Life Processes in Living Organisms-2
Based on Class 10-Science & Technology Part-2-Chapter-3- Maharashtra Board-Audio Notes, Solution, Videos, PDF
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction :
Important life processes in living organisms:
All those life processes i.e. nutrition, respiration, excretion, sensation & response (control & co-ordination), etc. are essential to each living organism to remain alive.
- Reproduction is also a one more life process but it does not help the organism to remain alive but it helps to maintain the continuity of the species of that organism.
Essential life processes for production of energy required by body :
- Respiration, circulation and nutrition are the life processes that are essential for production of energy required by body.
- Oxygen is supplied to cells by respiratory and circulatory system.
- The oxidation of nutrients that are absorbed in body is done because of oxygen supplied to cells.
- This helps in liberation of energy.
Mitosis and meiosis :
- Mitosis and meiosis are the main types of cell division.
- In mitosis, the chromosome number remains the same. Two daughter cells are obtained from one cell.
- In meiosis, the chromosome number is reduced to half. From one cell, four daughter cells are obtained.
Role of chromosomes in cell division :
Due to chromosomes, the DNA from parental cells enter into daughter cells. The hereditary characters are transmitted to next generation by cell division.
 |
- In picture ‘a’ vegetative propagation is shown. The twig is planted and it is showing rootlets. This indicates that new plant is being produced.
- In picture ‘b’ hen is laying eggs.
- In picture ‘c’ the seed is germinating and has produced radicle and plumule.
- In picture ‘d’ cell division or binary fission similar to mitosis is shown.
- All the pictures, show different types of reproduction.
Reproduction : Asexual and Sexual :
- Reproduction is formation of new offspring of same species by earlier existing parent organism.
- Reproduction is important character of living organisms.
- Evolution of every species occurs due to reproduction.
| Maintenance of species :
Maintenance of species means a species undertakes successful reproduction and produces individuals of its own kind. This keeps the species existing on the earth,
Relationship between the cell division and formation of new organism of same species by earlier existing organism :
|
Two main types of reproduction: Asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction :
Asexual reproduction is uniparental reproduction in which there is no formation of gametes.
- New organism is formed without the fusion of the gametes.
- The offspring produced is exactly similar to the parent organisms.
- It takes place by mitotic cell division.
- Demerit of asexual reproduction : Absence of genetic recombination.
- Merit of asexual reproduction : Rapid process of reproduction.
(A) Asexual reproduction in unicellular organisms :
There are different methods of asexual reproduction in different unicellular animals.
(i) Binary fission :
- The process in which the parent cell divides to form two similar daughter cells is binary fission.
- It takes place either by mitosis or amitosis.
- The division of nucleus and cytoplasm takes place initially.
- Binary fission is usually performed by living organisms during favourable conditions i.e. availability of abundant food material
- Prokaryotes, Protists and eukaryotic cell-organelle like mitochondria and chloroplasts perform binary fission.
Based on axis of fission there are three subtypes of binary fission.
(a) Simple binary fission : The plane of division is not definite, it can be in any direction due to lack of specific shape as in Amoeba.

(b) Transverse binary fission : The plane of division is transverse, as in Paramoecium.
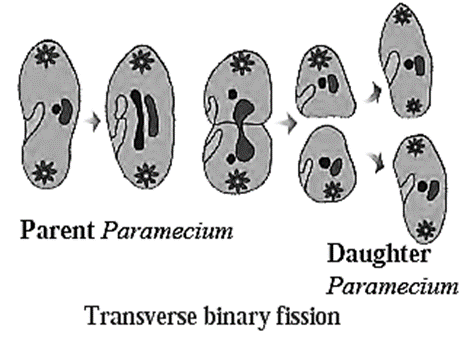
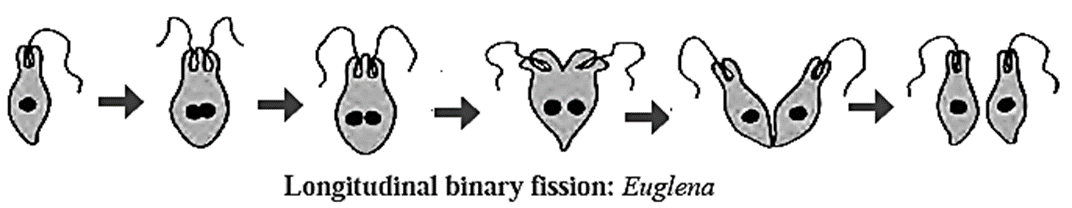
(c) Longitudinal binary fission : The plane of division is in length-wise direction as in Euglena.
