans. The aerobic respiration or cellular respiration in presence of oxygen performs complete oxidation of glucose.
Q. Which cell organelle is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose?
Ans. Mitochondria is necessary for complete oxidation of glucose.
Energy from different food components :
- Excess of the carbohydrates are stored in liver and muscles in the form of glycogen.
Proteins :
- Proteins are formed by amino acids which are held by peptide bonds. Therefore, it is called a macromolecule. When proteins are digested, they are converted back into amino acids. Amino acids are absorbed in blood circulation and transported to every cell.
- As per the type of cell, the amino acids are again used for making proteins that are required by the body.

- Proteins of animal origin are considered to be ‘first class’ proteins. Each gram of protein provides 4 Kcal of energy.
- If protein intake is more than required, it does not result into storage of amino acids in the body.
- Instead they are broken down forming ammonia which is then eliminated from the body.
- Sometimes, excess of proteins is converted into glucose by process of gluconeogenesis
Plants by themselves can produce the necessary amino acids from minerals and then also different proteins.
- The mast abundant protein found in nature is an eanzyme RUBISCO which is found in the plant chloroplasts.
Lipids :
- Lipids are formed of fatty acids and alcohol (glycerol) which have specific bond between them. When lipids are digested they are converted into fatty acids and alcohol. Absorbed fatty acids are transported to all the cells through blood.
- Fatty acids produce different substances in different cells.
- Examples : (1) Phospholipids - produce plasma membrane, (2) Progesterone, estrogen. testosterone, aldosterone. etc. are hormones produced from fatty acids,(3) Covering around the axons of nerve cells.
- Adipose connective tissue in the body stores excess of lipids. Each gram of lipids provides 9 Kcal of energy.
Vitamins :
- Vitamins are required for proper functioning and maintenance of the body.
- The main types of vitamins are : Fat soluble vitamins : A. D. E and K, Water soluble vitamins : B and C.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) and Nicotinamide (Vitamin B5) are necessary for their production of FADH2 and NADH2 respectively.
Water :
- Water is essential nutrient.
- Human body contains about 66 - 70% water. 70% water is present by weight in every cell. Blood- plasma has 90% of water.
- Loss of water or dehydration can cause problems with the functioning of cells and later that of the body.
Q. Many times, you cannot eat hot food due to inflammation /ulceration in mouth.
Ans. The inflammation or ulceration in the mouth occurs due to lack of enough vitamins in the diet, therefore hot and spicy food causes uncomfortable feeling. Particularly vitamin B complex deficiency is said to be responsible for such ulceration.
Q. Some persons experience difficulty in night vision since their childhood or adolescence.
Ans. For a better vision, vitamin A is essential. If there is deficiency of Vitamin A in the diet there is a difficulty in night vision even in childhood or adolescence.
Cell Division : An essential life processes :
Introduction :
- After injury, the cells and the tissues are not able to perform the regular functions immediately. At the site of injury. the blood capillaries rupture and the area gets inflamed. Many cells are damaged. The pain receptor nerves induce pain.
- As the wound heals there is a scab developed. The cells surrounding the wound start dividing rapidly and the cells lost in the injury are restored back. In this way new cells are formed by cell division to heal the wound.
- Recent discoveries have proved that plants also have sensations. The tissues that are lost get restored by cell division.
Growth of living organism : Any living organism grows due to the increase in the number of cells in their body. The cells divide regularly and add new cells which are essential for growth. The cell division is thus necessary for the growth of the body and also for the regeneration and repair of tissues.
Reproduction : Due to reproduction, the new individual is formed from the existing one. Reproduction can be asexual or sexual.
- In asexual reproduction, there is mitosis. This cell division helps in forming new individuals.
- In sexual reproduction, gametes are formed by reduction division called meiosis. Due to chromosomes, gene and DNA the new individual of a species becomes similar to the existing species.
Cell division is one of the very important properties of cells and living organisms
Significance of cell division :
- A new organism is formed from existing one,
- A multicellular organism grows up
- Injured, emaciated body can be restored.
Types of cell division : (i) Mitosis and (ii) Meiosis
(i) Mitosis :There are two stages of mitosis. These are (a) Karyokinesis or nuclear division and (b) Cytokinesis or cytoplasmic division. Karyokinesis takes place in further four phases, viz prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.

