Information Communication Technology
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-10
Solution
|
Topics to be learn :
|
ICT (Information Communication Technology) devices :
Different devices are used for producing information, for communicating, classifying, saving/storing information, managing information etc.
Devices that are used to collect, share, process or communicate / exchange information by electronic means are computer and networking hardware, radio, television, telephone, microphone, scanner, speakers, digital camera, video display unit (monitor), printer, plotter, modem, router, Internet and satellites. They are called ICT (Information Communication Technology) devices.
The computer, which is the most important device for information communication, is considered to have gone through five generations, since it was first created.
ICT (Information Communication Technology): Information and communication technologies are the forms of technology that are used to transmit, process, store, create, display, share or exchange information by electronic means.
This technologies uses in electronic equipment such as radio, television, video, DVD, telephone (both land line and mobile phones), satellite systems, and computer and network hardware and software, as well as the equipment and services associated with these technologies, such as video-conferencing, email and blogs,
Data : Data is a collection of unprocessed facts and figures. Information is a processed form of data. It is organized, meaningful, and useful.
Computer generations : A computer is the most important ICT device. Successive stages of evolution of digital computers are called computer generations.
Each generation is characterized by remarkable improvements in technology, internal organizations and programming languages over the previous generation.
- First generation computers were built using evacuated vacuum tubes called valves. Valves were large in size and generated large amount of heat. So, they had to be well spaced out.
- Consequently, computers had to be built big and cooled by huge air conditioners.
- A computer that is about ten times more powerful than other computers of its generation is called a supercomputer.
- Today’s supercomputers use multiple processors and parallel processing to achieve great processing speeds of more than one billion calculations per second.
- A computer works in an IPO (Input-Process-Output) cycle to complete an assigned task. It takes raw data as input from the user, uses a set of instructions (called program) to process the data, and gives the resulting information as output. The output can be used immediately or saved for future use.
Characteristics of a computer :
Components of a computer : Two basic components of a computer are
- Hardware : It is the physical parts of a computer. Hardware consists of all the electronic and mechanical parts used in computers.
- Software : Software is the programs (commands or instruction sets) that tell the computer how to perform tasks.
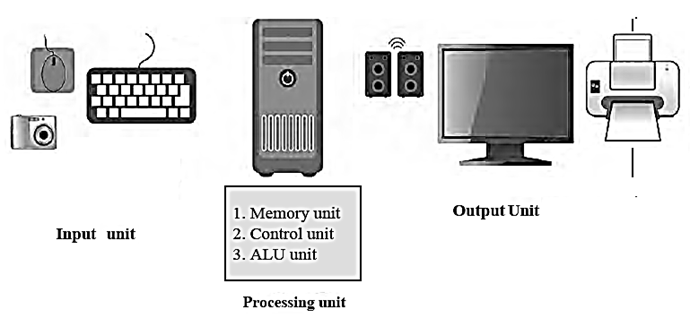
Components of computer hardware : Input devices : Input devices allow a user to enter data and instructions into a computer. Examples : keyboard, mouse, microphone, scanner, touchscreen, joystick, graphics tablet and digital camera. Central Processing Unit (CPU) : The three main parts of the Central Processing Unit and their functions are : Output devices Output devices are used by the computer to output the information (processed data) to the user. Examples : monitor (video display unit), printer, plotter, speakers, external memory. Computer memory : Memory is the place for storing data obtained from the input and also the generated solution or answer by the computer. There are two types of memories in a computer used to store data, instructions and information for a short term or a long term.
Computer memory is classified as follows :
- Internal or Primary Memory :RAM, ROM
- External or Secondary Memory : Hard disk, USB Memory Disk, Compact Disk - CD, DVD.
RAM (Random Access Memory) :This is a short-term memory which temporarily holds the program instructions and data that the processor can immediately access while processing. A computer can randomly access any of the memory locations of a RAM, and can both read and write at the memory location. When the computer is switched off, all the contents of this memory getserased.
ROM (Read Only Memory) : This long-term memory, known as the BIOS chip, permanently stores important instructions which should not be changed. It holds critical programs that are essential to bring the computer to a state of readiness after it is powered on. The memory locations are sequentially accessed and can only be read but cannot be changed. The contents of this memory does not get erased even when the computer is switched off.
External Memory (Storage devices) : They are used to permanently store software, as well as raw and processed data. Both the programs and data can then be repeatedly used whenever required. They can also be erased or overwritten by the user.
Softwares : Softwares are mainly of two types- Operating System (OS) is the most essential software of a computer, It is the interface between user and the computer's hardware and the other programs, Without an OS, we cannot use a computer, Application softwares :
How does a computer Work? : A computer works in a IPO (Input-Process—Output) cycle to complete a task.
Word processor : A word processor is a software which operates or processes words typed on a computer. Example : Microsoft Word
Spreadsheet : A spreadsheet is a table of rows and columns of related numerical or financial data. Example : Microsoft Excel
Precautions to be take while entering data :
|
Presentation : A presentation is an effective manner of putting across one’s thoughts and ideas to an audience so that they are easily understood. A slideshow is a visual aid that accompanies an oral presentation. Example : Microsoft Power Point Two other important general purpose application softwares are a web browser and a PDF file viewer.
Web browser : A web browser, like Internet Explorer, Google chrome, Firefox, is used to access websites on the Internet. It also uses one or more Search Engines that search for some particular document or website when specific keywords are entered.
PDF : A PDF (Portable Document Format) file is one that can be viewed or printed without requiring the application software that was used to create it. Adobe Reader, WPS office, is a popular PDF file viewer.
Some uses of ICT in science :
Job opportunities in the field of computers :
C-DAC : The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), Pune, is the leading institute in India which conducts research in the field of computers.
- The first Indian supercomputer, Param, was developed by a team led by senior scientist Dr. Vijay Bhatkar.
- C-DAC also participated in developing the ISCII (Indian Script Code for Information Interchange) code for writing in different Indian scripts on computer.
Fields of application of computers : Computers are now widely used in all fields of human activity : education and research, entertainment, tourism and transport, offices and banks, industries, medical and social services, law and order, meteorology (weather forecasting), agriculture, sports and defense.
Various devices used in communication of information : The various devices are computer and networking hardware, radio, television, fixed telephone, mobile phones video display unit, printer, plotter, modem, router, Internet and satellites.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 9: Environmental Management - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 11: Reflection of Light - online Notes |