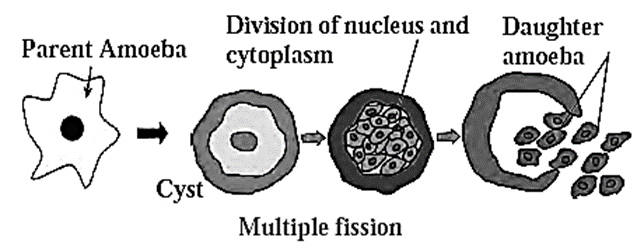
(ii) Multiple fission :
- During unfavourable conditions when there is lack of food, multiple fission is shown by amoeba.
- Amoeba forms protective covering and becomes encysted. Inside the cyst, amoeba undergoes repeated nuclear division.
- This is followed by cytoplasmic divisions.
- Many amoebulae are formed which remain dormant inside the cyst.
- When favourable conditions reappear, they come out by breaking the cyst.
Budding :
- The parent cell produces two daughter nuclei by mitotic division.
- This results in a small bulging bud on the surface of parent cell.
- One daughter nucleus enters the bud.
- It then grows and upon becoming big it separates from the parent cell to have independent life as new yeast cell.
- Organisms : Yeast is unicellular fungus that performs budding.

(B) Asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms :
(i) Fragmentation:
- Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction occurs in multicellular organisms.
- In this type of reproduction, the body of parent organism breaks up into many fragments and each fragment starts to live as an independent new organism.
- This type of reproduction occurs in algae Spirogyra, and sponges like Sycon.
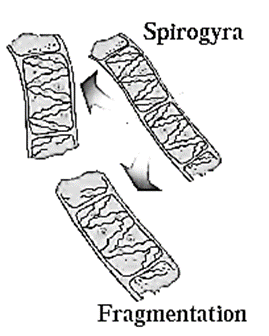
- In favourable condition i.e. whenever there is plenty of water and nutrients are available to Spirogyra, its filaments grow up very fast and break up into many small fragments. Each fragment starts to live independently as a new Spirogyra fiber.
- If the body of Sycon breaks up accidentally into many fragments, each fragment develops into new Sycon.
(ii) Regeneration :
- In developed animals like wall lizard the process of regeneration is used to restore the lost parts like tail or limbs.
- As the reproductive system is one of the full-fledged system in the body, the process of regeneration cannot be called type of reproduction.
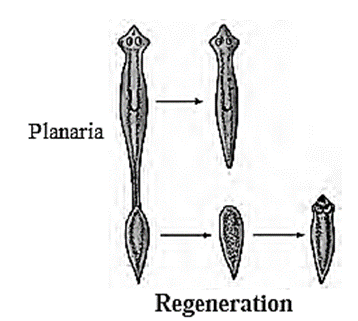
- But some primitive organisms such as Planaria use this method for procreation.
- Planaria breaks up its body into two parts. Each part has the ability to develop the lost part by process of regeneration. This forms two new Planaria.
(iii) Budding :
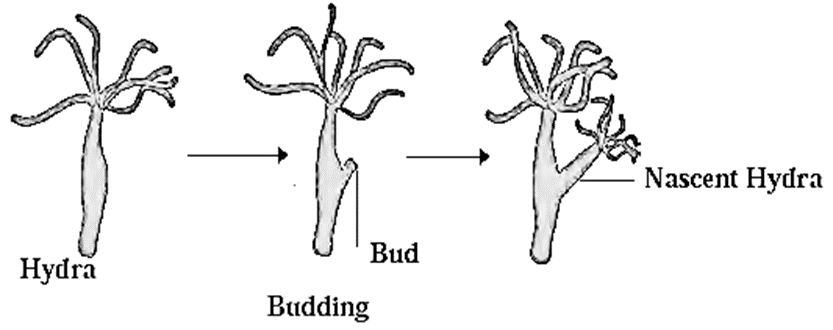
- In multicellular organisms asexual reproduction by budding is shown by hydra.
