Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Maharashtra Board-Class 7th-General Science-Chapter-14
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn:
|
Matter : Objects are made up of substances or matter
The particulate nature of matter and properties of matter :
The matter may be in the solid, liquid or gaseous states but their properties are due to the matter by which they are made. e.g., Chalk is in solid form, ink is in liquid and perfume is in gaseous state. The colour of a chalk, the blue colour of ink, the fragrance of a perfume are the properties of their matter which remain unchanged.
- Objects have mass. This means the matter from which this object is made also has a mass.
- Objects occupy space.
- Objects acquire properties from the matter from which they are made of.
- Substance : Many kinds of matter contain only one constituent. These are found in pure form in the nature. Matter made of only one constituent is called ‘substance’. e.g., Gold, diamond, water, chalk.
- Mixtures : Matter made of two or more substances are called ‘mixtures’.
Element :
Molecules : The smallest particles of substances are molecules.
- Molecules are formed by the combination of two or more atoms.
- Molecules can be subdivided to individual atoms. e.g., Water molecule can be further divided into oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
- When similar molecules combine together in any numbers, a simple product is formed.
- A molecule is usually stable to exist by itself.
Element : A substance whose molecules are made of exactly alike one or more atoms are called element. There are 92 elements in nature. Scientists have produced 26 man-made elements. Therefore totally, there are 118 elements. Scientists have discovered 118 elements
- The element cannot be decomposed further to obtain different substances.
- The smallest particles of elements are made of only one type of atoms.
- Atoms cannot be seen with the naked eyes, but when crores of atoms come together they form volume large enough to be visible to our eyes.
- The mass and volume of atoms of different elements are different.
- Some important natural elements : Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, iron, mercury, copper etc.
- Oxygen is in the gaseous state and in molecular state in the nature. Two atoms of oxygen are joined to form a molecule of oxygen.
- Elements can occur in solid, liquid or gaseous state.
- Atoms and molecules cannot be seen with the naked eyes.
Atom : An atom is smallest particle in an element that has the properties of the element.
- It is not possible to breakdown the atom further retaining the properties of the element.
- The atoms are bonded together in a molecule.
- An atom is not stable by itself
- Atomos means invisible in Greek language. Therefore, Democritus named the small particle of elements as ‘atom’.
- John Dalton’s theory (1803) :Atoms cannot be created or divided into smaller particles or destroyed.
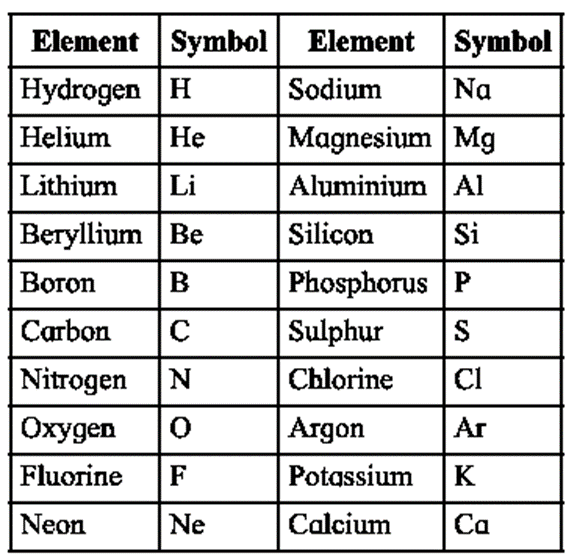
Symbols for elements : Berzelius introduced the method of using symbols for elements.
- Every element has its own symbol. To show this symbol the first letter of symbol’s name is used. e.g., for hydrogen, H is used, for nitrogen N is used.
- When the first letter in the names of two or more elements is the same, then a pair of letters is used to write the symbol. e.g., C is for carbon hence for chlorine, Cl is used and for calcium Ca is used.
- In such symbols, first letter is capital and the second is written in small script.
Metals, Non-metals and Metalloids : Elements are generally classified into metals and non-metals
- Non-metals : The elements which lack the properties such as malleability, ductility, conductivity of heat and electricity, density, lustre and sonority are called non-metals. e.g., phosphorus, sulphur, chlorine.
