Education
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-History-Chapter-5
Notes
|
Points to be learn :
|
Challenge of literacy :
- The first Census of India in 1951 revealed the extreme complexity and intractability of the educational issues in the country.
- In the first Census, the literacy level was 17%.
- The remedial measures led to increase in literacy.
Census year
Literacy
1971
34%
1981
43%
1991
52%
2001
64%
For improving this percentage of literacy, government of India were put several remedial schemes to deal with it.
Primary Education :
- Primary education refers to the schooling given to children in the age group of 6 to 14 years.
- Operation Biackboard : It was undertaken in the year 1988 by the Government of India.
- Funds were made available to improve the standard of the schools and to fulfill minimum educational needs such as at least two proper classrooms, toilets, one of the two teachers to be female, a blackboard, maps, laboratory apparatus, a small library, a playground, sports equipment, etc.
- This scheme gave momentum to primary education.
- Operation Blackboard was expanded in 1994.
- Provision was made for one additional classroom and for appointing one more teacher in schools with an enrolment of more than 100 students.
- The priority was given to girl’s schools, schools with a majority of scheduled caste and tribe students and schools in rural areas.
- It was made binding on the State Government to appoint 50% female teachers.
- District Primary Education Programme (DPEP) was started in 1994 with the objective of universalisation of primary education.
- It was implemented in seven states including Maharashtra.
- The programme aimed at 100% attendance in arresting student drop-out, education for girls and for the physically handicapped.
- It included programmes such as research on and evaluation of primary education, alternative education, creating societal awareness, etc.
- Midday Meals Scheme was started in 1995 to provide proper nourishment for students.
Know this :
|
Secondary Education :
- After independence Education Minister Maulana Abul Kalam set up University Education Commission in 1948.
- It recommended appointment of a separate commission for secondary education.
Mudaliar Commission : The Mudaliar Commission was appointed in 1952 to review the existing secondary education, the nature of the curriculum, medium of instruction and teaching methodology.
Kothari Commission : The Kothari Commission was appointed in 1964. It recommended the 10+2+3 pattern for secondary, higher secondary and university education. This system was implemented from 1972.
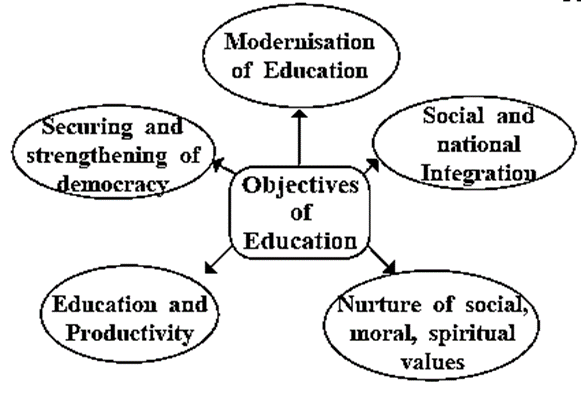
Maharashtra government adopted the 10+2+3 patterns in 1972 and conducted the first Std. X Board examination in 1975.
Higher Education :
Education in post-independence era :
- University Education Commission was appointed under the chairmanship Dr. Sarvapalli Radhakrishnan in 1948.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) was established by an act of parliament in 1956. It is the apex academic body that coordinates higher education and disburses grants to the universities and colleges.
- The UGC undertakes planning of university education, co-ordination of syllabii, giving priority to national needs through education and the planning and implementation of various schemes of higher education. It sets up university development councils, centres for advanced studies for post-graduate education, establishing new universities.
- It produces the ‘Countrywide Classroom programme which is telecast by Doordarshan.
| Know this :
Balbharati : The Maharashtra State Bureau of Textbook Production and Curriculum Research (Balbharati) was established in Pune on 27 January 1967. Balbharati prepares textbooks for school children. Textbooks are made in eight languages, namely, Marathi, Hindi, English, Urdu, Kannad, Sindhi, Gujarati and Telugu. ‘Kishor’, a monthly magazine for children, is also published by Balbharati. The Competency based Primary Education Curriculum 1995 :
|
National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) :
Maharashtra State Council of Educational Research and Training:
- It was established in Pune. It works for improving the standard of primary education, in-service training of teachers, training in syllabii and evaluation and vocational guidance for students.
