|
Topics to be Learn:
- Types of stars
- Life cycle of Stars
- Our solar system
- Sky watching
- Constellations
- Sun’s apparent motion and path
|
Introduction :
Galaxies : A group of stars and their planetary systems together form the galaxy. Our sun and its nine Planets and associated different components (e.g. satellites like moon) are part of a huge galaxy called ‘Milky Way’.
Types of stars : Contraction, expansion and rise in temperature bring about changes in stars over a long period of time. Accordingly, the stars are called :
- Sun like ordinary star
- Red giant star
- Red dwarf
- Massive star
- Red super giant star
- White dwarfs
- Neutron star.
Life cycle of Stars :
Life cycle of Stars :
- Stars are born out of Nebulae. Nebulae are clouds made of hydrogen gas and dust particles.
- Particles in the clouds are attracted by force of gravity. As a result, the cloud contracts and becomes dense and spherical. These spherical bodies are called stars.
- Various changes that take place during the star’s life is called ‘Life Cycle of Star’.
The processes such as contraction, expansion, rise in temperature etc. bring about changes in the nature of the star eventually. These changes are very gradual and spread over, a very long period of time. Astronomers identify these different forms of the stars at various stages during their lifecycle. They are then named with some identity.
[collapse]
Pole star :
Pole star : Since Pole star occupies a position on the earth’s axis passing through the north pole. Therefore, it always points the north in a sky map.
- The position of Pole Star can be also indicated by constellation of Saptarshi i.e. The Great Bear on one side and Sharmishtha i.e. Cassiopeia on the other side.
- The constellations of The Great Bear (Saptarshi) and Cassiopeia (Sharmishtha) are useful in locating the Pole Star. Cassiopeia is made up of five bright stars which are distributed
[collapse]
Our solar system :
- A small portion of ‘Milky Way’ galaxy is our solar system.
- There are lakhs of stars in ‘Milky Way’ galaxy.
- Some stars in this galaxy are larger than our sun and they have their own planetary systems.
- In the ‘Milky Way’ galaxy the various stars exhibit different colours and sizes.
Sky watching :
Sky watching :
- Horizon : When we stand under the sky and turn around, the sky appears to touch the ground. The line at which the sky and ground meet is called the horizon.
- elestial sphere : As we turn around ourselves and look up the horizon, the sky appears to be a half sphere. This virtual sphere is called the celestial sphere.
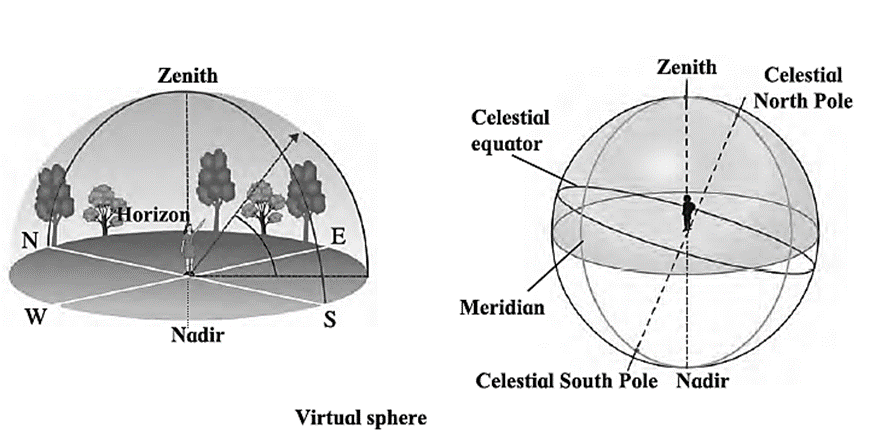
- Zenith : As we stand, the point on the celestial sphere exactly above the head is called zenith.
- Nadir : As we stand, the point on the celestial sphere exactly below our feet is called the nadir.
- Celestial poles : If the axis of rotation of earth is extended in the north and south direction it penetrates the celestial sphere at points called celestial North Pole and celestial South Pole respectively.
- Meridian : The great astronomical circle which passes through both the Celestial poles and the observer’s zenith and nadir is called a meridian.
- Celestial equator : If earth’s equator is expanded indefinitely, it penetrates the celestial sphere along a circle. This circle is called the celestial equator. It is in the same plane as earth’s equator.
