Environmental management
Based on Class 10-Science & Technology Part-2-Chapter-4- Maharashtra Board-Audio-Text Notes, Videos, PDF
Notes
Chapter-4- Environmental management
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction :
Ecosystem : Biotic and abiotic components are presents in any environment. Ecosystem is formed by biotic and abiotic components and their interactions with each other.
Components of Ecosystem :
The different components in the ecosystem are as follows:
- Abiotic components : Air, water, soil, sunlight, temperature, humidity, etc.
- Biotic components: All the types of living organisms, like bacteria, fungi, plants and animals.
Types of consumers :
- Primary, secondary, tertiary consumers or apex consumers are the different types of consumers in the ecosystem.
- These types are classified according to the trophic level to which they belong.
Food chain: In every ecosystem, there are always interactions between producers, consumers and decomposers. This sequence of feeding interactions is called food chain.
- In every food chain there are links between four to five trophic levels constituting the producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, tertiary consumers etc.
- The links of food chain are in linear sequence.
Food web : Food web is the collection of many small food chains. Food web is complex network of many small food chains. Thus, when many food chains are interlinked, they form food web.
Different trophic levels in food chain :
- Producers (First trophic level),
- Primary consumers (Second trophic level),
- Secondary consumers (Third trophic level),
- Tertiary consumers (Fourth trophic level) etc.
Refer below fig for food chain:
- In the presence of sunlight, the green plants perform photosynthesis. Thus, they are producers of the food chain.
- This food is consumed by the grasshopper. Thus, grasshopper is primary consumer.
- Frog is secondary consumer as its diet consists of insects like grasshopper.
- Snake is tertiary consumer as it feeds on frogs,
- The hawk is apex consumer as it can kill the snake and feed on it.
- Fungi shown in the picture of the food chain are acting as decomposers.
- Few bacteria are shown in the picture act on all the levels and are bring about decomposition.
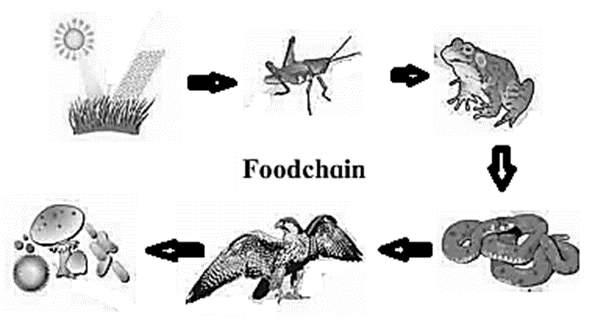
Conversion of above food chain into food web : If this food chain has to be converted into a food web, there should be interactions between the different components. Any living organism can be victim to different predators. Moreover, a predator can also be a target for other. Frog eats different insects. The same frog can be either eaten by snake or by hawk.
Ecosystem — A review :
- Biotic and abiotic factors and their interactions with each other form an ecosystem. Every element has important role to play for functioning of the ecosystem.
- Plants are main producers of the ecosystem. Various herbivores like deer, goats, sheep, cattle, horses, camels, etc. feed upon producers.
- Carnivorous predators e.g. lion and tiger control the population of the herbivores.
- The decomposers and scavengers like caterpillars, termites, insects present in the dung carry out decomposition and thus clean the environment.
- Existence of human beings is dependent on the balanced ecosystem.
| Know This :
Decomposition : Decomposition is the process by which bacteria and fungi break dead organisms into their simple compounds.
|
If the food chain is disturbed, the ecosystem suffers :
Example : ‘Paddy > Grasshoppers —> Frog > Snake’, this food chain is natural.
- When the number of frogs decreases for any reason, the secondary consumer decreases. This decline will also affect snakes at the tertiary consumer level. Primary consumers, such as grasshoppers, will proliferate because there is no longer a limit on their population. Paddy production will be reduced as their population grows. Because of the decreased number of snakes, rats and other rodents from neighbouring areas would increase, becoming secondary consumers.
