Life Processes in Living Organisms
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-15
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Transportation : A substance that is synthesized or absorbed in one part of the body is ‘taken to the other part with the help of transportation process.
Transportation in plants :
- Plants do not move from their places. Thus, they do not require high energy.
- There are many dead cells in the plant body. They need less energy as compared to animals.
- They need inorganic substances such as nitrogen, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese, sodium, etc.
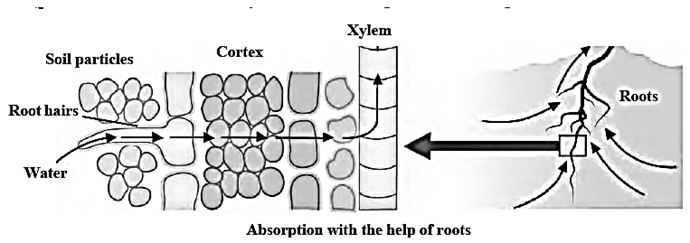
- Absorption of these substances from the soil is done by the roots.
- Then they are transported to other parts.
- Specific conductive tissues of xylem and phloem carry out this transportation.
- The xylem is for conduction of water and the phloem is for conduction of food.
Transportation of water in plants : Root Pressure : A small plant like Balsam or Tuberose if kept in coloured water and observed after 2 — 3 hours, it shows that colour water rises due to root pressure. Pressure exerted by the roots is called root pressure. Due to root pressure the minerals and water can rise up to the different parts of the plants through xylem and phloem respectively. Transpiration Pull :

Transportation of food and other substances in plants (Translocation) :
Excretion : Removal of waste or harmful substances from the body is called excretion.
- In living organisms many harmful and waste substances are produced during the different metabolic processes. E.g. Urea, uric acid, ammonia, etc.
- Nitrogenous waste substances are very harmful or even lethal if they are accumulated in the body. Hence, they are removed from the body by excretory system.
- There are different methods of excretion.
- In unicellular organisms, waste materials are directly eliminated across the cell surface by diffusion.
- The process of excretion in multicellular organisms is complex.
Excretion in plants :
Excretion in human beings : In our body due to the processes of metabolism, toxic substances such as ammonia, urea, uric acid, creatinine, etc. are formed.
- Carbon dioxide is given out through the nose.
- The excess of vitamins and minerals which find way into our diet are also thrown out through urine.
Process of excretion in humans :
- The blood is filtered through the pair of kidneys.
- The carbon dioxide escapes out from the lungs.
- The sweat glands present in the layers of skin also excrete some amount of excretory substances.
- The undigested and unwanted faecal matter is thrown out through anus in the process of egestion.
- In this way the excretory substances are thrown out of the body.
- The excretion in true sense happens only with the help of kidneys where the blood is filtered and the toxic unwanted materials form the urine.
Excretory system : Excretory system is the system that removes the toxic wastes from the body. Following organs form the human excretory system : Kidneys : The two bean-shaped kidneys are situated one on either side of the vertebral column, on the posterior side of abdomen. The right kidney is in a slightly lower position than the left. Bowman’s capsule : In kidneys there are nephrons that have a cup-like, thin-walled upper part called the Bowman’s capsule. Glomerulus : Network of blood capillaries.
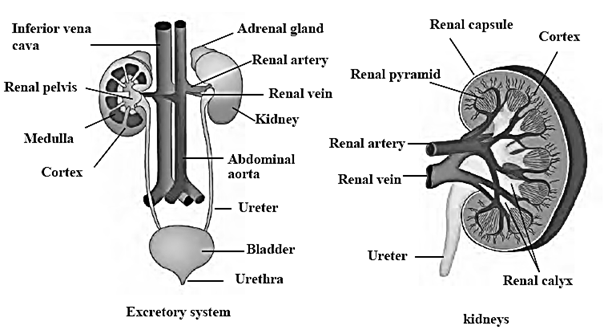
Formation of urine :

Dialysis : When functioning of the kidneys is affected, the toxic nitrogenous waste products accumulate in the body which may even cause death.
Coordination :
- Control : Systematic regulation of different processes of the body is called control.
- Coordination: Bringing about the different processes in the proper sequence can be called coordination.
- There is proper coordination between various systems of the body. At different steps too there is no randomness of any kind.
- Homeostasis : Proper coordination between various systems of an organism keeps the state of equilibrium which is called homeostasis.
- For successful completion of any body activity, proper coordination between different systems and organs participating at different steps of that activity is necessary. If due to some causes, when the coordination is lost then there is confusion at different steps. This results in loss of that activity.
- g. Proper coordination exists between internal activities of the body and body temperature, Water-level, enzyme-level, etc. or stimuli arising in the surrounding environment.
- In plants, there is no nervous system but the responses given to the stimuli shows coordination.
Coordination in Plants :
Tropism or Tropic movements : Movement or growth of any part of the plant in response to an external stimulus is called ‘tropism’ or ‘tropic movement’. These are of following types :
- Phototropic movements or phototropism : Movements in the direction of light.