- In fully grown Hydra, at specific part of its body there is development of bud.
- This development is only during favourable period.
- The bud is an outgrowth developed due to repeated divisions of regenerative cells of body wall.
- It grows up gradually to form a small hydra.
- Parent hydra’s dermal layers and digestive cavity are in continuity with those of the budding hydra.
- It receives all the nutrition from parent hydra.
- When the budding hydra grows sufficiently, it detaches from parent hydra. Then it leads an independent life.
(iv) Vegetative Propagation
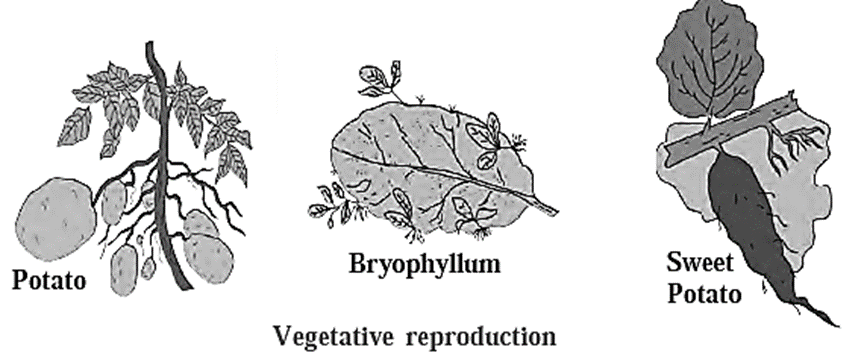
- Reproduction in plants with the help of vegetative parts like root, stem, leaf and bud is called as vegetative reproduction.
- Vegetative propagation in potatoes is performed with the help of ‘eyes’ present on tuber
- In Bryophyllum it is performed with the help of buds present on leaf margin.
- In case of plants like sugarcane & grasses, vegetative propagation occurs with the help of buds present on nodes.
(v) Spore Formation :
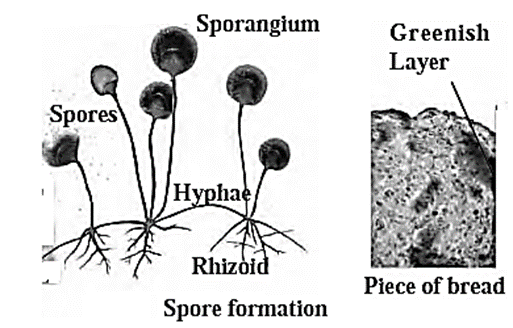
- Mucor reproduces asexually by spore formation.
- It has filamentous body that possess sporangia.
- When the spores are formed, the sporangia burst. The spores are released which settle down at suitable places.
- They germinate in moist and warm place forming a new fungal colony .
- Example, Fungus grow on wet bread or ‘bhakari’ within 2 – 3 days, if kept it in humid place.
Sexual Reproduction :
Reproduction with the help of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction. It has two main processes, viz. gamete formation and fertilization.
- Gamete formation: By meiosis the gametes are formed. The diploid germ cells give rise to haploid gametes.
- Fertilization : From union of haploid male and a female gamete a diploid zygote is formed during fertilization. Subsequent mitotic divisions of zygote form embryo which then develops into new individual.
Two parents i.e. male parent and female parent are involved in this type of reproduction.
- Male parent produces male gamete or sperm and the female parent produces female gamete or ovum.
- The fusion of these forms zygote.
- Zygote has recombined genes of both the parents. Hence, the offspring shows some Similarities and some differences in the parental characters.
