Energy Flow In An Ecosystem
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-7
Solution
Question 1:
Complete the following table (Carefully study the carbon, oxygen and nitrogen cycles).
| Bio-geo-chemical cycles | Biotic processes | Abiotic processes |
| 1. Carbon cycle | ||
| 2. Oxygen cycle | ||
| 3. Nitrogen cycle |
Decomposition by decomposers. Absorption by Water Decomposition by decomposers. Photo dissociation of water vapour in the upper atmosphere, as a result of which oxygen is released when water molecules are split by light
Bio-geo-chemical cycles
Biotic processes
Abiotic processes
1. Carbon cycle
Photosynthesis -Release of oxygen and Respiration - Release of oxygen CO2
Release of CO2 in the atmosphere by combustion.
2. Oxygen cycle
Photosynthesis and Respiration.
Combustion.
3. Nitrogen cycle
Decomposition by decomposers, Biological fixation by bacteria, ammonification
Industrial fixation, Nitrogen fixation in atmosphere and denitrification
Question 2:
Correct and rewrite the following statements and justify your corrections.
1. Carnivores occupy the second trophic level in the food chain.
Correction-Carnivores occupy the third trophic level in the food chain because the second level is occupied by herbivores. Herbivores are organisms who feed on plants. Carnivorous feed upon these Herbivorous animals therefore carnivores occupy the next level after herbivores.
2. The flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is considered to be a ‘one way’ transport.
Correction-The flow of nutrients in an ecosystem is considered to be cyclic. The continuous transfer of nutrients which are necessary for the growth of organisms occurs from abiotic to biotic factors and biotic to abiotic factors in an ecosystem. By photosynthesis green plants convert minerals and inorganic compounds into glucose. This food is transferred along with food chain from producers to primary consumers to secondary consumers. The decomposers of the ecosystem decompose all the dead and decaying organisms and return these nutrients back to the ecosystem. Thus, the flow of nutrients is cyclic and not one way transport.
3. Plants in an ecosystem are called primary consumers.
Correction-Plants in an ecosystem are called producers. Plants are autotrophs, they carried out photosynthesis with the help of solar energy and produce food. This food is utilized by other organisms. Other herbivorous organisms are dependent on the food produce by plant to meet their nutritional requirements. Therefore herbivorous are primary consumer and plants are producer
Question 3:
Give reasons.
1. Energy flow through an ecosystem is ‘one way’.
2. Equilibrium is necessary in the various bio-geo-chemical cycles.
3. Flow of nutrients through an ecosystem is cyclic.
Flow of nutrients through an ecosystem is cyclic as the nutrients move from one trophic level to another trophic level all the way up and then back down. The cyclic flow of nutrients occur in the following manner: Thus, we see that the flow of nutrients in the ecosystem follows a cyclic path.
Question 4:
Explain the following cycles in your own words with suitable diagrams.
1. Carbon cycle.
Carbon cycle
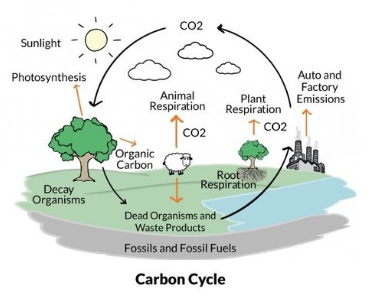
2. Nitrogen cycle.
The atmospheric nitrogen moves from atmosphere to the soil, from the soil to the plants, from plants to the animals and from all the living beings to the soil and back to atmosphere from the soil. This cyclic journey of the nitrogen is called nitrogen cycle. (1) Source of nitrogen : Plants cannot take the atmospheric nitrogen as it is. Therefore they take up various compounds of the nitrogen that are available in the soil. For the plants nitrogen compounds in the soil is the only source of nitrogen. (2) Nitrogen fixation : Nitrogen fixation is the process in which nitrogen is converted into compound such as nitrates and nitrites. There are two processes of nitrogen fixation. viz., physical fixation and biological fixation. Physical fixation Further divided into atmospheric fixation and industrial fixation (a) Physical fixation : The lightning in the sky brings about oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen and converts it into nitrogen oxide. Nitrogen oxide (NO2) dissolves in rain water and forms nitrous and nitric acid. These acids seep in the soil with the rain water. They undergo chemical reactions with other elements in soil and form different compounds of nitrogen. (i) Atmospheric nitrogen Lightening> Nitrogen oxide (ii) Nitrogen oxide + Rain water — Nitrous acid and nitric acid. (b) Biological fixation : It is the process wherein atmospheric nitrogen is converted into water-soluble nitrates. This step is performed by organisms like Rhizobium Azotobactea and blue-green algae, living in the root nodules of the leguminous plants carry out the function of biological nitrogen fixation. (3) Utilization of nitrogen compounds by the living organisms : In addition to nitrogen fixation there are other three processes which are important in nitrogen cycle. They are as follows :

3. Oxygen cycle.
Oxygen is an important component of life. We cannot survive without oxygen. It comprises about 21% of atmospheric air. It is also present in dissolved form in water bodies and helps in the survival of aquatic life. In combined form, it is found both in Earth’s crust and in the air. In the air, it occurs as carbon dioxide. In the crust, it is present as oxides of most metals and silicon and also as carbonate, sulphate, nitrate and other minerals. Oxygen is also a part of several essential bio-molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and fats. Oxygen is also a part of several essential bio-molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and fats.
