Animal Classification
Based on Class 10-Science & Technology Part-2-Chapter-6- Maharashtra Board syllabus
Solution
Question 1:
Identify me.
(i) I am diploblastic & acoelomate. Which phylum do I belong to?
I am from phyllum Cnidaria or Coeleterata
(ii). My body is radially symmetrical. Water vascular system is present in my
I am Star fish/Asterias. I belong to the phyllum Echinodermata.
(iii) I live in your small intestine. Pseudocoelom is present in my thread like body. In which phylum will you include me? I belong to the phyllum Aschelminthes, name is Ascaris.
(iv) Though I am multicellular, there are no tissues in my body. What is the name of my phylum?
I am from Phyllum - Porifera
Question 2:
Write the characters of each of the following animals with the help of classification chart.
(i) Bath sponge
Bath sponge: Classification
Kingdom
Subkingdom
Phylum
Animalia
Non-chordata
Porifera animal
Characters: Bath sponge is a marine round in shape and Blackish in colour. It has porous and asymmetrical body. It has spongin fibres and spicules which serve as skeleton. Bath sponges have good water-holding capacity. It is sedentary animal which is fixed to some substratum in the aquatic environment. Reproduction is by budding. It also has a good regeneration capacity.
(ii) Grasshopper
Grasshopper: Classification
Kingdom
Subkingdom
Phylum
Class
Animalia
Non-chordata
Arthropoda
Insecta
Characters: Grasshopper has jointed appendages. There are three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings. It is a terrestrial insect which is well adapted to the surrounding environment by showing camouflage. It has chitinous exoskeleton. The respiration is by tracheae.
(iii) Rohu
Rohu Classification:
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Sub Class
Animalia
Chordata
Pisces
Teleostei (Bony fish)
Characters: Rohu is a fresh water bony fish. It is a chordate having a vertebral column, hence included under subphylum vertebrata. The body is well adapted for aquatic mode of life. The shape of the body is streamlined. The exoskeleton is of scales. The gills are present which are used for respiration. The endoskeleton is of bones, hence called bony fish. There are paired fins and a unpaired caudal fin which is used in steering and changing the direction during swimming.
(iv) Penguin
Penguin Classification:
Kingdom
Subkingdom
Class
Animalia
Chordata
Aves
Characters: Penguin is a flightless bird inhabitant of cold snow-clad regions. It has exoskeleton of feathers. The body is well adapted to survive in cold regions. It is a warm-blooded bird. The forelimbs are modified into wings. But due to excessive body weight, the penguins are not seen flying. It can wade in the water with modified hind limbs.
(v) Frog
Frog: Classification
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Animalia
Chordata
Amphibia
Characters: The trog is a true amphibian that can live in water as well as on land. When on land it respires with the help of lungs while in water it uses its skin for breathing. It does not have exoskeleton. The skin is soft, slimy and moist. It is suitably coloured and hence the frog can camouflage in the surroundings. Body is divisible into head and trunk. Two pairs of limbs are seen. The forelimbs are short and used for support during locomotion. The hind limbs are long and strong, used for jumping when on land and for swimming when in water. The eyes are large and protruding. Since the neck is absent, such eyes help in looking around. The tympanum is present.
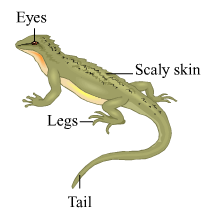
(vi) Lizard,
Lizard Classification:
Kingdom
Subkingdom
Class
Animalia
Chordata
Reptilia
Characters: The lizard is a cold-blooded reptile The limbs are weak and do not support the body weight, hence lizard is seen creeping. But the feet are provided with pads and suckers due to which lizards are well-adapted to climb on the vertical walls. The exoskeleton has fine scales. The body is divisible into head, neck and trunk. The capacity to regenerate is developed in lizards, hence it can produce the lost tail or limbs. The mode of reproduction is egg laying. It feeds on insects with the help of long and sticky tongue.
(vii) Elephant,
Elephant Classification
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Animalia
Chordata
Mammalia terrestrial
Characters: Herbivorous mammal adapted to survive in hot and humid tropical forests. It is a mammal and hence shows viviparity and milk secretion. The body is divisible into head, neck, trunk, and tail. The proboscis is a characteristic feature of the elephant which is actually modified nose.
(viii) Jellyfish.
