Substances in Common Use
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-14
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Salts : The ionic compounds which do not contain H+ and OH¯ ions and contain only one kind of cation and anion are called simple salts.
Examples : Na2SO4, K3PO4, CaCl2
The important salts found in sea water:
Sodium chloride (NaCl), magnesium chloride (MgCl2), magnesium sulphate (MgSO4),
potassium chloride (KCl), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), magnesium bromide (MgBr2).
(1) Sodium chloride (Table salt-NaCl) : This is the most commonly used salt in our day-t0- day life. Its chemical name is sodium chloride. Sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride is formed. This is neutralization reaction.
NaOH + HCl —> NaCl + H2O (Sodium Chloride +Water)
Electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride : When an electric current is passed through a saturated solution of sodium chloride, commonly known as brine (25% NaCl), it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. Chlorine gas (Cl2) is liberated at the anode and hydrogen gas (H2) is liberated at the cathode.
Electrolysis of fused sodium chloride: When sodium chloride is heated to high temperature, it melts. The molten state of sodium chloride is termed as fused state. NaCl in fused state conducts electricity.
During electrolysis of fused sodium chloride, Cl2(g) is liberated at the anode and liquid sodium is deposited at the cathode.
2NaCl(S) \(\frac{Electrolysis}{\text {Fused state}}>\) 2Na + Cl2(g)
Properties of sodium chloride :
- Pure sodium chloride is a colourless and crystalline ionic compound.
- It is soluble in water.
- It is a neutral salt and gives a salty taste.
- The pH value of its aqueous solution is 7.
- Impure sodium chloride is brown in colour and is known as rock salt.
Uses of sodium chloride :
- It is an essential constituent of our daily life and is used in all food items.
- It is used in the preparation of baking soda (NaHCO3) and washing soda (Na2CO3).
Sodium bicarbonate (Baking soda —NaHCO3) Chemical name : Sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Properties of baking soda :
- Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) is a white, amorphous powder.
- It turns red litmus blue, indicating it is alkaline in nature.
Uses of baking soda :
- Baking soda is used in the preparation of light and spongy bread, cakes and dhokla.
- It is used as an ingredient in antacid, which helps to reduce acidity in the stomach.
- It is useful in preparing CO2 gas and is one of the constituents of a fire extinguisher.
- It is used to clean an oven.
Bleaching powder : CaOCl2
Preparation : Bleaching powder is prepared by passing chlorine gas over solid slaked lime.
Ca(OH)2(S) + Cl2(g) —> CaOCl2(s) + H2O
Properties of bleaching powder :
- Bleaching powder is a yellowish white powder
- It has a strong odour of chlorine gas.
- Its chemical name is calcium oxychloride.
- It is an oxidising agent in many chemical reactions.
Uses of bleaching powder :
- It is used for disinfection of drinking water and water in the swimming pool.
- It is used for bleaching clothes.
- The road side and garbage sites are disinfected by using bleaching powder.
- Bleaching powder reacts with dil. sulphuric acid to release chlorine gas. CaOCl2 + H2SO4 —-> CaCO3 + Cl2
- Bleaching powder undergoes slow decomposition due to the CO2 in air and chlorine gas is released. CaOCl2 + CO2 —> CaCO3 + Cl2
Sodium carbonate (washing soda) : Na2CO3.10H2O
Properties of sodium carbonate:
- Sodium carbonate is a White crystalline substance.
- It is soluble in Water.
- It is hygroscopic i.e. it absorbs moisture if left exposed to air.
- It turns red litmus blue, indicating its basic nature.
Uses of sodium carbonate (washing soda) :
- Sodium carbonate (washing soda) is used as a cleansing agent in Washing clothes.
- It is used in the manufacture of detergent powder, paper and glass.
- It is also used to refine petroleum.
Water of crystallization : Water of crystallization is a fixed number of water molecules present in the crystal structure.
