Cell Biology and Biotechnology
Class 10-Science & Technology Part-2-Chapter-8- Maharashtra Board
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Cell : Cells are the body's structural and functional units.
Tissue: Tissue is a group of cells that performs a specific function
- The muscular tissues in the body perform contraction and extensions thereby helping in locomotion.
- The conducting tissues of the plants like xylem and phloem transport the water and food respectively.
Tissue Culture:
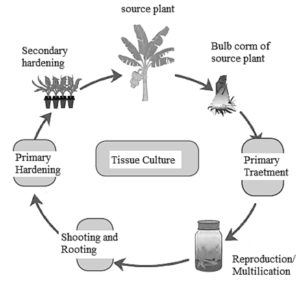
- Tissue culture is the technique in which ‘ex vivo growth of cells or tissues in an aseptic and nutrient-rich medium’ is done.
- While performing experiments of tissue culture, a liquid, solid or gel-like medium prepared from agar, is used. Such medium supplies nutrients and energy necessary for tissue culture technique.
- Different processes, such as primary treatment, reproduction, shooting and rooting, primary hardening, and secondary hardening, are performed.
- The tissues are taken from the source plant and carried out in an aseptic medium in the laboratory.
Cell Biology (Cytology) :
Cell biology, or cytology, is the study of cell structure, types, organelles, and division
In the field of human health, there are revolutionary changes due to advances of cell biology.
Research institutes in India for dedicated research in cell biology :
- National Centre for Cell Science at Pune
- Instem at Bengaluru
Stem Cells :
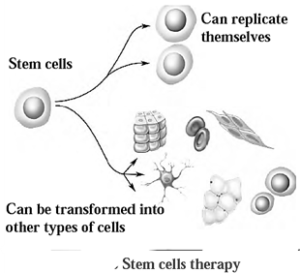
Stem Cells : Stem cells are unique types of cells found in multicellular organisms that can produce all other types of cells.
- They are formed from zygote formed after fertilization of gametes, which contain similar cells.
- Stem cells can be used to produce new tissues in the laboratory.
- Stem cells play a crucial role in wound healing.
Differentiation of stem cells : Stem cells undergo differentiation, which involves the formation of various types of tissues for specific functions. Once new tissues are formed, their ability to differentiate is lost, and they later form cells similar to them.
Locations of stem cells where they found:
- In the umbilical cord present in the uterus of mother.
- In the blastocyst stage of embryonic development.
- In red bone marrow
- In adipose connective tissue of adult human beings.
- In blood
Method of Stem Cell Preservation : Stem cell samples from umbilical cord blood, red bone marrow or blastocyst are taken and are kept in small, sterile vials, kept in liquid nitrogen at -135°C to -190°C. In this way, the stem cells can be preserved for a longer use.
Stem cell research : Stem cell research is a revolutionary biotechnology development that will fundamentally change medical science. It consists of two types: embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells, depending on the source.
Embryonic stem cells :
- Embryo formed by zygote divisions, forming stem cells.
- Cell differentiation begins by 14th day, forming 220 different cell types.
- Embryonic stem cells are primary, undifferentiated cells with the ability to multiply.
- Pleuripotency, a property of stem cells, allows them to develop into different cell types.
- Stem cells can be collected and cultured with specific biochemical stimuli before differentiation.
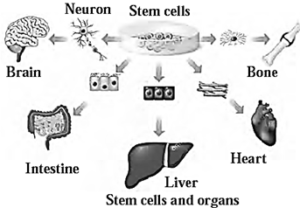
- Depending on the stimulus type, stem cells transform into desired cells, tissues, and organs.
Adult stem cells : Stem cells taken from the adult body are called adult stem cells.
Sources of adult stem cells :
- Red bone marrow
- Adipose connective tissue
- Blood
- Cord blood can also be used immediately after birth
- Placenta is also rich source of stem cells.
Uses of Stem Cells: (i) In Regenerative Therapy : (ii) In Organ Transplantation : In organ-failure such as kidney and liver, some tissues can be formed by stem cells and transplanted in a needy patient.
Organ transplantation :
- It helps to saves life of patients with less efficient or functionless organs.
- Kidney or skin transplantation can be performed if suitable donor is available.
- Matching is done before transplantation based on factors like blood group, diseases, disorders, age.
- Healthy donors are essential.
