Agriculture
Maharashtra Board-Class-7th-Geography-Chapter-9
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Agriculture :
Scope of agriculture :
- Agriculture has wide scope. Cultivation of the crops is considered to be the main and the most important occupation in agriculture.
- Animals and plants serve as our primary sources of food and clothing.
- Agriculture includes a variety of occupations in addition to the cultivation of various crops, such as raising cattle, sheep, and goats, maintaining poultry farms, keeping bees, sericulture, horticulture, orchardry, pisciculture, pig farming, emu farming, etc.
Resources in agricultural occupation : Resources like manpower, animals, implements, etc. are used in agricultural occupations.
Changes in the agricultural practices :

- Nomadic life : In the past, primitive man had to wander in the forest to sustain himself on the collected forest produce.
- Invasion of cultivation: Gradually man learnt the art of cultivation and started getting greater production from the land. Through this he could provide for the whole year’s need for foodgrains.
- Stable Life : Besides the cultivation of different crops, he also started obtaining number of products through floriculture, horticulture, rearing animals, pisciculture, etc. Abandoning the nomadic life, man undertook different occupations related to agriculture at the same time.
Animal husbandry :
Rearing different animals and obtaining various products from them for subsistence is the core of animal husbandry.
- Dairy farming : Dairy farming refers to the practise of raising milk animals and farm animals. Cows, oxen, buffaloes, and other farm animals are raised for agricultural purposes. Dairy farming is seen as an essential component of mixed farming. Dairy farming has just lately become commercial in India. Commercial dairy farming is mostly done for meat and milk.
- Sheep and goat raring : Sheep and goat rearing is a traditional occupation. This occupation is generally carried out in hilly tracts and semi-arid regions with dry climate. Sheep and goat survive on short grasses, shrubs and acacia. In India, this occupation is mainly undertaken for meat. It is also carried out for obtaining wool.
- Poultry : Keeping hens and other fowl is a traditional occupation. It is commonly practiced in all parts of the world. This occupation is carried out as a household occupation and also on a commercial basis.
- Rearing of other animals : In India, rabbit, pig and emu rearing is also undertaken in some areas.
Bee keeping :
- Bee keeping is an important occupation with respect to agriculture.
- This occupation is undertaken to obtain honey and wax.
- Bees, in order to collect honey, hover plants that bear flowers.
- This promotes the process of pollination.
- As a result, the trees bear large number of fruits and the crop yield increase.
Pisciculture (Fish farming) :
- Farm ponds are dug out for pisciculture. Water is stored in such ponds.
- Fish seeds are released in these ponds.
- For psiciculture, seeds of freshwater species are used.
- In order to achieve the best growth of fish, scientific methods are employed.
- Wam, Rohu, Rawas (Indian Salmon), Kolambi (Prawns), etc. are reared in fish farms.
- Fishing in open seas has a number of risk factors. As its effect, pisiculture has developed in India.
Sericulture :
- Rearing of silk moth is called sericulture. Sericulture gets included in allied activities in agriculture.
- Different organizations supply silk moth eggs to the farmers.
- Leaves of mulberry trees are the main food for the silk worms. Once planted, the Mulberry trees survive for a minimum period of 15 years.
- Silk threads are obtained from the cocoon of the silk moth. These threads are very fine and strong. These threads are used to weave soft silk cloth.
- Getting silk thread from cocoons and manufacturing silk cloth are independent occupations.
Nursery :
- In the last few years, the area under floriculture, cultivation of medical and aromatic plants and horticulture has increased.
- These plantations require a high standard of seedlings, cuttings, bulbs and seeds.
- This had led to the development of nurseries.
- Nurseries give good returns.
Greenhouse farming :
|
Types of farming :
The following typos of farming have evolved due to geographical and cultural diversity, technological differences, purpose and aims of farming, methods of farming, the crops being cultivated, the techniques used, land use, etc.
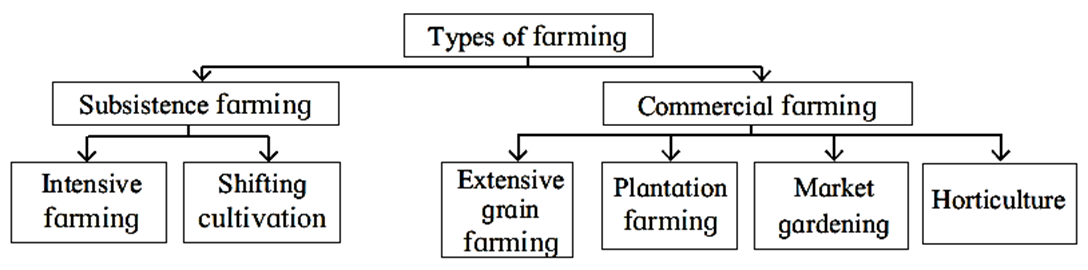
Subsistence farming: Subsistence farming is also called traditional farming. The following are the two subtypes of subsistence farming :
- Intensive farming : Intensive farming is carried out in one and the same farm for years together. It is mostly seen in developing regions.