Substances in our daily use which contain water of crystallization :
- Alum (Potash alum—K2SO4.Al2(SO4)3.24H2O
- Borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O)
- Epsom salt (Magnesium sulphate MgSO4.7H2O)
- Barium chloride (BaCl2.2H2O)
- Sodium sulphate (Glauber’s salt Na2SO4.10H2O)
Uses : -
Alum :
- Alum and burnt alum is used in medicines.
- In the paper industry, alum is used to give shine to the paper.
- Alum is used to stop bleeding from Wound.
- Alum is used in the process of purification of water.
Borax :
- Borax is used in the cosmetic industry to make lotions, shampoos and cold creams.
- It is used to remove the stain on clothes in a laundry;
- In the laboratory with the help of borax bead test, basic elements from the coloured salts are determined.
Epson Salt :
- Epsom salt is used in the manufacture of fertilizers and also to enhance the green colour of plants and vegetables.
- It is used in the manufacture of purgative medicines.
- It is used as body scrub.
- It is added in bath water (salt bath) to relieve muscle pain.
Barium chloride :
- It is used in the purification of brine solution. (saturated sodium chloride solution).
- It is used in the waste water management.
- It is used in the paper industry and also used in the dye industry, ceramics, oil purification and pesticides.
Sodium sulphate :
- It is used in the preparation of detergents.
- It is used to make paper pulp in paper industry and also used in the dye in the dye industry.
- It is used to make mild purgatives.
Blue vitriol :
- It is used in the blood test to diagnose anaemia.
- Blue vitriol and slaked lime is used in the Bordeaux mixture, which is used as a fungicide on fruits.
Soap : When oils or fats are boiled with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, sodium salt or potassium salt of carboxylic acid is obtained. These salts are known as soap.
Detergent : A substance either in powder or liquid form used to remove dirt from clothes is called a detergent. Detergent is a long chain of sodium salt of alkyl benzene sulphonic acid or sodium salt of alkyl hydrogen sulphate.
Radioactive substances :
Rutherford’s experiment on radio-activity : A radioactive substance is kept in the narrow cavity drilled in a thick lead block. [See Fig.] The lead block absorbs all the radiations emitted by the substance, except those emerging through the cavity. The radiations emerging from the cavity of the lead block pass through a strong electric field applied between the two metal plates and then fall on the photographic plate. The entire apparatus is enclosed in an evacuated chamber kept in a dark room.
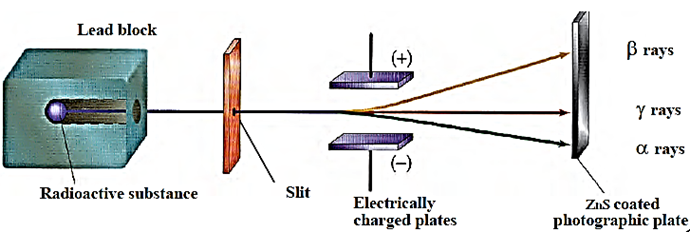
When the photographic plate is developed after exposing it to the radiation for some time, three distinct spots are observed on the plate. This shows that the radiations are split up into three parts in the presence of an electric field. The radiation deflected towards the negative plate is called alpha rays. The radiation deflected towards the positive plate is called beta rays. The rays which is not deflected by the electric field are called gamma rays.
Radioactive element: Elements with a high atomic number have a property of spontaneously emitting invisible, highly penetrating and high energy radiation. This property is called radioactivity. A substance having this property is called radioactive substance. The nucleus of radioactive element is unstable. Three types of radiation are given out by radioactive substances. These are alpha, beta and gamma rays.