- Genetic variation gives rise to diversity in living organisms. Those genetic variations that are helpful for adapting to the environment are retained. Such individuals exist and do not become extinct.
| Know This :
If meiosis does not happen the gametes produced will be diploid. Diploid (2n) gametes if united, they will form 4n, i.e. tetraploid variety. Such zygote will show severe abnormality. The chromosome number will not be maintained. |
Sexual reproduction in plants :
Flower is structural unit of sexual reproduction in plants
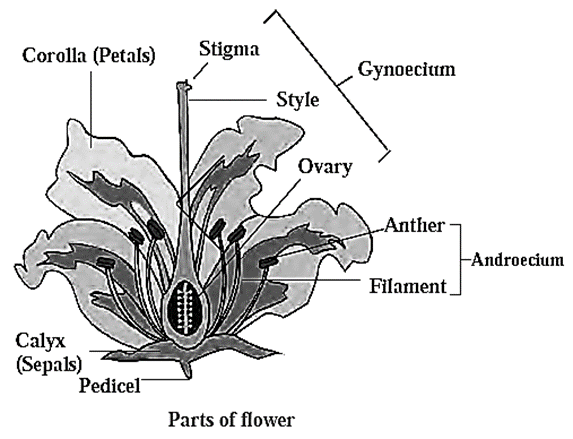
- There are total four floral whorls. Of these two are accessory floral whorls while two are essential floral whorls.
- Calyx and corolla are accessory whorls. They are protective in nature.
- Members of calyx are known as sepals. They are usually green in colour. They protect the inner whorls.
- The members of corolla are called petals. They can be of different colours.
- Androecium and gynoecium are essential whorls as they participate in sexual reproduction.
- The male whorl androecium is made up of stamens. Each stamen has a filament with anther located at the upper end. In the anther there are four locules. Inside the locules the meiosis takes place forming pollen grains. During suitable time, the pollen grains are released from anther lobes.
- Gynoecium is made up of carpels, either in separate form or are united. Each carpel is formed of ovary at the basal end, hollow ‘style’ and the stigma at the tip of style. There are one or many ovules inside the ovary.
Bisexual flowers : In bisexual flowers both androecium and gynoecium are located in the same flower. e.g. Hibiscus.
Unisexual flowers : In unisexual flowers, androecium is present in male flowers and gynoecium is present in the female flowers, e.g. Papaya.
Sexual reproduction in plants :
Plants reproduce sexually with the help of flowers. Androecium and gynoecium are male and female parts of the flowers respectively.
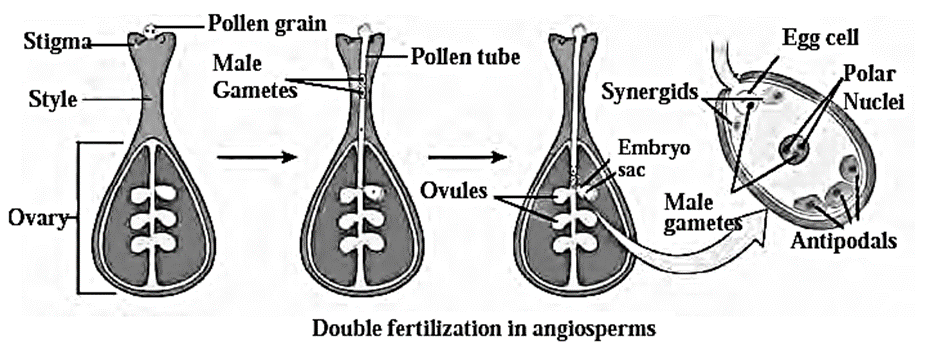
- In the carpel, the ovule undergoes meiosis and forms embryo sac.
- A haploid egg cell and two haploid polar nuclei are present in each embryo sac.
- The pollen grains from the anther reach the stigma of flower by the process of pollination. They germinate here on the stigma.
- As a result of germination, long pollen tube and two male gametes are formed.
- The pollen tube travels through the style of flower and the male gametes present in the pollen tube are transferred till the embryo sac in ovary. Upon reaching there, tip of the pollen tube bursts releasing two male gametes in embryo sac.