- Gravitropic movements or gravitropism : Movements in the direction of gravity.
- Hydrotropic movements or hydrotropism: Movements in the direction of water.
- Chemotropic movements or chemotropism : Movements in the direction of chemical stimuli.
Growth relevant movements : All the above movements of plants are related with growth so they are called growth relevant movements.
Growth irrelevant movements : The movements of the plants that do not result into growth are growth irrelevant movements.
Examples :
- In the plant called Venus fly trap, there is a trap that appears and smells like flowers and deceives insects. When an insect visits that flower-like trap, the trap closes up and the trapped insect is digested by the plant. These movements are for feeding and are not causing growth. Thus they are growth irrelevant movements.
- In another insectivorous plant, Drosera, the fibrils present on the leaves bend inwards as soon as an insect lands on the leaves. The prey insect is surrounded from all sides and thus is captured.
- The flowers bloom at a particular time of the day. E.g. The lotus flower opens during day-time while that of the tuberose (Polyanthus) opens at night.
- Dehiscence of the ripe fruits to disperse seeds at a right time is also a growth-irrelevant movement. E.g. as in Balsam.
The technique of plant movements : ‘Different hormones are responsible for the movements in the plants. These movements are in response to the environmental stimuli. Plant hormones & Function : Examples of plant movements :
Coordination in Human Beings : The different processes in the body always occur in the proper sequence which is called a coordination. In multicellular organisms several different organ systems function simultaneously.
Life can function smoothly if there is coordination between all of these different organ systems or organs and the stimuli in the surrounding. The systematic regulation of different processes is in control. E.g. Beating of heart and respiration is always coordinated with each other.
Nervous Control and Chemical Control :
The two mechanisms in the human body bring about control and coordination. These are : Nervous Control and Chemical Control
Nervous Control :
Impulse : In accordance with the changes in the surroundings, the impulses are generated in the body.
Response : Responses are given to the respective stimulus by the nervous system.
- The complex and evolved animals have highly developed nervous system. Unicellular animals like the amoeba do not have a nervous system which produces such impulses and response.
Neuron : Structure of a neuron :
| Sensory organs of organisms : Nose, eyes, ears, tongue and skin are the sense organs of human beings. The invertebrates have different types of sense organs as per their body forms. Higher and evolved organisms however possess similar sense organs.
Nerves in sense organs :
|
Types of Nerve cells/ Neurons : According to their function, nerve cells are classified into three types.
- Sensory neurons : Conduct impulses from sensory organs to the brain and the spinal cord.
- Motor neurons : Conduct impulses from the brain or spinal cord to effector organs like muscles or glands.
- Association neurons : Perform the function of integration in the nervous system.
The Human Nervous System :
The human nervous system has following three parts :
- Central Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System
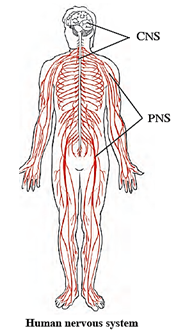
Central Nervous System or CNS : Central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord.
Brain : Brain is the main controlling part of the nervous system. Its weight is about 1300 – 1400 grams in adult human being. It consists of approximately 100 billion neurons.
- It is highly protected in the cranial cavity.
- Spinal cord is protected in the vertebral column.
- Meninges : Protective layers in the space between the central nervous system and the bony covering.
- Ventricles : Cavities present in various parts of the brain.
- Central canal : Long tubular cavity of the spinal cord.
- Cerebro-Spinal fluid : Fluid present in the ventricles, central canal and the spaces between the meninges. Function : Supplies nutrients to the central nervous system and protects it from shock.
- The right side of our body is controlled by the left side of our brain. The left side of our body is controlled by the right side of our brain. On the left side of the brain there are faculties of analytical thinking, logical thinking, language, science and mathematics. On the right side of the brain, there are located : Holistic thinking, intuition, creativity, art and music.
Structure of brain : Three main parts : Cerebrum : The largest part of the brain that occupies two-thirds of the brain. Functions of cerebrum : Controlling all the voluntary movements. Mental faculties such as concentration, planning, decision making, intelligence and intellectual activities. Cerebellum : Smaller part of the brain. Medulla oblongata : Functions of medulla oblongata : It controls all the vital and involuntary activities like beating of the heart, blood circulation, breathing, sneezing, coughing, salivation, etc.
Spinal Cord :
- Located firmly inside the vertebral column.
- Slightly thick but gradually tapers towards the end.
- Filum terminale is the thread-like fibrous structure at the end of spinal cord.
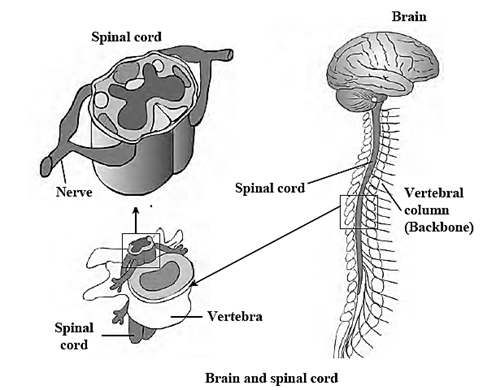
Brain: different regions and functions: Cerebrum : Cerebellum : Medulla oblongata : Spinal cord :
Peripheral Nervous System : Consists of the nerves originating from the central nervous system and connecting with all the body parts. They are of following two types :
- Cranial nerves : There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves. They originate from the brain and are associated with various parts in the head, thorax and abdomen.