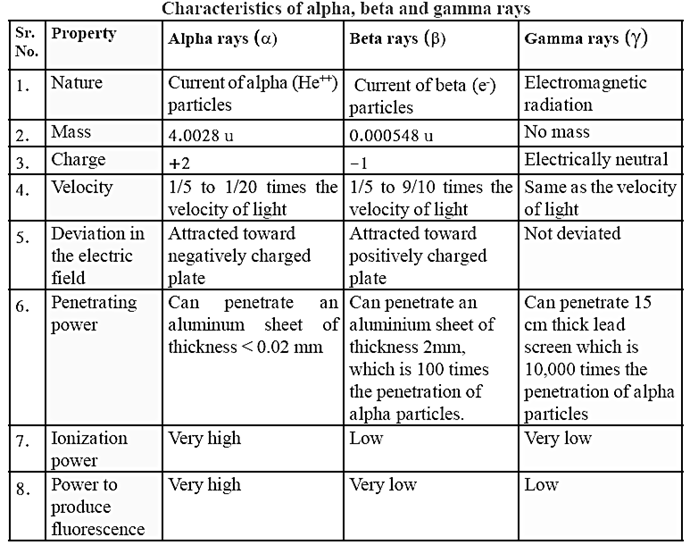
- Natural radioactivity : The elements with atomic numbers from 82 to 92 are found to radiate spontaneously in nature. These are called natural radioactive elements.
- Artificial radioactive elements : The radioactive elements produced in the nuclear fission processes brought about in the laboratory by bombardment of particles are called artificial radioactive elements.
Uses of radioactive isotopes : Radioactive isotopes are used in various fields such as industry, agriculture and medicine.
Industrial field :
- Isotopes like cobalt-60, irridium-192 are used in the radiography camera used for detecting flaws in the metal work.
- The radioactive substances radium, promethium, tritium with some phosphorus are used to make the hands of a clock visible at night, Krypton-85 is used in lamps while promethium-147 is used in portable X-ray units as the source of beta rays.
Field of agriculture :
- By means of radiation, the genes and chromosomes that give seeds properties like fast growth, higher productivity, etc. can be modified.
- Cobalt- 60, the radioactive isotope is used for food preservation.
- To prevent sprouting in onions and potatoes, they are irradiated with gamma rays from cobalt-60.
- In the research on various crops, strontium-90 is used as a tracer.
Medical science :
- Phosphorus-32 is used in the treatment of polycythemia (the disease which increases the red blood cell count).
- Strontium-89, strontium-90, samarium-153 and radium-223 are used in the treatment of bone cancer.
- Iodine-123 is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism occurs due to overproduction of hormones by the thyroid gland. The symptoms are enlargement of thyroid gland, weight loss inspite of appetite, insomnia.
- Boron-10, iodine-131, cobalt- 60 are used in the treatment of brain tumour, while arsenic-74 is used in detection of small tumours in the body.
Hazards of radioactive substances and radiation :
- Radioactive radiations affect the central nervous system.
- Bombardment of radiation on D.N.A. in the body causes hereditary defects.
- Diseases like skin cancer, leukemia are caused when radioactive radiation penetrates the skin.
- It is difficult to control the pollutants, created due to explosion, entering the body through air.
- The radioactive pollutants released in the sea enter the body of fishes and through them enter the human body.
- The radioactive paint on the watch causes cancer.
- The radioactive isotopes strontium-90 gain entry into the body through plants, fruits, flowers, cereals, milk, etc., to cause diseases like bone cancer, leukemia.
Some chemical substances in day-to-day life.
- Food colours and essence : Most of the soft drinks and food stuff available in the market contain food colours. These food colours are in the form of powders, gels and pastes in
- Ice cream, ice candies, sauce, fruit juices, cold drinks, pickles, jams and jelly.
- Food colours are natural as Well as artificial. The natural food colours are prepared from seeds, beetroot, flowers and fruits concentrate. Tetrazene, sunset yellow are artificial food colours used extensively.
- Due to excessive consumption of foods with added food colours causes diseases like ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder).
- It is always beneficial to use natural food colours as artificial food colours are detrimental to health.
Dye : The coloured substance which on applying to an article, imparts that colour to the article, is called a dye. A dye is soluble in water and insoluble in oil. To prepare a natural dye, plants are the main source of colour.