- One male gamete unites with the egg cell and forms zygote. While other male gamete unites with two polar nuclei forming the endosperm.
- Because there are two nuclei participating in this process, therefore it is called double fertilization.
- After fertilization ovule develops into seed and ovary forms a fruit. When the seed again gets favourable conditions, it can produce a new plant.
Pollination : Transfer of pollen grains from anther to stigma is called pollination.
Agents of pollination :
- Abiotic agents : Wind, water.
- Biotic agents : Insects, birds or other animals.
Types of pollination :
- Self-pollination : Pollination involves only one flower or two flowers borne on same plant.
- Cross-pollination : Involves two flowers borne on two plants of same species.
In artificial pollination for forming new high yielding and resistant varieties of plants, the pollination with the help of brush, is done by scientists.
Fertilization :
- Pollens fall upon sticky stigma and germinate.
- A long pollen tube and two male gametes are formed upon germination.
- The pollen tube carrying male gametes travels through style and reaches the embryo sac.
- In embryo sac, tip of the pollen tube bursts releasing two male gametes.
- Here fertilization occurs by union of one male gamete and egg cell.
- Second male gamete unites with two polar nuclei. This union forms endosperm.
- Since two nuclei take part in the process, it is called double fertilization.
Germination :
- The development of new plantlet from zygote after fertilization is called germination.
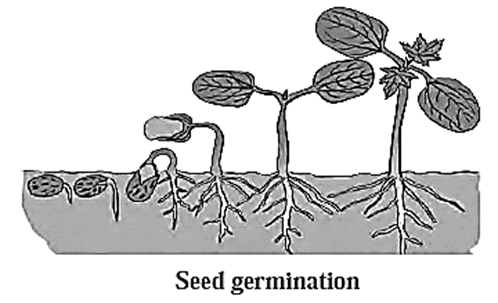
- After fertilization ovule develops into seed and ovary into fruit.
- Seeds from broken fruits fallen upon the ground start germinating if they get favourable conditions.
- Development takes place due to food stored in endosperm of seed.
Sexual reproduction in human being :.
Sex determination:
- Sex is determined according to the sex chromosomes,
- Human males have 44 somatic chromosomes and XY sex chromosomes.
- Human females have 44 somatic chromosomes and XX sex-chromosomes.
- Due to particular sex chromosomal complement, the masculine reproductive system or feminine reproductive system is developed.

Hormones :
- Pituitary gland secretes FSH and LH. LH is known as ICSH in males, as its function in the male body is different.
- From the gonads of male and female, hormones are secreted which are essential for male and female reproductive functions respectively.
- These hormones are testosterone secreted from testis in males and estrogen and progesterone secreted from the ovaries in females.
- Testosterone is essential for masculinity as well as for sperm production
- Female hormones estrogen are essential for changes in the female body leading to motherhood.
Human male reproductive system :
In human male reproductive system, the reproductive organs are as follows :
- Testes, different types of duct systems and glands.
- Testes are in pair. Each testis lies in the scrotum which lies outside to abdominal cavity.
- Testes consist of numerous seminiferous tubules. The germinal epithelium of seminiferous tubules form sperms by undergoing meiosis.
- These sperm cells are immature.
- They are pushed gradually through various duct systems till the penis.
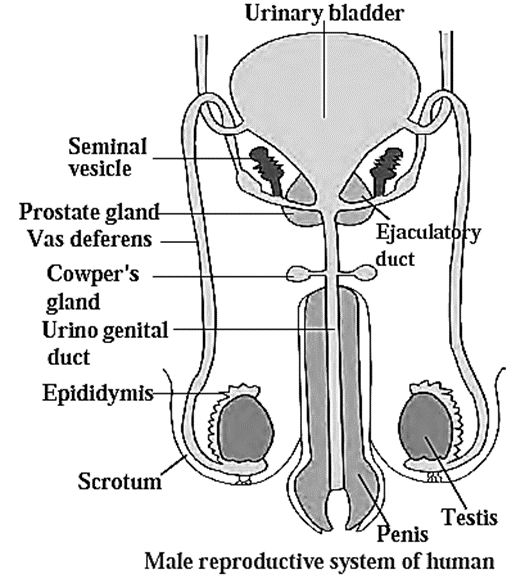
- This path is as follows : Rete testis —> vas efferentia —> epididymis —> vasa deferentia —> Ejaculatory duct —> urethra
- As the sperms are travelling, they gradually become mature. They are made capable to perform process of fertilization.