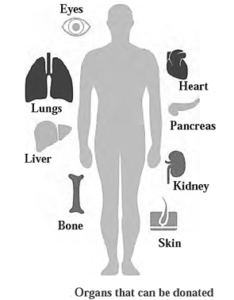
- Live donors can be taken for kidney and skin, but liver, heart, and eyes can be donated posthumously.
Organ and Body donation :
- Organ and body donation is a practice where the body is not used after death, but if in good condition, it can be used for donation.
- This can save the life of other needy patients and improve their quality of life. Advances in science have made it possible to donate organs, and awareness about posthumous donations should increase.
- Organ donation saves lives, such as blind persons receiving vision through eye donation, and can also be used for research in medical studies.
- The process is regulated by the Transplantation Human Organs Act 1994 and subsequent amendments, ensuring transparency and prevents bribery.
- Awareness about organ donation and transplantation should increase to encourage voluntary donation.
Awareness about organ donation after death :
Biotechnology and Its Applications :
Biotechnology : The methods used to artificially modify the genetic material of an organism or hybridize it for the benefit of humans is known as biotechnology.
Use of biotechnology :
- Biotechnology use in Agriculture, Horticulture, Medical Fields.
- Produces cash crops and improves plant varieties.
- Enhances plant's ability to withstand environmental stresses.
- Aids in vaccine production, early congenital disease diagnosis, organ transplants, cancer research, artificial skin and cartilage production.
- Involves genetic engineering and tissue culture techniques in laboratories.
Impact of biotechnology on agriculture and other related fields :
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) create crops with required features to avoid harmful natural traits.
- Genetic engineering allows for creation of varieties that can withstand environmental changes, such as temperature changes, droughts, and climate change.
- GM crops are resistant to insect pests, pathogens, and chemical weedicides, reducing the use and cost of harmful chemical pesticides.
- GM seeds improve the nutritive value of crops, leading to better quality seeds.
- GM crops decrease crop loss, increasing cultivable land and agriculture.
- Insect-resistant crops like Bt Cotton have been produced, widely used in Maharashtra.
Biotechnology and its Applications :
- Incorporates cytology, biochemistry, molecular biology, and genetic engineering.
- Significantly advances agriculture and pharmacy.
- Improves agricultural yield and produces high-quality crops.
- Supports pharmaceutical experiments for antibodies, vitamins, and hormones like insulin.
Inclusion of main areas in biotechnology :
- Microbiology : Using microbial abilities to form yoghurt from milk and alcohol from molasses.
- Biochemistry : By increasing the productivity of the specific cell to manufacture antibiotics and vaccines, etc.
- Molecular biology: Use of bio-molecules like DNA and proteins in human welfare.
- Genetic engineering: By techniques of genetic manipulations, the plant and animal varieties and products of desired quality can be obtained. E.g. From genetically modified bacteria, human growth hormone and insulin can be produced.
- Non-genetic biotechnology: By usingentire cell or tissue, non-genetic biotechnology experiments are done. E.g. In tissue culture, production of hybrid seeds, etc. such methods are used.
Benefits of Biotechnology :
Biotechnology offers numerous benefits, including
- increased crop yield per hectare,
- reduced disease control expenses,
- faster fruit setting varieties,
- stress-resistant varieties that can withstand changing environmental parameters like temperature, water-stress, and soil fertility.
These benefits make biotechnology a valuable tool for agricultural development.
Development of Biotechnology in India: Government of India had established the National Biotechnology Board in 1982. This board was transformed into department of biotechnology under the ministry of science and technology, in 1986. Institutes under the control of this department are as follows :
Commercial Applications of Biotechnology:
(i) Crop Biotechnology: Biotechnology is used in agricultural field to improve yield and variety.
- It includes hybrid seeds for fruits, genetically modified crops for resistance to diseases, alkalinity, and weeds.
- Bt cotton for a toxin that kills bollworm.
- Bt Brinjal improves brinjal by killing pests like Bt cotton.
- Golden Rice introduces a gene synthesizing vitamin A, containing 23 times more beta carotene than normal.
- Herbicide-tolerant plants enable selective weed destruction.
- Biofertilizers, such as bacteria and plants like Azolla, are used as biofertilizers.
(ii) Animal Husbandry :
- Two main methods as artificial insemination and embryo transfer are used in animal husbandry.
- It helps to improve both, the quantity and quality of animal Ex. Milk, meat, wool, etc.