Artificial dyes are prepared from petroleum products and minerals.
Uses of dyes : Adverse effects of dyes :
Artificial colours : Artificial colours are used during Rang Panchami and for decorating the house by painting. The red colour used during Rang Panchami contains a high proportion of mercury which is very dangerous.
It can cause blindness, skin cancer, asthma, itching of the skin, permanent blocking of sweat pores, etc. It is, therefore, necessary that artificial colours are used cautiously.
Deodorant : The bacterial decomposition of sweat causes body odour. A deodorant is used to prevent this odour. Deodorants contain parabens (methyl, ethyl, benzyl and butyl alcohol) in large proportions. Aluminium compounds and silica are also used to prepare deodorants. There are various types of deo such as ordinary deo, antiperspirant deo and clinical deo.
Harmful effects :
Teflon : Teflon is the polymer of tetrafluoroethylene. Its chemical name is polytetra fluoroethene (C2F4)n.
Properties :
Uses ;
Powder coating : A method of applying a layer harder than paint on the surface of an iron object to prevent rusting is called powder coating.
- In this method, a polymer resin, a pigment and some other ingredients are melt, mixed, cooled and ground into a homogeneous powder.
- This powder is sprayed on the polished metal surface by electrostatic spray deposition (ESD).
- Now, the particles are given an electrostatic charge due to which a uniform layer of powder sticks to the metal surface.
- Then the object is heated in the oven along with the coating. A chemical reaction takes place in the layer, resulting in the formation of long cross-linked polymeric chains.
- This powder coating is highly durable, hard and attractive.
In our day-to-day life, powder coating can be done on plastic and medium density fibre (MDF) board.
Anodizing : The surface of aluminium metal reacts with oxygen in air and forms protective layer naturally. This layer can be made of the desired thickness during the anodizing process.
- Anodizing is done by electrolysis. In the electrolytic cell, dilute acid is taken and the aluminium article is dipped in it as anode.
- When an electric current is passed hydrogen gas in liberated at the cathode and oxygen gas is liberated at the anode.
- A reaction with oxygen takes place and a layer of hydrated aluminium oxide is formed on the anode.
- This layer can be made attractive by adding colour in the cell during electrolysis.
Ceramic : A heat resistant substance formed by kneading an inorganic substance in water and then shaping it and hardening it by heating is called ceramic. Some common examples of ceramic articles are pots made by a potter, Mangalore roofing tiles, construction bricks, pottery, teracotta articles, etc.
Porcelain : A hard, translucent and white coloured ceramic is called porcelain. It is made by using the white clay called kaolin, found in China.
- In this method, glass, granite and the mineral feldspar is mixed with kaolin and kneaded with water.
- The resulting mixture is shaped and fired in a kiln at a temperature of 1200 °C to 1450 °C. On firing again after glazing, beautiful articles of porcelain are obtained.
Bone china : In the mixture of china clay (kaolin), feldspar and fine silica, some ash of animal bones are added while making bone china. This-ceramic is harder than porcelain.
Advanced ceramics : Instead of clay, oxides like alumina (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), silica (SiO2) and some other compounds like silicon carbide (SiC), boron carbide (B4C) are used for making advanced ceramic. Advanced ceramic requires a temperature of 1600 °C to 1800 °C and an oxygen free atmosphere for firing. This process is called sintering.
| All the medicines are made of organic compounds. These compounds are researched and studied on animals and human groups, they are then directed to Health Department of Government. After the approval of Health Department these medicines are sent for FDA (Food & Drug Administration) approval. Only after the approval of FDA, it is available at the chemist shop. We get these medicines from the chemist on Doctor’s prescription. These medicines are available in the form of capsules, tablets, solution, mixtures, colloid or injections. |
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 13: Carbon : An Important Element - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 15: Life Processes in Living Organisms - online Notes |