Jellyfish: Classification
Kingdom
Subkingdom
Phylum
Animalia
Non-chordata
Cnidaria or Coelenterata
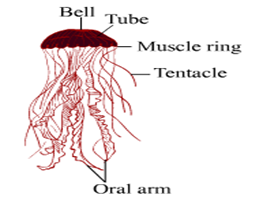
Characters: Jellytish or Aurelia is a coelenterate. Its body is medusa. It appears as a transparent balloon seen floating in the marine waters. Since it has appearance like a jelly, it is known commonly as jellyfish. The body is radially symmetrical and diplosblastic. There are tentacles provided with cnidoblasts or stinging cells. Tentacles are used for catching the prey. Cnidoblasts are used to secrete a toxin which paralyses the prey.
Question 3:
Write in brief about progressive changes in animal classification.
There were different methods of classification of animals, various scientists researched and contributed to biological classification. Based on their observations we have the current system of classification:
Question 4:
What is the exact difference between grades of organization and symmetry? Explain with examples.
Grades of organization: The grades of organization mean the way an organism has different body formation. There are different grades of organization like: Protoplasmic grade of organization: Unicellular organisms have a single cell in the body and hence the organization in its body is called protoplasmic grade of organization. Example amoeba Cellular grade of organization: Some organisms have only cells in their body Tissue grade of organization: In this, different cells performing similar functions are arranged into tissues. Exapmple- Coelenterates .They are said to have cell-tissue grade organization Symmetry : Symmetry on the other hand shows the base of the body formation. The symmetry can be understood by taking an imaginary cut through the animal body. Animals that can be divided into two identical halves in one plane exhibit bilateral symmetry. Most of the animals have bilateral symmetry and hence their organs are arranged in symmetric way on both the sides. Example Human beings and prawn Animals that can be divided into many identical parts exhibit radial symmetry. The imaginary cut passing through the central axis can give more than one equal halves. The organs of such animals are arranged in a radius of an imaginary circle. e.g Cnidarians, Hydra and some echinoderms. Animals that cannot be divided into identical parts are asymmetric. In asymmetric animals, there is no symmetry in any plane. e.g. Amoeba Both grades of organization and symmetry are the bases for classifying animals into different phyla.
which is called cellular grade of organization. It is a loose aggregation of cells in which the cells are functionally different from one another. Exapmle- Poriferans
Organ grade of organization: Here, different tissues are organized into organs and each organ is specialized for a particular function. Example- Platyhelminthes
Examples: Nematoda, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata and chordates.
Symmetry is a characteristic through which animals may be distinguished from each other.
Question 5:
Answer in brief. The classification of shark is as follows:
(i) Give scientific classification of shark upto class.
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Sub- phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Pisces
(ii) Write four distinguishing characters of phylum- Echinodermata.
Characteristic features of Echinodermata are:
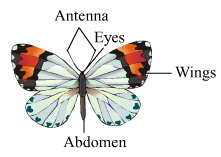
(iii). Distinguish between butterfly and bat with the help of four distinguishing properties.
Butterfly
Bat
1. It is classified as Non-chordate
It is classified as Chordate
2. It belongs to the phylum Arthropoda.
It belongs to the phylum Chordata and class mammalia.
3. Their characteristic feature is the presence of joint appendages.
Their characteristic feature is the presence of mammary glands.
4. It shows the presence of chitinous exoskeleton.
Exoskeleton is in the form of hair or fur.
5. They are cold blooded organisms.
They are warm blooded organisms.
6. Butterfly is diurnal insect (active during day)
Bat is nocturnal mammal (active at night)
(iv) To which phylum does Cockroach belong? Justify your answer with scientific reasons.
Cockroach belongs to the phylum Arthropoda and class Insecta. It shows all the features which are a characteristic of this phylum:
Question 6:
Give scientific reasons.
a. Though tortoise lives on land as well as in water, it cannot be included in class- Amphibia.
b. Our body irritates if it comes in contact with jelly fish.
c. All vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
d. Balanoglossus is connecting link between non-chordates & chordates.
e. Body temperature of reptiles in not constant. Reptiles are cold blooded organisms or poikilotherms, which means thermoregulatory is not present in their bodies Their body temperatures change with the change in the temperature of the environment. For example, if the outer temperature rises their body temperature also rises and vice or versa.
Question 7:
Answer the following questions by choosing correct option.
(i) Which special cells are present in the body of sponges (Porifera)?
1. Collar cells
2. Cnidoblasts
3. Germ cells
4. Ectodermal cells
Collar cells are present in the body of sponges (Porifera).
(ii) Which of the following animal's body shows bilateral symmetry?
1. Star fish
2. Jelly fish
3. Earthworm
4. Sponge
Earthworm shows bilateral symmetry
(iii) Which of the following animals can regenerate it’s broken body part?