- Similarly, animals with more strength have been developed for hard work.
(iii) Human Health :
- Biotechnology for human health management takes into consideration two important tasks, these are diagnosis and treatment of the diseases.
- Identifies gene role in disease, aiding early diagnosis of diabetes and heart diseases.
- Facilitates early diagnosis of AIDS and dengue, enabling early treatment.
- Facilitates the production of necessary treatments, like human insulin, using bacteria's bacterial genome.
- Produces various vaccines and antibiotics.
(a) Vaccines and Vaccination:
Vaccines : Vaccines are antigens used to acquire immunity against specific pathogens or diseases.
- Traditionally, pathogens were used, but this increased the risk of disease transmission.
- Scientists have now used biotechnology to artificially produce vaccines by using a gene isolated from the pathogen. This method allows for safer vaccines, as the antigen is produced in the laboratory and used as a vaccine.
- Currently, proteins acting as antigens are injected in pure form, keeping the immune system active. This is the safest way to administer vaccines, as they are more thermo-stable and remain active for longer periods.
- Examples of vaccines produced using biotechnology include polio and hepatitis vaccines.
Edible Vaccines :
- Edible vaccines are food-based vaccines produced through biotechnology.
- Transgenic potatoes contain vaccines against bacteria like Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli.
- Consumption of raw potatoes generates immunity against cholera and E. coli.

Proteins produced by biotechnology and the names of diseases they are used against-
- Insulin - Diabetes
- Somatostatin - Dwarfism
- Erythropoietin - Anaemia
- Factor VIII - Haemophilia
- Interleukin - Cancer
- Interferon -Viral infection
(b) Treatment: Biotechnology is useful for production of hormones like insulin, somatotropin and blood clotting factors.
(c) Interferon: This is a group of small sized protein molecule used in treatment of viral diseases. These are produced in blood. However, nowadays, with the help of biotechnology, transgenic E. coli are used for production of interferon.
(d) Gene Therapy : Biotechnology enables gene therapy to treat genetic disorders in somatic cells. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a case study of gene therapy. Somatic cell therapy treats all cells, except sperms and ova.
(e) Cloning: Cloning is the modern technique in which there is production of replica of any cell or organ or entire organism is done. There are two types of cloning, viz. (i) Reproductive cloning and (ii) Therapeutic cloning.
Reproductive cloning: In reproductive cloning, a clone is produced by fusion of a nucleus of diploid somatic cell with the enucleated ovum of anybody. In the process, the sperm or male gamete is not needed.
Therapeutic cloning: This technique is largely used for treatment purpose. Stem cells are derived from the cell formed in laboratory by the union of somatic cell nucleus with the enucleated egg cell.
- Cloning technique is used for therapy of various diseases.
- Gene cloning can also be done to form millions of copies of same gene. Such genes are used for gene therapy and other purposes.
- Due to cloning technique, the inheritance of hereditary diseases can be controlled, continuation of generations can be achieved and certain characteristic genes can be enhanced.
- However, for human cloning, there is worldwide opposition due to ethical reasons.
(iv) Industrial Products / White Biotechnology :
- Manufacturing alcohol by using transgenic yeast on sugarcane molasses is one of the example of white biotechnology.
- Similarly, many other industrial chemicals are produced through less expensive processes by substituting them with biotechnology.
(v) Environment and Biotechnology :
Biotechnology in Environment and Waste Management :
- Microbial processes are used for sewage and solid waste treatment to speed up decomposition.
- Oxidation of organic matter in water bodies prevents oxygen depletion, affecting aquatic life.
- Solid organic waste is treated with microbes to produce large-scale compost.
- Biotechnological methods include bio-remediation, biopesticides, biofertilizers, and biosensors.
- Bioremediation involves absorption or destruction of toxic chemicals and pollutants using plants and microorganisms.
Phytoremediation : Phytoremediation is the method of bioremediation in which plants are used for this process. Examples of Phytoremediation :
| Know This :
Cleaning of Oil Spillage in Oceans : · Through the oil tankers or oil wells, there is oil spillage in the marine waters. This adversely affects the marine flora and fauna. · By using oil-digesting and fast multiplying bacteria, such oil spills can be cleared in a lesser cost and without affecting the marine environment. · Dr. Anand Mohan Chakravarti discovered the use of such bacteria. |
(vi) Food Biotechnology :
- Microorganisms are used for the manufacture of food items like bread, cheese, wine, beer, yoghurt, vinegar, soya sauce, etc.
