Humidity and Cloud
Maharashtra Board -Class 8-Geography-Chapter-3
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Weather conditions :
- Different weather conditions prevail at different places.
- Different weather conditions prevail in different seasons at same place.
Evaporation :
The process of converting water into steam or water vapour is called evaporation.
The factors like dryness of air, temperature and speed of wind affects evaporation as follows :
- As dryness of air increases rate of evaporation increases.
- At more temperature rate of evaporation is more.
- Rate of evaporation is more if wind speed is more
- The rate of evaporation is high in the coastal regions. Therefore, humid climate is found in the coastal regions.
- The equatorial region on the earth receives perpendicular sunrays. Therefore, the temperature of the air in the equatorial region is found to be high. Due to high temperature, the rate of evaporation is more in the equatorial region. Therefore, humid climate is found in the equatorial region.
Humidity in the air :
- The proportion of water vapour in the air is called humidity.
- The proportion of water vapour determines the dryness or dampness of the air.
Moisture-holding capacity of the air :
- The capacity of the air to hold water vapour is called moisture-holding capacity of the air.
- Warmer air’s moisture-holding capacity is comparatively more. On the other hand, cold air’s moisture-holding capacity is comparatively low.
- The condition of air at a certain temperature, in which the moisture holding capacity of air becomes equal to the proportion of moisture present in it, is called saturation of the air.
- Saturation of the air leads to precipitation or snowfall.
Absolute humidity : Absolute humidity is measured with the help of the following formula : Absolute humidity = \(\frac{\text{Mass of water vapour}}{\text{Volume of air}}\)
Relative humidity : Relative humidity is measured with the help of the following formula : Relative humidity (%) = \(\frac{\text{Absolute humidity}}{\text{Vapour holding capacity}}\) x 100
Condensation and Sublimation :
- The process of changing water vapour in the air into water is called condensation. It is also called densification.
- The process of changing water vapour in the air into snow is called sublimation.
- Due to fall in temperature, the relative humidity of the air increases. This in turn leads to condensation or sublimation.
- Condensation of vapour in the open air occurs around the dust or salt particles in the air.
- Dew, frost and fog are the forms of condensation at ground level.
- Clouds are a form of condensation at higher altitude.
Clouds and types of clouds :
- A visible mass of fine particles of ice and water accumulated around the dust particles in the air at high altitude is called a cloud.
- Clouds causes rainfall or snowfall on the earth.
- The proportion of water vapour in the air near the surface of the earth is more.
- Therefore, clouds of larger size are seen at a lower altitude. The proportion of water vapour in the air at higher altitude is less.
- Therefore, clouds of smaller size are seen at a higher altitude.
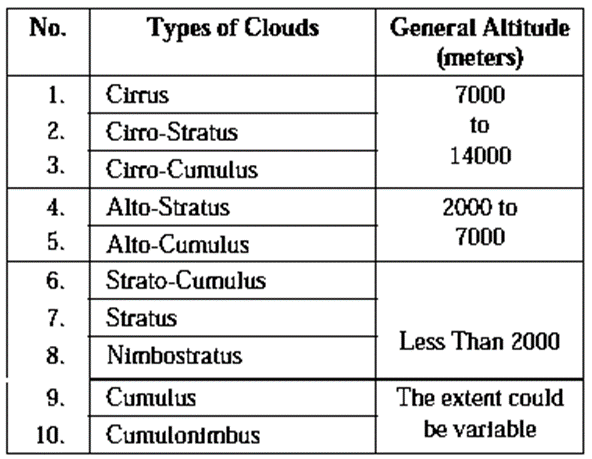
According to international classification, clouds are classified into following types :
(i) High clouds : Features of high clouds :
(ii) Medium clouds : Clouds at an altitude of 2000 m to 7000 m are considered as medium clouds. Alto-Stratus and Alto- Cumulus are medium clouds. Features of medium clouds :
(iii) Low clouds : Features of low clouds :

Click on link to get required pdf from store :
Chapter-3-Humidity and Cloud-Notes
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 2-Interior of the Earth -online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 4-Interior of the Earth -online Notes |