1. Cockroach
2. Frog
3. Sparrow
4. Star fish
Star fish can regenerate it’s broken body part.
(iv) Bat is included in which class?
1. Amphibia
2. Reptilia
3. Aves
4. Mammalia
Bat is included in the class Mammalia.
Question 8:
Complete the following chart.
| Body cavity | Germ Layer | Phylum |
| Absent | ------------- | Porifera |
| Absent | Triploblastic | ----------- |
| Pseudocoelom | ------------- | Aschelminthes |
| Present | ------------- | Arthropoda |
Answer:
Body cavity
Germ Layer
Phylum
Absent
Absent
Porifera
Absent
Triploblastic
Platyhelminthes
Pseudocoelom
Triploblastic
Aschelminthes
Present
Triploblastic
Arthropoda
Question 9:
Complete the following chart.
| Type | Character | Example |
| Cyclostomata | ||
| Gill respiration | ||
| Amphibia | ||
| Whale | ||
| Poikilotherms |
Type
Character
Example
Cyclostomata
Jaw less mouth
Myxine
Pisces
Gill respiration
Rohu
Amphibia
Aquatic and aerial respiration
Frog
Mammalia
Mammary glands
Whale
Reptilia
Poikilotherms
Lizard
Question 10:
Sketch, label and classify
Hydra, Jellyfish, Planaria, Round worm, Butterfly, Earthworm, Octopus, Star fish, Shark, Frog, Wall lizard, Pigeon.
(1) Kingdom- Animalia Division-Non-chordata Phylum- Coelenterata Genus- Hydra (2) Kingdom- Animalia Division-Non-chordata Phylum- Colenterata (3) Kingdom- Animalia Division-Non-chordata Phylum- Platyhelmenthis Genus- Planaria (4) Division-Non-chordata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Aschelminthes Genus- Ascaris (5) Division-Non-chordata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Arthropda Genus- Rhopalocera (6) Kingdom- Animalia Division-Non-chordata Phylum- Annelida (7) Division-Non-chordata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Mollusca Genus- Octpous (8) Division-Non-chordata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Echinodermata Genus- Asterias (9) Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Choradata Class- Pieces Genus- Isurus (10) Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Chordata Class- Amphibia Genus- Rana (11) Sub-phylum - Vertebrata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Choradata Class- Reptilia Genus- Hemidactylus (12) Sub-phylum - Vertebrata Kingdom- Animalia Phylum- Choradata Class- Aves Genus- Columba
Hydra
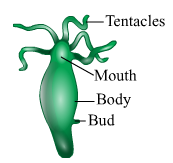
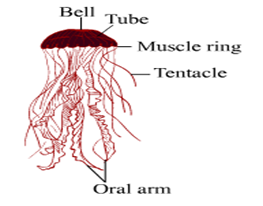
Jelly Fish
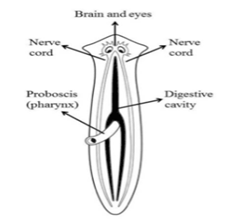
Planaria
Round Worm

Butter fly
Earth Worm

Octopus
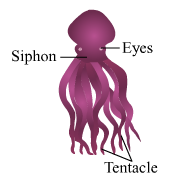
Star Fish
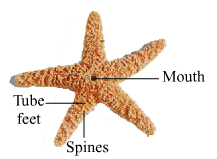
Shark
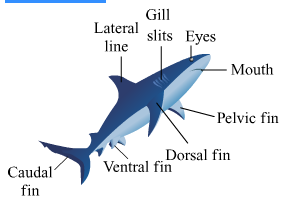
Frog
Wall lizard
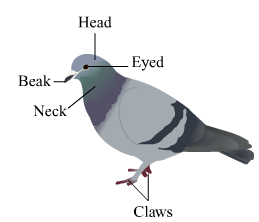
Piegon
Question 11:
Label the following.
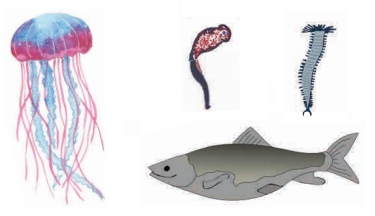
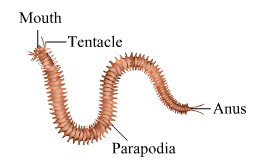
1. Planaria

2. Scolidon

3. Nereis
4. Jelly fish
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 10 Science & Technology Part-1,Part-2 - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter-5-Towards Green Energy - Online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 7- Introduction to Microbiology -Online Solution |