- Shifting cultivation : Shifting cultivation is a primitive type of cultivation. In this type of farming, every year a new area is chosen for cultivation. After a specific period of time, old areas are again used for cultivation. People involved in shifting cultivation also practice allied occupations.
Commercial farming : Commercial farming is another type of farming. The following are the three subtypes of commercial farming :
(i) Extensive grain farming :
- This type of farming is carried out with the help of the machines.
- A single crop cultivation is the striking feature of this type of cultivation.
- This type of farming is mainly carried out in the Temperate Grassland region.
- Heavy capital investment is necessary for this type of farming. Since huge expenditures are needed for the purchase of machinery, fertilizers, pesticides, godowns, transport cost etc.
- The problems in extensive grain farming are droughts, attack by pests, locusts, etc. and market fluctuations.
(ii) Plantation farming :
- This type of farming is mainly practiced in hilly tracts.
- Local manpower plays important role in this type of farming.
- A single crop cultivation is the main feature of this farming.
- This type of farming is practised in tropics.
- This type of farming requires large scale capital investment due to the long duration of crops, use of scientific methods, exportable production, processing etc.
- Climate, manpower, deterioration of environment, economic and managerial problems are the major issues faced by this type of agriculture.
- It is practised in India and other South Asian countries, Africa, South and Central America.
(iii) Market gardening : This type of cultivation is developed in modern times. In this type of farming, farmers cultivate vegetables and other items in the vicinity of urban centres to cater the demands of city dwellers. This type of farming is also known as truck farming.
Subtypes of market gardening :
(a) Horticulture :
- Horticulture is one of the subtype of market gardening.
- In this type of farming modern as well as traditional methods are used.
- The size of the farm is small and every plant is cared for properly.
- Different native and exotic fruits like mangoes, custard apples, grapes, bananas, pomegranates, dragon fruits, cherries, oranges, raspberries, strawberries, mulberries, etc. are cultivated in fruit farming.
- Mahabaleshwar, Panchgani, Pune, Nagpur, Jalgaon, Nashik, etc. cities of Maharashtra are famous for fruit farming.
- Countries having Mediterranean climate, France, Italy, etc. practice horticulture on a large scale.
(b) Floriculture :
- Floriculture is one of the subtype of market gardening.
- In this type of farming modern as well as traditional methods are used.
- The size of the farm is small and every plant _is cared for properly. A variety of flowers such as lily, gerbera, tulip, dahlia, Chrysanthemum, marigold, etc. are grown in this type of farming.
- Countries having Mediterranean climate, France, Italy, etc. are famous for floriculture.
| Irrigation :
Supplying water to the crops artificially is called irrigation. The ground water is obtained for irrigational purpose by digging wells, bore wells, ponds, etc. With various techniques of irrigation facilities, crops are grown on a large scale_ Well irrigation, cannel irrigation, tank irrigation, etc. are some of the methods of irrigation. |
Agro tourism :
- Agro tourism is a new field of tourism. In the tropics, there is a greater scope for agro tourism.
- City dwellers are curious about farmer’s life and environment.
- Many of them visit rural area to see the rural life.
- Agro tourism is financially beneficial for the farmers and his village.
Artificially ripened produce and naturally ripened produce :
- At times, in order to get the produce earlier, artificial chemicals, pesticides are employed profusely. These facilitate quicker production and the produce appears fresh and attractive. However, such products are harmful to the health.
- On the other hand, naturally ripened produce are good for health.
Marketing system :
Marketing systems are necessary for marketing the goods produced by the farmers available to consumers at a fair price and in time. The importance of marketing system in countries like India, can be explained with the help of the following points :
- Scattered nature of agriculture
- Lack of organization of farmers
- Weak economic condition of farmers
- Perishable produce
- Produce used as raw material in industries
- Availability of international market due to globalization
- Great demand from hotel industry and malls.
Click on below link to get PDF from store
MSBSHSE-Class-7-Geography-Chapter-9-Agriculture-Notes
MSBSHSE-Class-7-Geography-Chapter-9-Agriculture-Solutions
MSBSHSE-Class-7-Geography-Chapter-9-Agriculture-Text Book
All Chapter Class-7-Geography Notes Set (11-PDF) Rs. 35-Buy
All Chapter Class-7-Geogarphy Solutions Set (10-PDF) Rs. 28-Buy
All Chapter Class-7-Geogarphy Notes + Solutions Set (21-PDF) Rs. 55-Buy
All Notes -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-30-PDF) Rs. 80-Buy
All Solutions -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-29-PDF) Rs. 72-Buy
All Notes + Solutions -Social Science (History_Civic+Geography-59-PDF) Rs. 135-Buy
Useful links for Class 7
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 8 : How Seasons Occur - Part 2 - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-10-Human Settlements -Online Notes |