Static Electricity
Based on Maharashtra Board Class 7th General Science Chapter 8
Static Electricity
| Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. |
- All objects in our surroundings hold abundance electric charge.
- Electric charge is stored even in our own bodies.
- Electric Charge is an intrinsic property of particles.
Though electric charge is abundantly present in surrounding substances, it is always in hidden state, this is because two opposite charges are present in equal numbers in all these substances.
When an +ve charge & -ve charge on an object are balanced, the object is neutral. there is no net charge on the object.
If that charges are not balanced the object is said to be charged.
It's called "static" because the charges remain in one area rather than moving or "flowing" to another area.
All substances are made up of particles, which are made up of very tiny atoms. Each atom has stationary positive charge and moving negative charge

Atoms are made up of tiny particles called neutrons, protons, and electrons.
The neutrons and protons make up the nucleus. The electrons spin around the outside of the nucleus.
Protons have a "positive" (+) charge.
Electrons have a "negative" (-) charge.
Neutrons have no charge, they are neutral.
Positive charge and negative charge of an atom are perfectly balanced, therefore an atom is electrically neutral.
When certain objects are rubbed against each other, the negatively charged particles on one object go to the other object.
- The object to which they go, becomes negativity charged due to an excess of negativity charged particles.
- Where as the first object becomes positively charged.
Such charge is called electric charge.
| If the electric charge is generated by friction then it is called frictional electricity. |
- The electric charge generated by friction is produced only at the place of friction. Hence it is called static electricity.
- It remains in object only for short duration.
Items with similar charges [(+)and(+) or (-)and(-)] will push away from each other. This is called Repulsion.
Items with different charges (positive and negative) will attract each other. This is called Attraction.
Attraction may occur between two oppositely charged bodies or a charged body and an uncharged one. That is why in attraction, one is not sure if both bodies are charged.
However in repulsion, there are two bodies that have the same charge. That is why repulsion is the sure test of electrification.
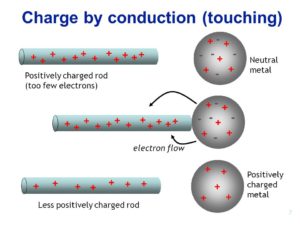
| Charging By Conduction | Charging By Induction |
| In this process the conductor is touched with the charged body | In this process the charged body is brought nearer to conductor. |
| The charge produced on the conductor is similar to that on the charged body | The charged body induces opposite charge at the near end and similar charge at the far end of the conductor |
| The charge produced on the conductor is permanent.
For removing the charge, the conductor has to be earthed. |
The charge produced on the conductor is temporary.
The induced charge disappears at the removal of the inducing body. |
| The amount of charge transferred depends on the area of the charged body that touches the conductor. | The amount of the induced charge depends on the amount of the inducing charge and its distance from the conductor. |
| In conduction there is a transfer of charge. | In induction there is no transfer of charge. |
| Conductors as well as insulators can be used. | Only conductors can be used |
 |
Charging by Induction
|
In the sky where air and clouds rub against each other, the upper part of some clouds on the upper side becomes positively charged and the lower sides becomes negatively charged.

Due to this the charge from the bottom of the cloud being larger than the charge on the ground, comes towards the ground in stages. This is very rapid travelling in less than a second, producing heat, light and sound energy, along with electric current.
Lightning is caused due to static charges. So, before we understand lightning, let us understand about electric charges.
- Electric charges at rest(without motion) is referred to as Static Electricity.
- There are 2 types of static charges : Positive (+) and Negative (-)
- Static charges are produced by the friction between two interacting bodies (See examples below)
- Static electric charges exert a force on each other. This force could be attractive or repulsive depending on the charge
- Two like charges repel each other.

- Unlike charges attract each other

During rains, a bright flash of light is seen in the clouds. It is known as lightning.
Lightning is a phenomenon that occurs due to atmospheric electricity where a flash of light is accompanied by a thundering sound.
- When the constituent particles of clouds collide with each other, charge is created due to friction.
- A layer of electrons (negatively charged particles) build up at the bottom of a cloud and make it negatively charged.
- While the other water droplets which now lack electrons move up and gather forming a positively charged layer at the top of the cloud.
- Thus a charge separation is created. When these charges become adequately powerful, the electricity is discharged towards the earth which results in lightning.

- Lightning also creates a loud noise called thunder.
- Lightning strikes carry huge amounts of energy. A typical lightning strike carries an electric current of over 30,000 amps and delivers 500 mega joules of energy.
Lightning Strike :
When lightning strikes, an opposite charge is generated on the roof of a building or on the top of the tree by induction. Therefore an attraction between opposite charges on the cloud and building, which makes the charge on the cloud flow towards the building. This flow is called lightning strike.
Lightning on striking the earth can cause a lot of destruction and kills people.
The damage due to lightning can be prevented by installing lightning conductors on top of buildings.