- Ecliptic : The earth moves around the sun. But when seen from the earth, the sun appears to move along a circle on the celestial sphere. This circle which shows the apparent motion of sun around the earth is called ecliptic.
- Sky : The portion of earth’s atmosphere and beyond, which can be seen by our eyes as ceiling of the earth, is called the sky.
- Space : The vast empty space in the sky between the stars and planets is called the space. It may contain gas and dust particles.
- Rising and setting of celestial bodies : As earth rotates from west to east, the sun, moon and the stars in the sky appear to rise in east and set in west. But these celestial bodies do not rise and set at same time daily. The stars rise and set four minutes earlier every day.
- Owing to motion of earth around sun and that of moon around the earth, the sun moves one degree every day and moon moves 12 to 13 degrees.
[collapse]
Constellations :
- A group of stars occupying the celestial sphere and appear to take shapes of animals, humans and objects are called a constellation.
- The constellations have been named after certain events and beliefs.
- Western observers have divided celestial sphere into 88 constellations.
- The ancient western astronomers have put forward 12 zodiac signs but Indian astronomers suggested 27 nakshatras
Zodiac signs or Raashi :
Zodiac signs or Raashi :
- The ecliptic has been imagined to be divided into 12 equal parts of 30 degrees at the centre of ecliptic sphere. Each of these parts is called zodiac sign or raashi.
- The zodiac signs are :Aries, Taurus, Gemini,‘ Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius and Pisces.
[collapse]
Nakshtras :
Nakshtras :
- The moon completes one revolution around the earth in about 27.3 day. The portion traversed by the moon in one day is called a nakshatra.
- If one revolution (360 degrees) is divided into 27 equal parts, each part is 13 degrees and 20 minutes. Thus, moon traverses through 27 nakshatras in 27.3 days,
- A nakshatra is known from the brightest star that it contains. This brightest star is called yogatara.
- Depending on position of the earth along its orbit a particular nakshatra can be seen during sky watch.
- One zodiac sign = 12 Nakshtras
[collapse]
Sun’s apparent motion and path :
Sun’s apparent motion and path:
- Owing to sun’s bright light an observer cannot see the constellation behind sun, but it is present behind the sun.
- When the earth is at A, for an observer on earth, the sun appears to be in Scorpio zodiac sign. As earth moves from A to B, the observer says sun has entered Libra zodiac sign. In reality sun does not move, but observer perceives it due to motion of earth around the sun.
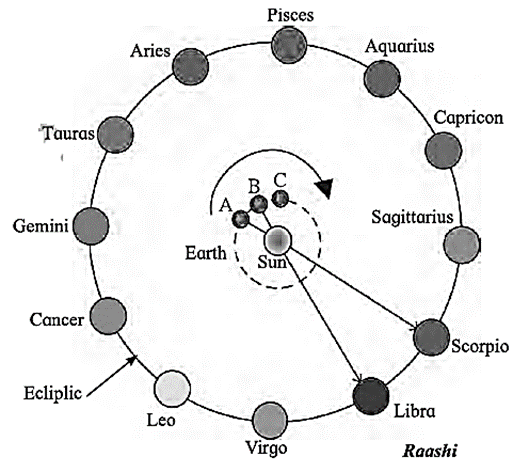
- As the earth changes its position, a different constellation appears behind the sun. But, astrologers express it as if sun has entered into the constellation or zodiac sign or raashi. This motion of the sun is called apparent motion and its path is called as apparent path.
- The rising of the sun in east and setting in the west is also an effect of apparent motion.
[collapse]
National Institutions for Astronomy :
- Inter University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA) located in Pune carries out fundamental research in astronomy.
- In India, planetariums named after Jawaharlal Nehru have done virtual projections of various stars and constellations.
| Remember :
Science has proved that the constituents of the solar system e.g. planets, satellites and comets as also distant stars and constellations do not have any influence on human life.
Man stepped on the moon in the twentieth century. He will conquer Mars in the twenty-first century. Hence, in this age of science, holding on to beliefs which have been proved to be wrong through numerous scientific tests, is an unnecessary waste of one’s time, energy and money. It is necessary to consider all these issues with a scientific frame of mind.
|

