Structure of Ocean Floor
Maharashtra Board -Class 8-Geography-Chapter-4
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Introduction :
- The proportion of water and land is uneven on the earth.
- Around 71% of the surface is covered by water but there is land even below this water.
- Like water, land is not at the same level.
The Relief of Ocean Floor :
- Land submerged below oceanic water is called the ocean floor .
- The depth from the sea floor and the shape of the land are the parameters for classifying the various submerged forms of ocean relief.
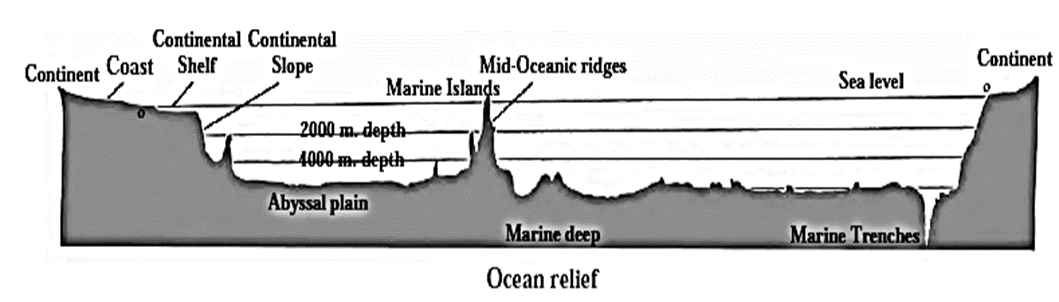
Submerged landforms :
Natural forms of land surface found on the ocean bed are called submerged landforms.
- The ocean floor relief consists of all submerged landforms.
- The structure of the ocean floor differs from ocean to ocean.
- As we go away from the coast, the structure of the ocean floor changes.
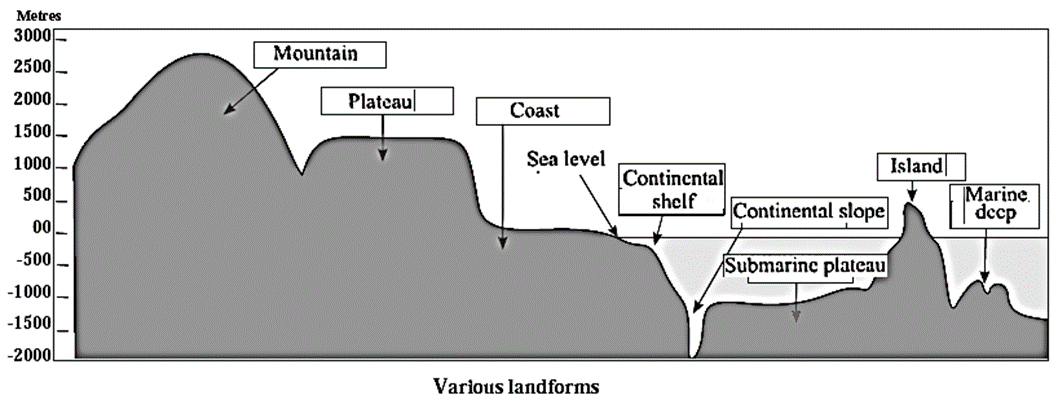
(i) Continental shelf:
- The land near the seacoast and submerged under the sea is called continental shelf. The depth of continental shelf is about 200 metres below the sea level.
- Continental shelf is found to be narrow along the coasts of some continents and broad along the coasts of some other continents.
- Being a shallowest part of the ocean bed, sunlight reaches up to continental shelf easily. As its effect, the food for fish like algae, plankton, etc. grows on a large scale on continental shelf. Therefore, continental shelf is useful for fishing occupation.
- Various minerals, natural gas and mineral oil, etc. can also be obtained from mining the continental shelf. For example, Mumbai High located on the continental shelf of the Arabian Sea is a source from where the mineral oil and natural gas is obtained.
(ii) Continental slope :
(ii) Abyssal plains :
- Beyond the continental slope lie the abyssal plains which are the flat part of the sea bed.
- Various submerged landforms like submerged hills, submerged mountains, etc. are seen on abyssal plains.
- Submarine plateaus are also found on the abyssal plains.
(iv) Mountain ranges and plateaus :
- The hills and mountains found on the ocean-bed are called submerged hills and mountains. These hills are hundreds of kilometers wide and thousands of kilometers long.
- Islands : Peaks of some of the submerged hills come above the sea level. They are visible to us as marine islands. Examples : Iceland in the Atlantic Ocean, Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal.
- Submarine plateaus : The summits of some marine islands are flat and extensive. They are called oceanic or submarine plateaus. Example : Chagos Plateau in the Indian Ocean.
(v) Marine deeps and Marine trenches :
| Remember
Mean Sea Level : Elevation or depth of any place is measured from the sea level.
|
Marine deposition :
Marine deposit :
- Marine deposit is a type of marine deposition.
- The rivers and glaciers flowing from the continent bring pebbles, clay, soil, etc. with them when they meet sea or ocean.
- These materials get deposited on the continental shelf. The deposits are known as marine deposits.
- Due to pressure of sea water and deposition of layers over layers of sediments, sedimentary rocks are formed.
- Marine life and the availability of minerals in the sea bed can be studied with the help of marine deposits.
Marine oozes :
- Marine oozes is a type of marine deposit.
- Lava and ash erupting out of volcano, fine soil particles, remains of plants and animals, etc. get deposited on marine abyssal plains. Deposits of these materials on the abyssal plains are known as marine oozes.
- Marine oozes are in the form of fine clay. The percentage of remains of plants and animals in marine oozes is up to 30 per cent.
- Marine oozes are also useful to study marine life and the availability of minerals in the sea bed.
Deposition of man disposed materials :
Click on link to get required pdf from store :
Chapter-4-Structure of Ocean Floor-Notes
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 8th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 3-Humidity and Clouds -online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 5-Ocean Currents -online Notes |