(vii) DNA fingerprinting :
- In every organism, the nucleotide sequence in the DNA molecule is unique.
- In human beings as a fingerprint is unique for every person, similarly DNA is also unique.
- Therefore, the technique to identify any person can be proved by his or her DNA.
- In India at “Centre for DNA fingerprinting and Diagnostics”, located at Hyderabad DNA fingerprinting is done.
DNA fingerprinting technique is mainly used in
- Investigations of forensic sciences.
- To establish identity of the criminal.
- To identify parents of any child in case of disputed parentage.
Important Stages in Development of Agriculture :
(i) Green revolution :
- Norman Borlaug and Dr. M. S. Swaminathan have significantly contributed to the green revolution, which focuses on improving methods for harvesting maximum yield from minimal land.
- This has saved a large sector of the Indian population from starvation, leading to increased food grain production.
- The green revolution also involves the development of new crop varieties through various agricultural research institutes, including those under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
- These institutes perform active research in various cash crops, fishery, and other agricultural related products.
| Know This :
• Indian Institute of Science has developed a transgenic variety of tobacco. If cattles feed upon leaves of this plant, they do not contract a viral disease- rinderpest. |
Various Indian research institutes and laboratories :
(ii) White revolution :
- The white revolution, initiated by Dr. Verghese Kurien in Anand, Gujarat, utilized biotechnology to promote abundant milk production.
- The movement, which led to the establishment of AMUL, an international brand, aimed to achieve self-sufficiency in the dairy business.
- The movement also involved quality control experiments, the development of new dairy products, and preservation of existing ones.
(iii) Blue revolution :
- The blue revolution involves the production of aquatic organisms using water.
- In East Asia, fish species are raised in farm ponds, known as aquaculture.
- In India, fish, prawns, marine organisms, and sea weeds are also cultivated.
- The Indian government encourages aquaculture activities through the 'Nil-Kranti Mission-2016' program, offering subsidies at 50% to 100%.
- Aquaculture and Mariculture can be carried out on a large scale along the Indian coastline, allowing for the cultivation of fresh water fishes like rohu, catla, marine and brackish water prawns, and lobster.
(iv) Fertilizers :
Two types of fertilizers are used in agriculture. One of those is organic manure and others are chemical fertilizers.
Organic (Manure) :
- Improved water holding capacity of the soil. Soil conservation takes place.
- Due to humus formation, upper layer of the soil is formed.
- Essential elements (N, P, K) are easily available due to activities of earthworms and fungi.
Chemical fertilizers :
- Decrease in fertility of soil due to excessive use.
- Toxic for soil bacteria, cattle, human.
- Contamination of the environment.
(v) Insecticides :
- Insecticides are used to eradicate pests on plants, which can be harmful to the environment.
- Natural pest control measures like frogs and birds help control the pest population.
- However, excessive use of pesticides and insecticides can be toxic to all living organisms and show biomagnification, increasing concentrations according to the food chain.
- Insecticides like DDT, malathion, and chloropyriphos also contaminate water and soil.
(vi) Organic farming :
- When the chemical fertilizers and pesticides are not used, only local, sturdy varieties are cultivated, and a natural balance is maintained, then such type of farming is called organic farming.
- Organic farming and organic products are in demand these days.
- The use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides cause many environmental problems due to pollution. The soil fertility is decreased, the insect-pests become resistant and cause more damage.
- Organic farming can help to save the environment from such effects.
(vii) Apiculture :
- Apiculture is rearing of honey bees to obtain products such as honey and wax.
- In such practice, artificial hives are placed. By such practice, the honey can be extracted without causing any harm to the honey bees or their hives.
(viii) Cultivation of Medicinal Plants :
- In Ayurveda, different medicines’ are traditionally obtained from plants. The rich biodiversity of India was conducive in gathering such medicinal herbs from forests.
- Now due to deforestation, the medicinal plants and herbs are becoming rare. Hence their cultivation is to be done.
(ix) Fruit Processing :
- Fruit processing can form following products : Chocolates, juices, jams and jellies. Since fruits are perishable agro-produce, processing is a must.
- Different methods of fruit processing are depositing in cold storage, drying, salting, air tight packing, preparing jams (muramba), condensing, etc.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 7. Introduction to Microbiology - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 9 -Social Health - Online Notes |