There are processes that utilize atmospheric oxygen. At the same time, the balance of oxygen in the atmosphere is also maintained.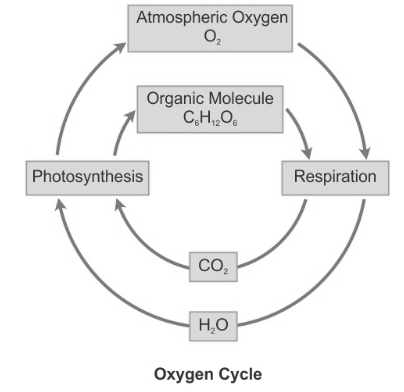
There are processes that utilize atmospheric oxygen. At the same time, the balance of oxygen in the atmosphere is also maintained.
Question 5:
What would you do to help maintain the equilibrium in the various bio-geo-chemical cycles? Explain in brief.
Biogeochemical cycles are the basis of life and play an important role in maintenance of life on earth. Any kind of disturbance to these cycles can result in the destruction of life. For maintaining the balance in the bio-geochemical cycles, following measures have to be taken : (1) We have to conserve plants like trees, creepers and the entire available flora. For this, we have to at once stop felling of the trees. If plants are destroyed, the productivity of the ecosystem is hampered. Therefore the flora has to be well maintained. (2) We should not kill and poach carnivorous wild animals. This results in disturbance in the ecological balance. (3) Under any condition, apex consumer should not be killed. The hunting makes the valuable species to become extinct. By exterminating the apex consumers, the interrelationships between food chains and food web will suffer. Deforestation due to industrialisation and increased population has resulted in the lost of forest cover on earth. In order to maintain the equilibrium in biological cycles following steps should be undertaken:
Question 6:
Explain in detail the inter-relationship between the food chain and food web.
The energy flow among the various constituent animals is known as the food chain and the length of a food chain depends upon the number of organisms. A food chain represents the relationship between organisms. The energy flow among the various constituent animals is known as the food chain and the length of a food chain depends upon the number of organisms. A food chain represents the relationship between organisms. Food web or food cycle is the connection between different food chains and represents what species eats what in an ecological system. A food web starts with the producers in ecosystem and then branches off into interconnected food chains that show who eats whom in an ecosystem. e.g. Insects (Primary consumer) nibble grass (Producer). Frogs (Secondary consumer) feed on insects. This is a straight food chain. Insects are also eaten by sparrow. Sparrow becomes food forowl. Owl also kills snakes. Snakes (Tertiary consumer) feed on frogs. Apex carnivore, hawk, feeds on sparrow, snake or frog too. In this way, smaller food chains are interconnected in a web form constituting the food web. Thus, there is an interrelationship between the food chain and food web.
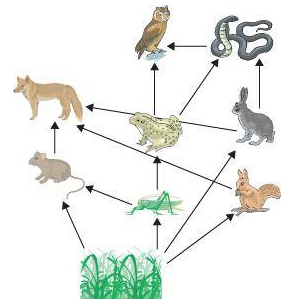
Question 7:
State the different types of bio-geo-chemical cycles and explain the importance of those cycles.
To maintain the concentrations of different naturally occurring substances in the environment, there are mechanisms that constantly recycle these substances. These recycling mechanisms are called bio-geochemical cycles. So, bio-geochemical cycles are the cyclic flow of nutrients between non-living environment and living organisms. Types of Biogeochemical Cycles There are two major types of biogeochemical cycles viz. gaseous cycle and sedimentary cycle. Importance of bio-geochemical cycle :
Question 8:
Explain the following with suitable examples.
1. What type of changes occur in the amount of energy during its transfer from plants to apex consumers?
(1) Green plants of the ecosystem store large amount of energy in the form of carbohydrates and proteins. (2) Before reaching the decomposers, this energy is passed through different trophic levels like primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, etc. (3)The amount of energy reduces as we move from lower trophic levels to higher ones. Energy is lost as it gets transferred from one organism to another because energy is lost as metabolic heat when the organism of one trophic level consumes the organisms of another trophic level. This can also be explained on the basis of 10% rule which states that when energy is passed in an ecosystem from one trophic level to the next, only ten percent of the energy will be passed onto the next trophic level. As, we move from lower trophic level to the higher trophic level, there is a decrease in the amount of energy which is transferred.
This can be explained with the help of energy pyramid in case of an aquatic ecosystem.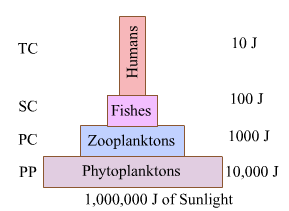
2. What are the differences between flow of matter and of energy in an ecosystem? Why?
The major difference between flow of matter and of energy is that the flow of matter occurs in a cyclic manner i.e. it is recycled, however, the flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional which means, it is not recycled. Flow of matter: The flow of matter follows the following path- Energy Flow : In case of flow of energy, the energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction, from photosynthetic organisms to herbivores to omnivores and carnivores and decomposers, less and less energy becomes available to support life. This loss of useable energy occurs because each energy transfer results in the dissipation of some energy into the environment as heat.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 6:Classification of plants - view online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 8: Useful and Harmful Microbes -view online Solution |