- Metals : The elements which show all the above properties are called metals, e.g., iron, copper, gold, silver
- Metalloids : The elements having some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals are called metalloids. e.g., Arsenic, silicon, selenium are examples of metalloids.
Alloy : Some metals cannot be used in their pure form. In such case, the properties of the original metal are modified by mixing one or more elements in it. This type of a mixture of metals is called an alloy. e.g., Brass, steel, twenty-two carat gold.
Compound : A compound is made of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion.
- A compound can be further subdivided into simpler substances by chemical means only.
- If the atoms in the molecule are of different types, then compound is formed. e.g. Water. In one molecule of water there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- The properties of a compound are different from those of the constituent elements. e.g. common salt, sugar, water. Hydrogen is combustible and it can burn. Oxygen supports combustion. But in water, even if these both atoms are present, water does not support combustion.
Molecular formula : A molecular formula of a compound is a short form of its name written with the help of the symbols of the constituent elements and the number of their respective atoms.
Mixture : A mixture is obtained by just mixing two or more substances in any proportion.
- By mixing different elements or compounds, a mixture is formed
- A mixture can be further subdivided into simpler substances by simple physical processes.
- There is no fixed proportion of various components in a mixture.
- While preparing the mixture, no chemical change takes place and no new substance is formed. e.g., air, sea water.
Separation of substances :
- Mixing unwanted substances in any foodstuff is also a type of mixture. This is known as adulteration.
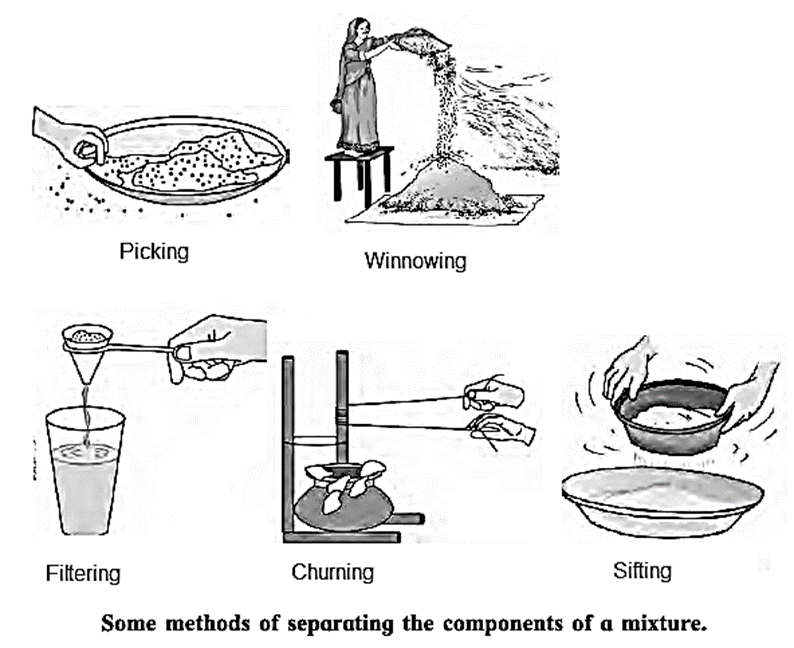
- To separate the unwanted ingredients from the mixture, the simple and easy method are straining (filtering), sifting, picking, sorting, winnowing, combing with a magnet and sublimation.
- The properties of matter and the effects of heat can also be used for separating the components of a mixture.