- Seminal vesicles (in pairs), Single prostate gland and a pair of Cowper’s glands secrete their secretions. These secretions and the sperms together form semen.
- This semen is deposited in the vagina with help of penis.
Human female reproductive system :

- All the organs of the human female reproductive system are located inside the lower abdomen.
- There are pair of ovaries, pair of fallopian ducts and a single median uterus.
- The uterus opens out by vagina. In vaginal walls there are Bartholin’s glands.
- The urethra in female body is separate and not a common passage as in male body.
- The free end of fallopian duct is funnel-like having an opening in the centre. The oocyte released from the ovary due to ovulation is picked up by this funnel.
- The other end of fallopian duct opens into uterus. There are cilia on inner surface of oviduct.
- With the help of the cilia the oocyte is pushed to the uterus through the fallopian duct.
- The fertilization of oocyte can take place only in the middle part of the fallopian duct.
- The lower end of uterus opens into vagina. The contractions of uterus help in the process of parturition.
- Vagina is the birth canal as well as copulatory passage. It is also a passage for menstrual flow.
Why has the Government of India enacted the law to fix the minimum age of marriage as 18 in girls and 21 in boys?
Ans. The full growth of female body is not completed till the age of 18. Till 18 years of age the physical and emotional maturity is not attained. Therefore, she is not suitable for marriage, sexual relationship and pregnancy.
Similarly, boy attains complete growth only by the age of 21. Therefore, to keep individuals and their progeny safe and healthy the Government of India enacted the law to fix the minimum age of marriage as 18 in girls and 21 in boys.
Formation of gametes :
- Sperm from father and ovum from mother are haploid gametes formed by meiosis.
- Man can produce sperms from puberty till death.
- But in a woman the function of reproductive system stops at menopause.
- In mature woman a single matured oocyte is released from ovary every month.
- In woman’s body from birth, there are 2 – 4 million immature oocytes in the ovary of female foetus. Till the age of 45 years woman can produce ova.
- Later she attains menopause due to lessened secretion of female hormones. The reproductive functions then completely stop.
Fertilization :
Formation of zygote by union of sperm and ovum is called as fertilization.
- There is internal fertilization in humans in which semen is deposited in vagina during intercourse. In the semen there are few millions of sperms. They swim from vagina through uterus and reach fallopian ducts. Only one sperm is required for fertilizing a single ovum that female produces.
- Women with advanced age have Strong chance of conceiving abnormal child. The ova that develop around menopausal age are 45-50 years old and hence they can be abnormal due to faulty meiosis. If such ovum is fertilized there are increased chances of getting genetically abnormal child. e.g. Down’s syndrome or Turner's syndrome.
Development and Birth :
- The fertilization takes place in fallopian duct. The zygote thus formed undergoes rapid and repeated mitotic divisions to develop embryo.
- It travels from fallopian tubes to uterus. In uterus it gets implanted and grows for next 40 weeks or 9 months.
- The nutrition during this period is provided by placenta which is an organ developed in pregnant mother.
- After completion of embryonic development for 9 months the pregnant mother gives birth to a baby.
Hormone oxytocin :
|
Sex determination in human beings:
- The gametes develop from germ cells which are diploid (2n).
- Each diploid cell has 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex-chromosomes i.e. (44 + XX or 44 + XY).
- Germ cells undergo meiosis forming haploid (n) gametes having chromosomal combination of 22+ X or 22+ Y.
- Sperms produced are of two types viz. (22 + X) or (22 + Y) but ova/oocytes are all (22 + X) types.