- Therefore if ‘frogs’ population declines, there would be imbalance of entire ecosystem. The number of prey and predator populations will change and thus the food chain will come to an end.
Energy pyramid : Energy pyramid is the diagrammatic representation, that depicts the energy levels at the various trophic levels.
There are interactions in the form of energy transfer in all the food chains and food web. The energy pyramid shows how energy travels up a food chain
Ecosystem chart :

Relationship between Environment and Ecosystem :
Environment : Everything that is around a living organism is called environment.
- Environment includes physical, chemical and other natural factors which surround the living organism.
- Many biotic, abiotic, natural and artificial factors together constitute conditions of the environment.
Two main types of environment :
- Natural environment : Air, atmosphere, water, land, living organisms, etc.
- Anthropogenic/Manmade/ Artificial environment : Artificial environment, directly or indirectly affects the natural environment.
Two main factors in environment : (1) Biotic factors (2) Abiotic factors.
- Continuous interactions occur between all the factors in the environment.
- Ecology : Ecology is the science that deals with the study of interactions between biotic and abiotic factors of the environment
- Ecosystem : Ecosystem is the basic functional unit used to study the ecology. Many ecosystems together form an environment. Ecosystems constitute biotic and abiotic factors occupying a definite geographical area and their interactions.
Cycles operated in environment : In environment there are ‘bio-geo-chemical’ cycles. These are of two types, viz. Gaseous cycles e.g. nitrogen cycle, oxygen cycle, etc. Sedimentary cycles e.g. phosphorus cycle.
Importance of bio-geo-chemical cycle :
- Plants require water, CO2, phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen, etc. as nutrients while animals require, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc. as nutrients.
- Producers and consumers after their death undergo decomposition and release elements which mix with the soil.
- The cyclic movement of nutrients is possible through bio-geochemical cycle.
- The cyclic movement of elements like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc. continuously occur on the earth.
- By the bio-geo-chemical cycles, the environmental balance is always maintained.
Remember :
- If the environment is in proper condition, then human existence is possible. Therefore, it is our responsibility to preserve nature and maintain environmental balance.
- The planet Earth was given to us on lease from our future generations and not as an ancestral property from our ancestors. Therefore, we must conserve it for ourselves and for future generations.
Environmental Conservation :
Due to natural and man-made causes, there are many environmental problems on the earth. These problems affect the existence of various living organisms. In order to save these organisms and maintain the environmental balance, there is need for environmental conservation. Sensible or proper use of natural resources is a way of environmental conservation.
Factors affecting the environment : The natural as well as artificial or man-made factors affect the environment.
Natural Factors :
- Among natural factors, the sudden changes in the weather, the different types of natural disasters etc. affect the normal environment. Due to such changes there are problems in the interrelationships that exist between food chain and food web.
- Example : If number of consumers increase gradually, it will create the scarcity of prey organisms. Then due to lack of prey, the number of consumers will also decline.
Man-made factors :
- Due to various man-made causes, there are extreme destruction of environment. Industrialization, the pollution due to such industries, Urbanization, hunting and poaching of wild animals, construction of dams, roads, bridges etc. are all man-made changes that cause lot of damage to environment.
- Example : If there are industries established on the river bank, then there is threat to the aquatic ecosystem. It is most likely that the hazardous effluents can be released into the river water. This can cause water pollution resulting into mortality of aquatic organisms. Moreover, this water will no longer remain potable. Hence the health of resident population may also be affected. The food chains and the food web in the river may be terminated due to such pollution.
Pollution :
- The environment is affected due to some natural factors of environment and some man-made factors such as pollution. Such factors create imbalance in the environment which in turn affect the existence of biota.
- Environmental pollution: Pollution brings about environmental degradation. It is largely due to natural or man-made causes. Pollution contaminates and makes the unnecessary and unacceptable changes in the surrounding environment. This causes direct or indirect changes in physical, chemical and biological properties of air, water and soil. These changes are usually harmful for all living beings, including human.
