Tides
Maharashtra Board-Class-7th-Geography-Chapter-3
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
High tide and low tide :
- Sometimes, the sea water is very close to the coast and at other times, it is far away from the coast. This natural phenomenon is called high tide and low tide respectively.
- Barring a few exceptions, all the coasts on the earth experience tides.
Cycle of high title and low tide :
- Tides are movements of sea water occurring daily and regularly.
- The level of sea water changes after a specific period of time.
- After every 12 hours and 25 minutes, a cycle of high tide and low tide gets completed.
Science behind tides :
- The regularly occurring events of high tide and low tide appear to be quite simple and natural.
- However, tides are directly related to the sun, the moon and the earth and the gravitational and centrifugal forces that interact between them.
Centrifugal force :
- The power or force that the earth gets due to its rotation, is called centrifugal force.
- This force works away from the centre of the earth.
Gravitational force .
- Due to the centrifugal force any object on the earth would be thrown into the space. However, the gravitational force is working towards the centre of the earth at the same time.
- Due to the gravitational force any object on the surface of the earth remains at the place where it exists.
Factors responsible for the occurrence of tides: The factors responsible for the occurrence of the tides are :
Effectiveness of the gravitational force of the moon and that of the sun :
- The moon is closer to the earth than the sun.
- As its effect, the gravitational force of moon becomes more effective than that of the sun.
Tides :
- A place on the earth located at the opposite point of the place experiencing high tide or low tide also experiences high tide or low tide respectively at the same time.
- When there is high tide at 0° meridian, the 180° meridian also experiences high tide.
- If there is high tide at 0° and 180° meridian, then low tide will occur at 90° E and 90° W meridians.
Types of tides :
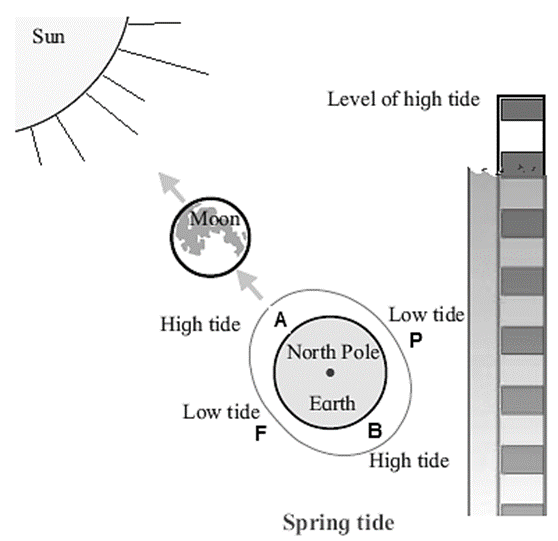
Spring tides :
On the new moon day and full moon days, the gravitational pull of the sun and the moon act in the same direction leading to spring tides. Spring tides are higher than the average high tides and lower than the average low tides.
Explanation : Click here to View Figure-1
Neap tides : On the first and the third quarter day of each month, the forces of both the sun and the moon operate at right angles on the earth leading to neap tides. Neap tides are a little lower than the average high tides and a little higher than the average low tides.
Explanation : Click here to View Figure-2

Effects of tides :
Timings of the tides change daily :
- The timings of the tides change daily.
- The time difference between two high tides/ two low tides within a day is of 12 hours and 25 minutes.
- The timings of tides of any particular day are 50 minutes ahead of the timing of tides of its previous day.
Click here to View Figure-3

Waves :
- The sea water gets pushed by the wind and ripples are generated on the water surface. These are called waves.
- The sea water moves up and down or slightly forward and backward due to the waves. The waves bring energy contained in them to the coast. They break in the shallow waters near the coast.
- Large or small waves are formed continuously at the surface of the sea. Generation of waves is a natural and regularly occurring phenomenon.
Structure of waves :
Effects of waves :
- The waves cause erosion along the headlands.
- They create beaches in the protected locations in the bays.
Velocity of waves :
Reasons of wave generation :
- The main reason of wave generation is wind.
- At times, waves are also generated due to earthquakes or volcanic eruptions occurring below the floor of the sea.
Tsunami :
- Destructive waves of great height that are generated due to earthquakes or volcanic eruptions occurring below the floor of the sea are called tsunami.
- Tsunami waves cause huge loss of property and life.
- In 2004, tsunami waves were generated because of the earthquake that took place near Sumatra island of Indonesia. They devastated the east coast 01' India as well as Sri Lanka.
- At the time of risk of tsunamis, it is better to go away from the coasts or towards higher altitudes. This way, loss of the loge can be avoided.
Click on below link to get PDF from store :
Class-7-Geography-Chapter-3-Tides-Notes
Class-7-Geography-Chapter-3-Tides-Solutions
Class-7-Geography-Chapter-3-Tides-Book
All Chapter Class-7-Geography Notes Set (11-PDF) Rs. 35-Buy
All Chapter Class-7-Geogarphy Solutions Set (10-PDF) Rs. 28-Buy
All Chapter Class-7-Geogarphy Notes + Solutions Set (21-PDF) Rs. 55-Buy
All Notes -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-30-PDF) Rs. 80-Buy
All Solutions -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-29-PDF) Rs. 72-Buy
All Notes + Solutions -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-59-PDF) Rs. 135-Buy
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 2 :The Sun, the Moon and the Earth - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-4-Air Pressure- Online Notes |