- Sperms complete process of meiosis before they leave male reproductive tract. But the oocytes complete meiosis after ovulation, i.e. only if they are fertilized.
- Type of sperm of father decides the sex of the child. If X bearing sperm fertilises the oocyte, the girl is born and if Y bearing sperm fertilises oocyte, it’s a boy. Mother has all X bearing oocytes, hence she is neutral in sex determination of the child. Thus mother is not responsible for the sex of child.
Girls are equal to boys in every aspect, therefore, female foeticide should be stopped. It is a crime to kill the unborn girls.
Menstrual Cycle :
- Menstrual cycle is the naturally occurring repetitive changes in mature human female.
- These cyclic events are controlled by four hormones: (a) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) (b) Luteinizing hormone (LH) (c) Estrogen (d) Progesterone.
- FSH and LH are secreted from pituitary and estrogen and progesterone are secreted from ovary.
- One ovarian follicle develops along with the oocyte present in it due to effect of FSH. This developing follicle secretes estrogen.
- This follicle produces estrogen under the influence of FSH.
- Under the effect of estrogen, uterine endometrium develops or regenerates.
- The oocyte also undergoes development.
- Then under the influence of LH, ovulation takes place. Ovulation is bursting of ovarian follicle to release an oocyte.
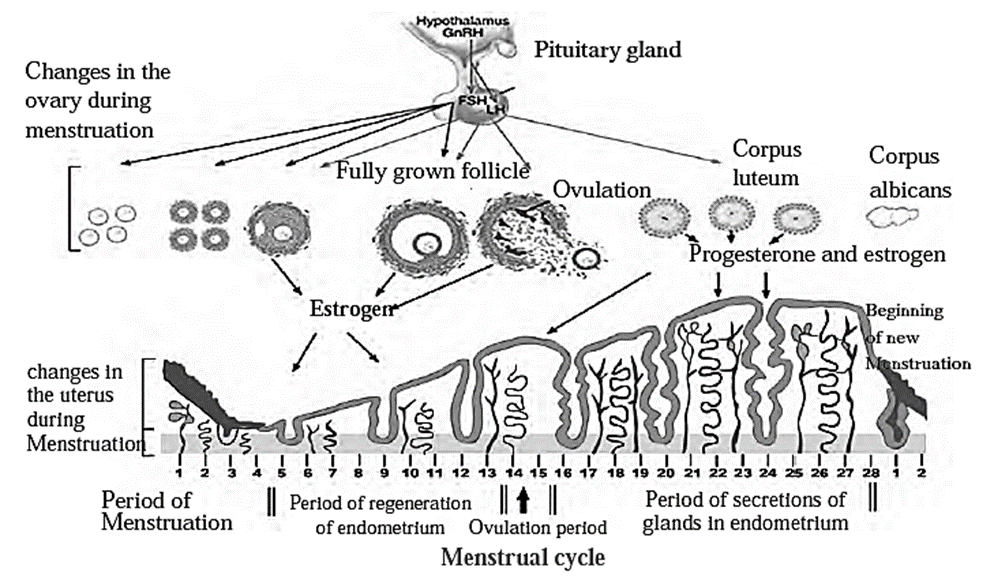
- The remaining tissue of empty ovarian follicle forms a body called the corpus luteum. It is a secondary endocrine source and it starts producing progesterone.
- Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine endometrial glands secrete and make this endometrium ready for implantation of embryo.
- If oocyte is fertilized the endometrium forms placenta along with developing foetus.
- But if it is not fertilized, corpus luteum loses its function and becomes a degenerate body called corpus albicans.
- Corpus albicans does not secrete estrogen and progesterone.
- Due to this, endometrium degenerates and starts sloughing off.
- Degenerating endometrium, unfertilized ovum and blood is discarded out through vagina.
- This results into continuous bleeding for five days which is called menstruation.
- This process is repeated every month. It is interrupted only by pregnancy.
- In breast feeding after parturition, menstrual cycle is suspended.
