Motion, Force and Works
Based on Maharashtra Board General Science Chapter 7-Motion, Force and Works-Audio Notes, Solution, Video, PDF, Test
Notes
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Motion : Displacement of an object from one place to another in a specific time is called the motion of that object.
Distance : The length of the route actually traversed by a moving body, irrespective of the direction, is called distance. Distance is a scalar quantity.
Displacement : The minimum distance traversed in a particular direction along a straight line is called displacement. Displacement is a vector quantity. Both magnitudes of distance and direction are taken into account while describing the displacement.
The unit of measurement of distance and displacement is the metre, in the SI as well as in the MKS system of measurement
Velocity : Velocity is the distance traversed by a body in a specific direction in unit time.
Velocity = \(\frac{Displacement}{\text{Period of time required for the displacement}}\)
Speed : The distance traversed by an object in unit time is called the speed of that object.
Speed = \(\frac{\text{distance traversed}}{\text{Time required for traversing the distance}}\)
Speed and velocity :
When speed is taken into account, the direction is not specified. If a car is moving with a speed of 40 km/hours then specifying its direction is not needed. But while predicting a storm‘s motion, its direction is always mentioned.
The unit of speed and velocity is metre/second (m/s).
Average velocity and instantaneous velocity :
The velocity of an object can change even while it is moving along a straight line. "
(1) Average velocity = \(\frac{Displacement}{\text{Total time}}\)
(2) The velocity at a particular moment of time is called instantaneous velocity. It may be different at different times.
Acceleration :
(1) The change in velocity with reference to time is called acceleration. This is a vector quantity. When the velocity rises, the acceleration is positive and when it is declining the acceleration becomes negative. If velocity is not changed, then the acceleration is zero.
Acceleration = \(\frac{\text{Change in velocity}}{\text{Time taken for change}}\)
Unit of acceleration = \(\frac{metre/second}{Second}\) = \(\frac{metre}{second^2}\)
Force :
(1) Force is the interaction that brings about the acceleration. Due to force there is change in the velocity of an object.
Force = mass x acceleration
Force is a vector quantity,
(2) The scientist Sir Isaac Newton studied force and the resulting acceleration for the first time.
[/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Newton's First Law of Motion :
(1) If no force is acting on a body, its velocity will not change, The body will not show acceleration. If a body is stationary, it will remain stationary. If it is in motion, it will continue moving with the same velocity and in the same direction.
(2) If the force acting on the object is zero, then its acceleration is also zero.
1 Newton: If 1 kilogram standard weight is placed on a surface with no friction and pulled it with an acceleration of 1 m/s2, then the force applied is called 1N (1 Newton).
OR
The force required for producing acceleration of 1 m/s in a mass of 1 kg, is called a Newton (1N) force.
1N= 1 kg.m/s2
The force required for producing acceleration of 1 cm/s2 in a mass of 1 g, is called a 1 dyne force
1N= 105 dynes
Force, displacement work and energy :
The relationship between the force, displacement and work is given in the following formula
Work (W) done by the force = force (F) applied to the body x displacement (s) of the body that takes place in the direction the force,
W=F X s
- Force and displacement are vectors while work is scalar quantity
- Unit of work in SI is Joule (J).
- Unit of force in SI is Newton (N)
- Unit of displacement in SI is metre (m).
- The unit of work in CGS system is erg
If on a wooden block a force of I N parallel to the surface of the table is applied and if the block is displaced by 1 metre, then the force has done 1 Joule of work.
1 Joule = 1 Newton.1 meter (1J=1N.m)
Energy is the capacity to do work. Energy is a scalar quantity. The unit of energy in SI system is Joule while in CGS system is erg, 1 Joule= 107 erg. [/responsivevoice]
Solution
Question 1:
Fill in the blanks with the proper words from the brackets.
(stationary, zero, changing, constant, displacement, velocity, speed, acceleration, stationary but not zero, increases)
(a) If a body traverses a distance in direct proportion to the time, the speed of the body is ...............
(b) If a body is moving with a constant velocity its acceleration is .......... .
(c) .............. is a scalar quantity.
(d) ............. is the distance traversed by a body in a particular direction in unit time.
(a) If a body traverses a distance in direct proportion to the time, the speed of the body is constant.
(b) If a body is moving with a constant velocity its acceleration is zero.
(c) Speed is a scalar quantity.
(d) Velocity is the distance traversed by a body in a particular direction in unit time.