Method of distillation :
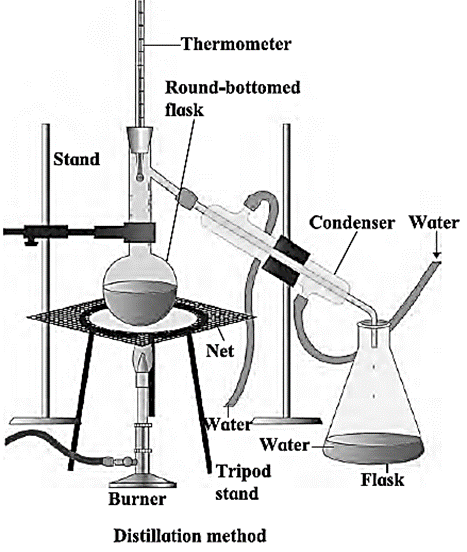
- The method of distillation is used to separate solute from solution. It can also be used to remove impurities from the solution and make it pure.
- The sea water in the round bottom distillation flask is heated. This produces the steam.
- As this steam is passed through the condenser, it turns into liquid due to condensation.
- The pure water which drips down in the conical flask can be separated. The salts in the sea water remains in the distillation flask.
Method of separation using separating funnel :
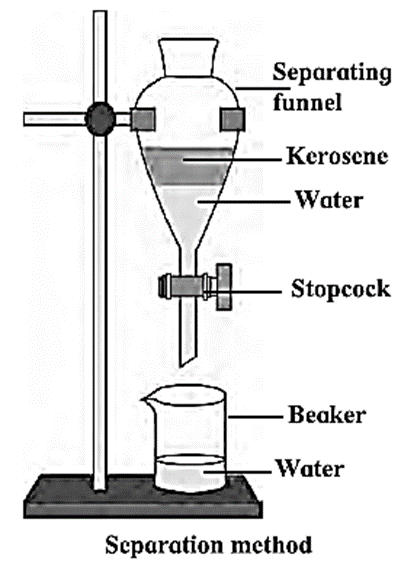
- When two immiscible liquids are to be separated from one mixture then the separating funnel is used.
- The immiscible mixture of two liquids is left undisturbed in the separating funnel.
- In the mixture, two layers are clearly seen.
- The lighter liquid floats on top in the separating funnel while the heavier of the liquids always remains below.
- By opening the stopcock without disturbing the funnel, the lower solution can be separated. e.g. Kerosene and water can be separated by such technique.
Method of centrifugation :

- To separate solids from a mixture of a liquid and solid, the method of centrifugation is used in the laboratory.
- A centrifuge machine is used for this purpose. It has a disc, which rotates in circular motion with a great speed. Test tubes are attached to the rim of this disc.
- When theses tubes attached to the disc rotate at the high speed, there is a centrifugal force generated. This force is pushes the particles away from the centre.
- Due to this the solid particles in the mixture are thrown to the bottom of the tubes and are thus separated from the mixture.
- In this way the small and lighter particles in the mixture get assembled together.
The other methods of separation such as filtering or settling do not become useful for separation of such fine particles.
Method of chromatography :
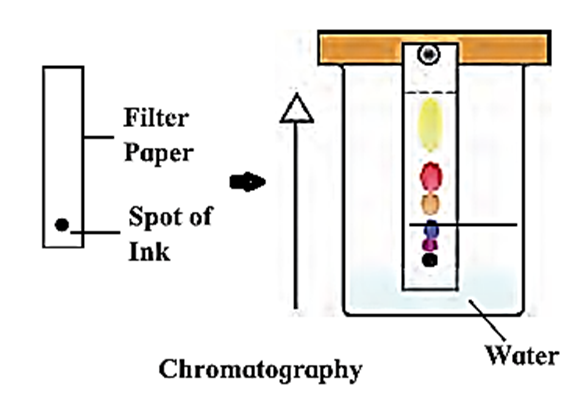
- If two or more substances are dissolved in small proportions in the same solution, the method of chromatography is used to separate these substances.
- In chromatography, two mutually opposite properties of substances are used.
- Solubility of the substance in the solvent that moves up.
- Ability of the substance to stick to the stationary filter paper.
- These properties are different for different substances. Therefore, all the components of the mixture do not rise for different heights.
- This method is used in pharmaceutical science, factories and scientific laboratories for detecting new ingredients and for identifying and separating components of a mixture.
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 13 :Changes - Physical and Chemical - Online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter-15- Materials we Use- Online Notes |