- The menstruating woman is in pains, she is bleeding, weak and Susceptible for infections. Therefore, she needs rest and facilities for personal hygiene.
Reproduction and Modern Technology :
Some couples want a child but they are not able to bear one due to various problems either in mother or in father. In such cases modern techniques such as IVF, surrogacy and sperm bank are useful in conceiving a child.
Causes of sterility :
- Causes of sterility in females : In Woman if there are problems like irregularity in menstrual cycle, difficulties in oocyte production or implantation in uterus, obstacles in the oviduct, etc. then she can resort to any one technique of the above.
- Causes of sterility in males : In man if there are no sperms in the semen, slow movement of sperms, or anomalies in the sperms then he becomes sterile.
Modern reproductive technologies :
(i) In Vitro Fertilization : This is the technique in the modern medical field where childless couples can be blessed by their own child.
- IVF technique is used for childless couples who are faced with problems such as less sperm count, obstacles in oviduct, etc.
- The IVF technique is done by removing the oocyte from the mother and artificially fertilizing by the sperms collected from father. This fertilization is done in a test-tube. Thus it is also called test tube baby. The embryo formed is implanted in uterus of real mother or a surrogate mother at appropriate time.
(ii) Surrogacy :
- In Woman if there is problem regarding the implantation of embryo in uterus, then help of another women is taken. This women is called surrogate mother.
- Oocyte from real mother is taken out and fertilized with sperms collected from her husband. These gametes are fertilized outside in a test-tube and then the fertilized zygote is implanted in the surrogate mother.
(iii) Sperm Bank / (IVF) Semen Bank :
If man has problems with the sperm production, then the sperms are collected from the sperm bank. Sperm bank is the place where the donor’s donate the sperms and such sperms are kept stored. The donor’s identity is kept secret and he should also be physically and medically fit person.
Twins :
Twins are two embryos that develop simultaneously in the same uterus producing two offspring.
Two main types of twins are (i) Monozygotic twins (ii) Dizygotic twins.
(i) Monozygotic twins: Formed from single embryo these twins are exactly alike and are of same gender. If within 8 days of zygote formation during the embryonic development cells of that embryo are divided into two groups, then monozygotic twins are formed.
- Siamese twins : In case of monozygotic twins, if the embryonic cells are divided into two groups 8 days after the zygote formation; there is high possibility of formation of conjoined twins (Siamese twins). Such twins are born with some parts of body joined to each other. Some organs are common in such twins.
(ii) Dizygotic twins: When two oocytes are released from the ovary of woman and both are fertilized by two separate sperms then there is formation of dizygotic twins. These twins are formed due to two embryos that are separately implanted in the uterus. Such twins are genetically different and may be same or different by gender.
Reproductive health :
- The physical, mental and social well-being is called health.
- In India, there is lack of awareness about reproductive health. Social customs, traditions, illiteracy, shyness, etc. keep the society under pressure. There is always indifference towards the reproductive health of women.
- Reproductive health can be achieved by keeping genitals clean.
- Syphilis and gonorrhoea are sexually transmitted or bacterial venereal diseases which affect people on a large scale.
- Symptoms of syphilis : Occurrence of chancre (patches) on various parts of body including genitals, rash, fever, inflammation of joints. alopecia, etc.
- Symptoms of gonorrhoea : Painful and burning sensation during urination, oozing of pus through penis and vagina, inflammation of urinary tract, anus, throat, eyes, etc.
Population Explosion :
- Within a short duration if there had been excessive growth of population, then it is called population explosion.
- Population is growing by leaps and bounds in India. The problems due to population explosion are unemployment, decreasing per capita income and increasing loan, stress on natural resources, etc.
- For population control, therefore in India, family planning is a must.
Click on below link to get PDF from store :
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Notes
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Solutions
Class 10-Science & Technology-2-Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2-Books
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech-2-Chapter-2-Life Processes in Living Organisms-1 - Online Notes Next Chapter : Class 10-Sc. & Tech.-2-Chapter-4-Environmental management - Online Notes |
I really like this but I want more big answers
I like it and make my notes from this