Question 2:
Observe the figure and answer the questions.
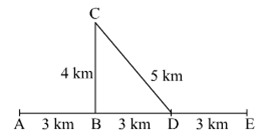
Sachin and Sameer started on a motorbike from place A, took the turn at B, did a task at C, travelled by the route CD to D and then went on to E. Altogether, they took one hour for this journey.
Find out the actual distance traversed by them and the displacement from A to E. From this, deduce their speed. What was their velocity from A to E in the direction AE? Can this velocity be called average velocity?
The distance covered by Sachin and Sameer : A → B (3km), B → C (4 km), C → D (5km), D → E (3 km) Total distance: 3+4+5+3=15km The actual distance covered = 15 km. Total displacement : from A to E=3 +3 + 3=9km Total displacement = 9 km Speed = \(\frac{distance}{time} = \frac{15 km}{1 hr}\) =15 km/hour Velocity = \(\frac{displacement}{time} = \frac{9km}{1 hour}\) = 9 km/hour The velocity from A to E is 15 km/hour which can be called the average velocity.
Question 3:
From the groups B and C, choose the proper words, for each of the words in group A.
| A | B | C |
| Work | Newton | erg |
| Force | Metre | cm |
| Displacement | Joule | dyne |
A
B
C
Work
Joule
erg
Force
Newton
dyne
Displacement
Metre
cm
Question 4:
A bird sitting on a wire, flies, circles around and comes back to its perch. Explain the total distance it traversed during its flight and its eventual displacement.
The total distance travelled by the bird during its flight = 2 X (Distance between the point where the bird was sitting and the point from where it takes a turn)
The eventual displacement of the bird is zero as it returns to its initial point i.e. where it was sitting.
Question 5:
Explain the following concepts in your own words with everyday examples : force, work, displacement, velocity, acceleration, distance.
Force: It is any kind of push or pull on a body due to another body when the bodies interact with each other. It is a vector quantity. For example, a person applies a force in the form of push or pull to open a door. Work: It is defined as the work done by a force that causes a displacement in an object. It is a scalar quantity. For example, a child does work when he drags a toy car on the ground. Displacement: It is the shortest distance between the initial and final position of an object. It is a vector quantity. For example, when we go to a mall for shopping from our house and then return to the house, the displacement would be 0 as our initial position (house) and final position (house) is same. Velocity: Velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement. It is a vector quantity. For example, a car running on a straight road has some velocity. Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity is known as acceleration. It is a vector quantity. For example, if a car is moving on a straight with variable speed, it will posses some acceleration. In case the speed of the car remains same but the direction of car changes, then also the car would be accelerating. Distance: It is the actual path length covered by an object during its motion. It is a scalar quantity. For example, when we go to a mall for shopping from our house and then return to the house, the distance travelled by us would be twice the distance between our house and the mall.
Question 6:
A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
The ball is rolling on a flat and smooth surface. Therefore, it will not face the frictional resistance. The speed of ball from A to B is 2 cm/sec. At B the speed of ball is 2 cm/second. From C to D there is force acting on a ball. Therefore, the speed of the ball is 4 cm/sec (the speed of the ball at D) The speed of the ball is same at all the points as it is linear motion. Therefore, the magnitude of velocity of ball = speed of the ball. Therefore, increase in the speed from B to C = 4 cm/sec — 2 cm/sec = 2 cm/sec Acceleration in the displacement = change in the velocity/ time = 2 cm/s/2 sec = 1 cm/s2 Thus the acceleration between B to C = 1 cm/s2 The acceleration of the ball between A to B is zero as the speed and direction of the ball is constant. After point B, a force is applied. Thus, the ball will get accelerated.
Question 7:
Solve the following problems.
(a) A force of 1000 N was applied to stop a car that was moving with a constant velocity. The car stopped after moving through 10 m. How much is the work done?
Here the direction of force and displacement are opposite to each other. That means, F= 1000 N and s = -10m . W=F x s = 1000 N x (-10 m) = - 10000 J Ans. The work done W = -10000J
(b) A cart with mass 20 kg went 50 m in a straight line on a plain and smooth road when a force of 2 N was applied to it. How much work was done by the force?
Force (F) = 2 N Displacement (s) = 50 metre . W=F x s (work done by force) . W=2N x 50m = 100 J
Videos
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 7 Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Previous Chapter : Chapter 6 : Measurement of Physical Quantities - Online notes Next Chapter : Chapter 8 : Static Electricity -Online notes |