- Reasons for pollution : Population explosion, fast industrialization, and indiscriminate use of natural resources, deforestation, and unplanned urbanization are factors that pollutes environment.
- Our responsibility : Pollution of air, water, noise, soil, thermal, light pollution etc. are different types of pollution that cause adverse effects. It ultimately affects existence of all the living organisms on the earth. Thus it is our responsibility to curtail polluting substances and aim at environmental conservation.
Types of pollution : Air pollution, water pollution and soil or land pollution are main types of pollution. In addition to these, light pollution, plastic pollution, noise pollution and radioactive pollution are also other hazardous types of pollution. Radioactive pollution : Radioactive pollution is caused by following two causes : Effects of radiations:
Need of environmental conservation :
Due to natural and man-made causes, there are many environmental problems on the earth. These problems affect the existence of various living organisms. In order to save these organisms and maintain the environmental balance, there is need for environmental conservation. If this is not done then there will not be any quality of life for the resident humans.
Steps taken for environmental conservation :
- Discussion of the environmental problems- In 1972 at UNO, Stockholm, (Conference arranged on human and environment.)
- Later establishment of United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) .
- In India, discussion of environmental issues took place in IVth planning commission.
- A separate environmental department was established later.
- Ministry of environment and forests started various programs since 1985 in planning, inducting and increasing awareness about environment and forest.
People’s participation for environmental conservation :
- Awareness about environment conservation rules and laws should be developed for common people.
- Large scale participation of the people in environment conservation can bring about environmental protection and effective conservation.
- Values like positive attitude towards environment and knowledge and quest for the conservation should be imbibed right from school days. Increasing environmental awareness through schools and colleges is essential.
- Every nation has their own future plans about environmental protection and for this purpose they have formulated the laws.
| Know This :
Jadav Molai Payeng from Assam has made barren land into a forest which now stands on 1360 acres land. Now, this forest is known as ‘Molai Jungle’. It is rightly said that “Many people come together to destroy the forest, but a single person, if determined, can establish a new forest”! We must also have such a vision. |
Environmental Conservation. Our social responsibility :
- Human - environment interrelationship existed since origin of man.
- Human being has become supreme on the earth due to his intelligence, memory, imaginations, creative ability etc.
- Human has used up natural resources without any thought. The development processes have caused extreme damage to the environment.
- Maintaining the environmental balance is the duty of humans.
- Since we have disturbed the environmental balance, only we should think of protection and conservation of nature.
Laws enacted about environmental conservation:
Forest Conservation Act-1980 : The land reserved for forest conservation has been prohibited to use for any other purpose by this law.
Ex. Permission of central government is compulsory for mining activities. Any person who disobeys this law is entitled to imprisonment for 15 days.
Environmental Conservation Act-1986 : Purpose of this act is to control the pollution and punish the persons or institutes harming the environment.
Any person or factory is prohibited by this act from releasing the pollutants in atmosphere beyond a permissible limit. The person breaching this rule is entitled for either five year imprisonment or fine up to Rs. 1 lakh.
National Green Tribunal-2010: NGT has been established in 2010 for effective implementation of environment related laws.
Wildlife Protection Act -1972 : Established for Protection of the wild life.
- Complete ban on trading of rare animals as per clause 49A
- Complete ban on use of articles prepared from skin or organs of wild animals as per clause 49B
- Compulsory disclosure of the stock of artefacts made from rare wild animals as per clause 49C
- There are various punishments for person or organization who disobeys this law.
Attempts at various levels to be perform for conserving environment : Conservation : Conserving the available resources. Control : Production : Preservation Awareness : Prevention
Environmental management : Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity :
- Environmental pollution affects the living organisms and reduces biodiversity.
- Living world had a rich biodiversity. This richness of biodiversity is getting depleted at a very high rate only due to various activities of human beings.
Biodiversity: The richness of living organisms in nature due to presence of varieties of organisms, ecosystems and genetic variations is called biodiversity. Biodiversity occurs at following three different levels.
Levels of biodiversity:
Biodiversity is documented on the following three levels, viz. genetic diversity, species diversity and ecosystem diversity.