- Spinal nerves : There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves which originate from the spinal cord. These are associated with arms, legs, skin and some other parts of the body.
Autonomic Nervous System : The working of this nervous system is not under the control of our will. E.g. the nerves of involuntary organs like the heart, lungs, stomach, etc.
Reflex action : Reflex action is an immediate and involuntary response given to a stimulus from the environment. We do not have any control over reflex actions.
Most of the reflex actions are without intervention of the brain.
Example : Sometimes, we choke while eating in a hurry. Choking at the time of eating in a hurry is a reflex action.
Chemical Control :
- Chemical control is done by hormones and neurotransmitters.
- Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands
- Endocrine glands are ductless glands whose secretion mixes in the blood circulation directly. Through the blood circulation they reach the entire body.
- Nerve impulses are fast but short lived whereas the action of hormones is very slow but long lasting.
- There is a special mechanism which controls the quantity and timing of hormone secretion.
Endocrine glands: Location, Hormones and important functions : Secretion of some hormones. 2-Adrenocorticotropic hormone 3-Thyroid stimulating hormone 4-Prolactin 5-Follicle stimulating hormone 6-Luteinizing hormone 7-Oxytocin 8-Antidiuretic hormone 2- Stimulates adrenal gland 3- Stimulates thyroid gland 4- Stimulates milk production 5- Controls growth of gonads 6- Controls menstrual cycle and ovulation 7- Contracts uterus during parturition. 8- Regulates water-level in the body 2-Calcitonin 2-Controls calcium metabolism and calcium level in blood Four types of cells 1-Alpha-cells (20%) 2-Beta-cells (70%) 3-Delta-cells (5%) 4-P.P. cells or F-cells (5%) 2-Insulin 3-Somatostatin 4-Pancreatic Polypeptide glucose 2- Stimulates liver to convert excess blood glucose into glycogen 3- Controls levels of insulin and glucagon 4- Controls movements of intestine and thereby glucose absorption - Controls secretion of pancreatic juice 2-Corticosteroid emotional situations - Stimulates heart and its conducting tissue and metabolic processes. 2-Maintains balance of Na+ and K+ and stimulates metabolism uterus in women 2-Progesterone -Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics in women 2-Prepares the endometrium for conception and maintains the pregnancy.
Glands & Location
Hormones
Functions
Hypothalamus - Above the pituitary gland, in the forebrain
Secretes the controlling hormones which regulate the activity of the secretory cells of the pituitary gland.
Controls the pituitary gland.
Pituitary - At the base of brain
1-Growth Hormone
1-Stimulates growth of bones
Thyroid - Anterolateral sides of trachaea in neck region
1-Thyroxine
1-Controls growth of body and metabolic activities.
Parathyroid - Four glands behind thyroid gland
Parathormone
Controls metabolism of calcium and phosphorus
Pancreas- Behind the stomach.
1-Glucagon
1- Stimulates liver to convert glycogen into
Adrenal Gland - Anterior end of each kidney
1-Adrenaline and Nor-adrenaline
1-Controls behaviour during crisis and
Ovary- On either side of
1-Oestrogen
1-Stimulates growth of endometrium
Testis- In scrotum
Testosterone
Stimulates growth of secondary sexual characteristics like beard, mustache, hoarse voice, etc. in men
Thymus- In thoracic cage, near the heart
Thymosin
Controls the cells which give rise to immunity
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 14: Substances in Common Use - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 16: Heredity and Variation - online Notes |

Such a helpful website
Thank you so much.
But
Some point are lengthy but it maybe for understanding quickly in simple words or may be it’s imp points.
Good website for studying. Nice notes but too long.And so many ads that are annoying. I think you need to do it better.
Very nice notes I have this notes and I think that some point are very lengthly but it may be quickly understanding thank you so much
This website is very good and it has made it easier to understand the lesson. Thank you very much.
😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊😊
I would like to take a moment to express my heartfelt gratitude to [website name] for being an invaluable resource in my academic journey. The comprehensive and well-organized content, coupled with clear explanations, has been instrumental in deepening my understanding of complex topics. From detailed notes to practice questions, every aspect of the platform has enhanced my learning experience. Your dedication to providing quality educational materials has truly made a difference, and I am incredibly grateful for the support and guidance I received. Thank you for empowering students like me to achieve our academic goals!
😌😌😌😌☺️☺️☺️☺️☺️😊😊😊☺️☺️🙂↕️🙂↕️😀😀😀😀😀😀😃😃😃😃😄😄😄😄😄😄
Very helpful website it is!
👌👌