(a) Karyokinesis :
- Prophase : During prophase, condensation of chromosomes starts. The thin and thread like chromosomes start thickening. They are seen with their pair of sister chromatids. In animal cells the centrioles are seen to duplicate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear.
- Metaphase : Chromosomes complete their condensation and each one is seen with its sister chromatids. The chromosomes are seen in equatorial plane of the cell. The spindle fibres are formed from polar region, where centrioles are present, and they attach themselves to the centromere of each chromosome. Nuclear membrane now disappears completely.
- Anaphase : The centromeres of the chromosomes now divide forming two daughter chromosomes. The spindle fibres pull apart the chromosomes from equatorial region to the opposite poles. Chromosomes moving to the poles appear like bunch of bananas. One set of chromosomes reach each pole by the end of the anaphase.
- Telophase : Telophase is reverse of events that occurred in prophase. The thickened chromosomes decondense. They again assume the thin and thread like appearance. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus appear again. The spindle fibres are completely lost. The cell looks as if it has two nuclei in one cytoplasm.
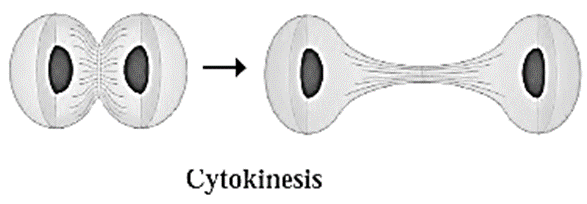
(b) Cytokinesis : In animal cells a notch develops in the middle of the cell. This notch goes on deepening down and later the cytoplasm divides into two. In plant cells, cell plate formation takes place and then cytokinesis takes place.
Significance of mitosis :
- Essential for the growth of the body
- Necessary for restoration of emaciated body
- For wound healing
- For the formation of blood cells, etc.
(ii) Meiosis :
There are two stages of meiosis : : (a) Meiosis-I and (b) Meiosis-II.
- By meiosis from one diploid cell, four haploid cells are formed.
- In meiosis crossing over between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes occur. This results in genetic recombination.
- The four daughter cells formed after completion of meiosis are genetically recombined and not exactly alike and also not exactly similar to their parent cells.
- Spores and gametes are formed by meiosis.
- Meiosis helps to restore and maintain the chromosome number.
(a) Meiosis I :
- Homologous chromosomes undergo crossing over and hence there is genetic recombination.
- The homologous chromosomes are divided into two groups and from these, two haploid cells are formed.
- Prophase I of meiosis is lengthy phase which is subdivided into five phases, viz. leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis. During pachytene, crossing over takes place.
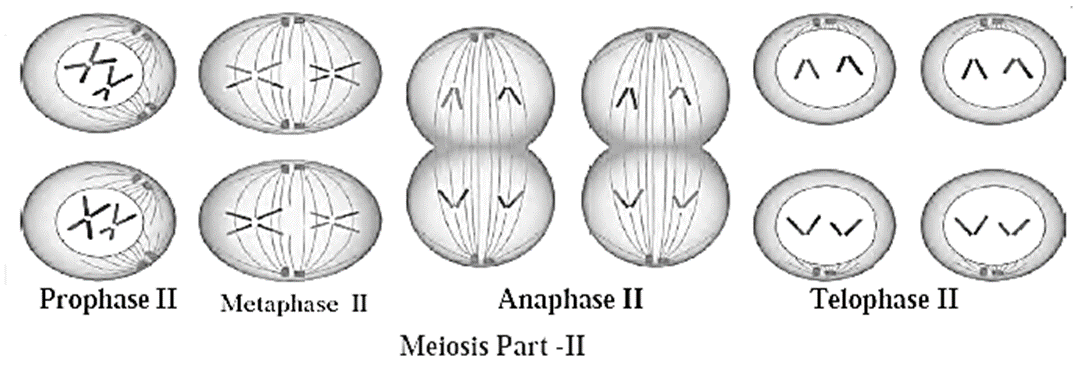
(b) Meiosis II :
- Meiosis II is similar to mitotic division. The two haploid cells that are produced in meiosis II now undergoes further division forming four haploid
- The diploid cells are 2n and the haploid are n. All the normal body cells are always 2n while only gametes formed by reduction division are n.
- In ‘2n’ condition, each type chromosome is in pairs while in ‘n’ condition, there is a single chromosome of each type.

Important features of mitosis and meiosis : 2-Takes place in two stages- Karyokinesis-division of nucleus and Cytokinesis-division of cytoplasm 3-Karyokinesis takes place in four stages. It is followed by cytokinesis. 4-Chromosome number does not change. 4-Mother cell gives rise to 2 daughter cells. 2-Takes place in two parts-Meiosis-I and Meiosis-II. In Meiosis -I there is crossing over and genetic recombination. Homologous chromosomes are divided into two groups forming two haploid cells. 3-Meiosis I and Meiosis II take place in four stages each, i.e. Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, and Telophase I followed by Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II. 4-Chromosome number is reduced to half . 5-Mother cell gives rise to 4 daughter cells.
Mitosis
Meiosis
1-Occurs in somatic cells and in stem cells.
1-Occurs in germ cells.
Know This :
Chromosomes are seen only at the time of cell division. Chromosomes are rod shaped and has a primary constriction or centromere. The arms of the chromosome seem to be attached at the centromere. Depending upon the position of centromere and the length of the arms of the chromosome, there are four types of chromosomes.
Chromosome :
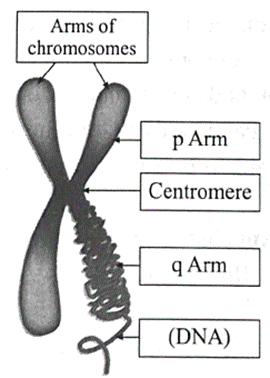
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter 1. Heredity and Evolution - Online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 3. Life Processes in living organisms Part -2 - Online Solution |

it was quite imaginative
hi I am prerna Iam 10 th class thyaks for nots
Hi thanks for a important notes..☺️
Thanks for easy and important notes 🙂
It’s very helpful notes in this notes every imp point were highlighted!
Well but im cbse student but im convert my bord into state so some objection in thse :- jo topic main vo to thik hain par unne define karne main assani ki hain jo bhaut bhetrin lagta hain par jo jis kam hi nahi hain usse bewefesol he define kiya please correct this ! I write its note postive point and negtive point also may be next you work upon these but some examples we there to know what is negative point :- some recall section are not important in topic so be must be care to know plaese correct this …..