- It brings out a periodical called Jeevan Shikshan.
| The Art Department was established in 1965 in Maharashtra, to frame the policy for Art Education and for its implementation by institutes of art. This Department undertook the responsibility of organizing the drawing grade examinations at school level |
National Policy of Education 1986 :
Satellite for Education :
- The use of satellite for education was made in 1975 with the help of Eknath Chitnis, a scientist with ISRO.
- SITE (Satellite Instructional Television Experiment) was undertaken under the leadership of the Space Application Centre at Ahmadabad. America had helped India in this programme.
- The concept of satellite education helped to improve the standard of education in the rural areas.
Establishing Open University :
- The United Nations declared 1970 as the International Education Year.
- The idea of establishing an Open University was thought of in the seminar at Delhi on the subject open University.
Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU)
Research institutes – science :
Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) : In the post-independence period in 1950, CSIR was established with the objective to promote scientific research in the country and to take the benefits of the research to all the people. Work :
National Institute for Research in the Mathematical and Physical Sciences : It was established in Tamil Nadu in 1962. It encouraged the highest level of research in mathematics.
Indian Statistical Institute -1969 : Made first indigenous computer named the ISIJU computer with the help of Jadavpur University.
Tata Consultancy Services, (TCS) : In 1974, TCS, obtained an American contract in the area of software production. That was the beginning of the software industry in India. Computers also helped to step up the speed of scientific research.
Centre for Development for Advanced Computing (C-DAC) : In 1988, the Central Government established C-DAC in Pune and in 1991 the Centre under the leadership of Dr Vijay Bhatkar developed the Param-8000 supercomputer.
Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC)-1948 : (1)
- Research in field of nuclear physics, soiid state physics, spectroscopy, chemical and life sciences
- Started a school to train scientists for setting up nuclear reactors.
Engineering Institutes :
Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT) : India’s first IIT was set up at Kharagpur in West Bengal in 1951. Objective : To provide higher and advanced education in all branches of engineering.
Indian institute of Management (IIM) :
Objective : To mould skilled managers.
Other objective /Work :
- Set up at Ahmadabad by the Central and State government.
- Help from Harvard Business School in America.
- Also set up at Kolkata, Bengaluru, Lucknow, Kozhikode, Indore and Shillong.
National Institute of Design (NID)-1961 :
Objective : To impart training in Industrial Design
Other objective /Work :
- Courses in design, graphic design, product design, visual communications
- Designing of transistor radio, calculators and logos for Indian Airlines and State Bank of India.
Film and Television Institute of India (FTII) :
|
Research institutes – medicine :
Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) : In 1949, the Indian Council for Medical Research (ICMR) was established for conducting research in the medical field.
All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) : Objective : To give impetus to advanced education and research in medicine Other objective /Work :
Medical Council of India :
- The Medical Council of India was restructured in 1958.
- It was entrusted with the task of determining criteria for quality of medical education, its supervision and inspection.
The Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer :
- It is a branch of Tata Memorial Centre
- Functions as national centre for treatment, research and education in cancer.
Central Council for Research in Indian Medicine and Homoeopathy : In 1969 the Central Council for Research in Indian Medicine and Homoeopathy was established to conduct research and bring about development in the Ayurvedic, Naturopathy, Unani and Homoeopathy systems of medicine. In 1979, this institute was dissolved and replaced by three others, namely, the In accordance with their respective clinical methodologies. These institutes have the responsibility of conducting research on various diseases, developing tests and standardisation of medicines.
Research institutes – agriculture :
Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI) : In India, research in agriculture had begun as early as 1905. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute was given the status of a University in 1958 Objective : Research Agriculture Other objective /Work :
Click on link to get PDF from store :
MSBSHSE-Chapter-5-Education-Notes
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th History & Political Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 4: Economic Development - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 6: Empowerment of Women and other Weaker Sections - online Notes |