Safety measures during lightning Do's
- Take shelter in house that has lightning conductor.
- It is safer to be inside a house, a car or bus.
- Get off from motorcycles, scooters etc.
- Stay away from wire fences and metal pipes, rails etc.
- If nothing is available nearby drop on your knees and bend forward putting your hands on your knees.
Don't
- Avoid using phones.
- Do not stand under a tall tree.
- Do not lie flat on the ground.
Lightning Conductors :

- It is a device used to protect the buildings from the effect of lightning.
- A metallic rod is erected along the walls of the building during construction such that the tip is protruding outwards at the top of the building.
- The top end is in air and is not in touch with any metallic surface.
- The other end is connected to a plate of cast iron buried in the ground.
- In a pit dug in ground , coal and salt filled, The iron plate is placed upright in the pit
- Some provision also done to pour water in a pit, This is help to spread the electric charge quickly into the ground and prevent damage.
- When a lightning strikes, this provides a direct path for the charges to discharge to the ground, thereby not affecting anybody.
The electric charges where named as positive charge (+) and negative (-) charge by Benjamin Franklin
Thales found that feathers are attracted towards a rod of amber that had been rubbed against a woollen cloth.
In the greek language amber is called elektron . This property of amber to attract the things was named electricity.

English words "electric" and "electricity", which made their first appearance in print in Thomas Browne's book in 1646
Instruments and Experiments
Experiment 1: Comb and Pieces of Paper
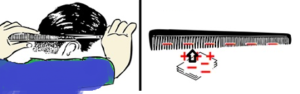
Experiment
- Rub your hair with a comb.
- Place it near small pieces of paper.
Observation
- The pieces of paper are attracted towards the comb.
Analysis
- Earlier, the comb and the pieces of paper were neutral
- When we rubbed the comb on our hair, the electrons were transfered from hair to the comb. Now the comb is charged negatively.
- When the comb is brought near the pieces of paper, the electric field of the comb influences the paper and it gets polarised ie the positive charges move near the comb and the negative charges on the other side of the comb. And hence they attract each other.
Conclusions
- Static charges are produced by the friction between two interacting bodies
- They exert a force on each other - Unlike charges attract each other

Experiment
- Rub a glass rod with a piece of silk cloth.
- Place it near a plastic straw.
Observation
- The straw is attracted towards the glass rod.
Analysis
- Earlier, the glass rod and the straw were
- When we rubbed the glass rod on a piece of silk cloth, the positive charges were transferred from silk to the glass rod. Now the rod is charged positively.
- When the rod is brought near the pieces of straw, the electric field of the rod influences the straw and it gets polarized ie the negative charges move near the rod and the positive charges on the other side of the rod. And hence they attract each other.
Conclusions
- Static charges are produced by the friction between two interacting bodies
- The charges exert a force on each other - Unlike charges attract each other

Experiment
- Rub 2 glass rod with a piece of silk cloth
- Bring the two glass rods closer
Observation
- They repel each other.
Analysis
- Earlier, the glass rods were
- When we rubbed the glass rods on a piece of silk cloth, the positive charges were transferred from silk to the glass rods. Now the rods are charged positively.
- When 2 such glass rods are brought closer, they repel each other.
Conclusions
- Static charges are produced by the friction between two interacting bodies
Like charges repel each other
It is an instrument used to detect electric charges.A simple electroscope can be constructed as follows.
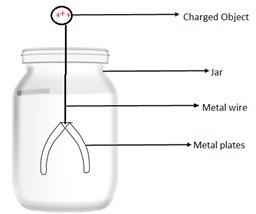

- Take a glass container.
- Insert a metal wire inside it.
- To the ends of the wire, which are inside the jar, attach 2 metal plates(say aluminium or gold plates).
- The other end is outside the glass container is connected or brought in contact with charged body.
The electroscope detects charge in the following way:
- A charged object is brought in contact with the open end of the wire .
- The charges are transferred via the wire which is a good conductor of electricity.
- The aluminium plates also get charged and since they are similarly charged, they repel and move away from each other.
- This confirms the presence of charge on the body.
Grounding & Discharging
If the charged body was brought close to the electroscope and then, we simultaneously touch the metal plates with your hand, then this would cause the charges to flow through your body ( your body is a good condutor of electricity) to the ground. This is called grounding. The plates no longer repel because their charges are 'discharged' to the ground because of grounding.
Test
![]()
Click on link to Download PDF:
Class 7th-General Science-Chapter 8 : Static Electricity-Maharashtra Board-Notes PDF
Class 7th-General Science-Chapter 8 : Static Electricity-Maharashtra Board-Solution PDF
Class 7th-General Science-Chapter 8 : Static Electricity-Maharashtra Board-Text Book PDF
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 7 Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Previous Chapter : Chapter 7 : Motion, Force and Work - Online notes Next Chapter : Chapter 9 : Heat - Online notes |

Thank you
it was very useful for me and its test was very well adorable . thank you and keep sending us such useful lesson answer , but try to increase number of MCQ question.
Thanks, stay connected.
Thank u