(i) Genetic Diversity : Diversity seen among the organisms of same species due to genetic differences is called genetic diversity. e.g. The individual human beings are different from each other. No two animals or plants are exactly alike.
(ii) Species Diversity : The difference between the different species is the species diversity. e.g. All the species of plants, animals and microbes which are seen in any natural environment.
(iii) Ecosystem Diversity : In one region there may be different ecosystems, such diversity in the ecosystems is called ecosystem diversity. Ecosystems are natural or artificial. Every region shows different types of ecosystems such as aquatic, terrestrial, desert or forest ecosystems. Each ecosystem has its own habitats with resident flora and fauna.
Sacred Groves :
- A sacred grove is a green patch of forest that is protected by locals in the name of God.
- It does not belong to the Forest Service. It is similar to a sanctuary that is protected by the locals and tribals.
- It is abundant in biodiversity.
- It is preserved because there is a belief that God or a deity lives in the sacred grove. As a result, they are known as Deorai in the local language. People do not cut down trees because of this.
- Hunting of any kind is also prohibited here.
- In India, over 13000 sacred groves have been reported.
- Most of these are in Western Ghats in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Kerala. Also, in remaining parts of India sacred groves are reported.
- Role of sacred grove is tremendous in conserving the biodiversity.
How can biodiversity be conserved?
Biodiversity can be conserved by the following ways :
Hotspots of Biodiversity :
- Highly sensitive biodiversity spots in world : 34
- Areas of the Earth were occupied by these hotspots : 15.7%
- Currently, sensitive areas that are destroyed : 86%
- Presently left over sensitive spots on the earth : 2.3%.
- Hotspots have 1,50,000 plant species which are 50% of the world count.
- In Eastern India jungles, 85 species are found out of 185 species of animals.
- In Western Ghats about 1,500 endemic plant species.
- Out of the total plant species in the entire world, 50,000 are endemic.
Three Endangered Heritage Places of the Country :
- Western Ghat : The Western Ghat spread over the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Tamilnadu and Kerala has been endangered due to mining industry and search for natural gas. Habitats of Asiatic lion and wild bison of this region have been under threat.
- Manas sanctuary : Manas sanctuary of the Assam is under threat due to dams and indiscriminate use of water. Tiger and rhino of that region are under threat.
- Sunderban sanctuary : Sunderban sanctuary of West Bengal is reserved for tigers. However, the tiger population and overall local environment is seriously challenged by dams, deforestation, excessive fishing, trenches dug for same, etc.
Classification of Threatened Species :
- Endangered Species : Number of organisms is declined. Shrunken habitat which can lead to extinction. Ex. Lion tailed monkey, Lesser florican.
- Rare Species : Considerably declined number of these organisms. Endemic organisms may become extinct very fast. Ex. Red panda, Musk deer.
- Vulnerable Species : Extremely less number of organisms which further declines. Continuous declining number of organisms is a threat. Ex. Tiger, Lion.
- Indeterminate Species : Organisms appear to be endangered. The data is not enough as they have typical behavioural habits (like shyness). Ex. Giant squirrel Our state animal : ‘Shekhrw’
Know This :
- 22nd May is observed as a World Biodiversity Day.
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) prepares the ‘Red List’.
- Red list contains the names of endangered species from different countries.
- The names of endangered species are on pink pages.
- The names of previously endangered but presently safe species are on green pages.
Slogans to spread environmental wisdom:
| Know This :
As per report of WWF, 30% of the animal species faced extinction during last 30 years, it is very alarming situation. Once lost the flora and fauna will never get replenished. If in future, this rate of extinction continues, there will not be a single animal left on the earth. Only human species will outnumber all others due to no concern for the nature. |
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : -Chapter-3-Life Processes in Living Organisms-2 - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 5. Towards Green Energy - Online Notes |
Wow
I can’t find the 5th lesson Towards Green energy of science 2 standard 10th ?
Thanks for suggestion, we have corrected and updated it. Now you can view it.