In the World of Star
Maharashtra Board-Class 7th-General Science-Chapter-20
Solutions
Question 1:
Write the proper words in the blanks.
(meridian, horizon, twelve, nine, apparent, celestial, ecliptic)
(a) When seen from a great distance, the sky seems to be touching the ground along a circle. This circle is called the ............. .
(b) The ............. is used while defining the zodiac signs.
(c) Classified according to seasons, one season will have .............. nakshatras.
(d) The rising of the sun in the east and its setting in the west is the .................. motion of the sun.
(a) When seen from a great distance, the sky seems to be touching the ground along a circle. This circle is called the horizon. (b) The ecliptic is used while defining the zodiac signs. (c) Classified according to seasons, one season will have nine nakshatras. (d) The rising of the sun in the east and its setting in the west is the apparent motion of the sun.
Question 2:
A star rises at 8 pm tonight. At what time will it rise after a month? Why?
The star will rise at 6 pm after a month. This is because each star rises or sets 4 min early every next day. Therefore, after a month, the total advancement in the rising time of a star = 4×30=120 min=2 h Thus, if a star rises at 8 pm today, it will rise before 2 h i.e. at 6 pm after a month.
Question 3:
What is meant by 'The sun enters a nakshatra' ? It is said that in the rainy season the sun enters the Mrug nakshatra. What does it mean?
As the earth changes its position due to its revolution, a different constellation or raashi appears behind the sun every 18° 20’. But this is expressed as if sun has entered a particular raashi. So, when we say sun has entered Mrug nakshatra, actually Mrug constellation is behind the sun.
Question 4:
Answer the following question.
(a) What is a constellation?
A group of stars occupying a small portion of celestial sphere is called a constellation. Some of these stars appear to form certain animal or human figures and objects. These constellations are known by the brightest star present in it. Few examples of constellations are Orion, Big Dipper.
(b) What points should be considered before a sky watch?
(Students should write answer to this question based on their own experiences.)
(c) Is it wrong to say that the planets, stars and nakshatras affect human life? Why?
Question 5:
Write a paragraph on the birth and lifecycle of stars using figure.
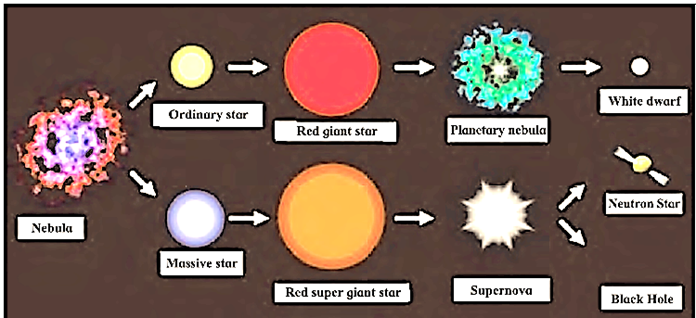
The processes such as contraction, expansion, rise in temperature, etc. bring about changes in the nature of the star eventually. These changes are very gradual and spread over a very long period of time. They constitute the lifecycle of stars. Other stages of a star during its life cycle is
Sun-like Stars: These are particularly similar to the sun in size but there is a lot of variation in terms of temperature. Examples are Alpha Centurai, Tau Ceti etc.
Red Giants: These stars do not have as hot outer layer as that of the Sun with temperature ranging from 3000 oC to 4000 oC but they have a very high luminance than the Sun. They are red in color and their diameter is 10 to 100 times that of the sun.
Super Nova: They are larger and even brighter as compared to the red giant stars and even the Sun. They are also considered as the primary source of heavy elements in the universe.
Binary or Twin Stars: A pair of two stars in which one revolves around the other or they both revolve around a common center is known as binary or twin stars.
Variable Stars: These stars have a variable shape and brightness i.e it keeps on changing whenever they expand or contract. Their brightness decreases when they expand and increases when they contract. Example Polaris or Pole Star.
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Books : Maharashtra Board-Class 7 Science Text Books – Chapter wise PDF for download Videos : Video playlist of Class7- General Science -All Chapters Previous Chapter : Chapter 19 : Properties of a Magnetic field - Online Solutions |
