Observing Space : Telescopes
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-18
Notes
|
Topics to be learn :
|
Sky : A visible portion of the atmosphere and outer space seen by simple eyes, without any equipment from the earth is known as the sky.
Space : An infinite, boundless, limitless three dimensional expanse in which the solar system, stars, celestial bodies, galaxies and endless Universe exist is known as space.
- Both sky and space lack a definite boundary.
- However, the sky is a very tiny part of space.
Space observation : ‘A study of planets, stars, celestial bodies and galaxies with the help of satellites and telescope; situated either on the earth or in the space and attempting to understand the extent of universe, its structure, etc. is known as space observation.
Importance of space observation :
Need of sky observation and equipment :
Different forms of light : Light is an electromagnetic wave.
- The light which our eyes can see and known as visible radiation, is a very tiny part of electromagnetic spectrum.
- Light has electromagnetic waves and wavelength is a characteristic of light.
- Visible light/ radiation has a wavelength of 400 nm to 800 nm.
- However, there is a light having different electromagnetic wavelength and we cannot see such lights as our eyes are not sensitive to these types of lights.
Wavelength of light rays (radiation) :
Information about light rays with different wavelength and its characteristic is given in the table below :
Type of radiation
Wavelength
Characteristics
Radio waves
Longer than about 20 cm
Wavelength is longer than the wavelength of visible light.
Micro waves
0.3 mm – 20 cm
Wavelength is longer than the wavelength of visible light.
Infrared waves
800 nm – 0.3 mm
Our eyes cannot see these types of light rays.
Visible light rays
400 nm – 800 nm
Light visible to our eyes
Ultraviolet rays
300 pm – 400 nm
Wavelength is shorter than wavelength of visible light.
X-rays
3 pm – 300 pm
Wavelength is shorter than wavelength of visible light.
Gamma rays
Shorter than 3pm
Even this light is not visible to human eyes
Need and structure of telescope : The structure of the telescope is shown in the diagram below : Types of telescopes : Types and sub-types of telescope are as follows : (i) Optical telescope : (ii) Radio telescope Both types of telescopes are installed on the earth as well as in space.

Types of optical telescopes :
Most of the optical telescope are made with lenses. But some optical telescopes are made using concave mirrors. Two main subtypes of optical telescope are as follows :
Refracting telescopes :
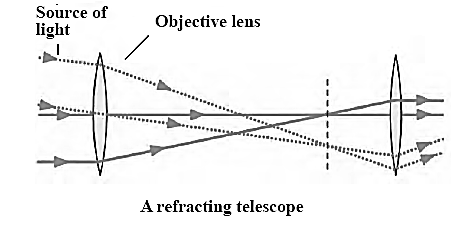
Limitations of Refracting telescopes : To overcome these difficulties, telescopes are made using concave mirrors. As light rays get reflected by mirrors in these telescopes, they are called reflecting telescopes.
Reflecting telescope :
- Reflecting telescopes are designed as such to overcome the limitation of refracting telescope.
- Light rays get reflected by concave mirrors in these telescopes. Hence, these are called reflecting telescopes.
- It is easier to make large mirrors in compare to making large lenses. Big mirrors can also be made by combining several smaller pieces of mirrors and thus, the weight of such concave large mirror is too less than that of lens of the same size.
- Images formed by mirrors do not have errors of colours.
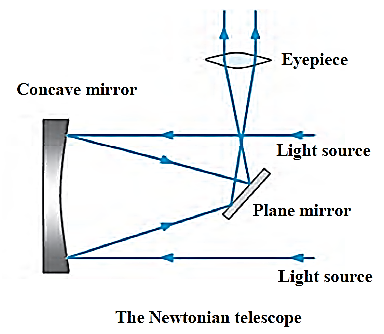
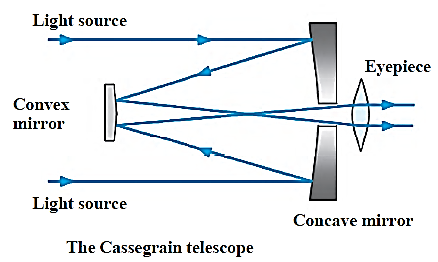
Two sub-types of reflecting telescope are as follows: (1) The Newtonian telescope : In this, one concave and one plane mirror is used. Concave mirror is used to receive the light coming in from the source and reflect it to the plane mirror. Plain mirror then deflect these rays for focusing to pass through eyepiece. (2) The Cassegrain telescope : In this telescope, one concave and one convex mirror are used.
| Optical telescopes having a mirror of 3.6 m diameter situated in Aryabhatta Research Institute, Nainital is the largest optical telescope in India and Asia. |
Radio telescope : Many heavenly objects emit radio waves in addition to visible radiation. We cannot see this radiation with our eyes. Hence, a special type of telescope is used to receive these rays. It is called a radio telescope.
- Many heavenly bodies like stars, planets, Galaxies, emit radiation other than visible light like X-rays, gamma rays, infrared rays, etc. Radio Telescopes are capable to receive and produce images from such rays.
- Radio telescopes are made from one or more dishes of a particular parabolic shape.
- As in optical telescope, the incident radio waves are reflected from the concave part of the parabolic dish and converge at the focus.
- A radio receiver placed at the focal point gathers such waves and later image is constructed with the help of computers.
- Giant Meterwave Radio Telescope (GMRT) is erected at Narayangaon near Pune. This telescope studies the light rays having the wavelength of about a meter coming from heavenly bodies. This large radio telescope is actually an interconnected 30 parabolic dishes. Each dish is 45 m in diameter. These 30 dishes are spread in 25 square kilometer area in such a way that it works as a single dish as if having a diameter of 25 sq. km.
- GMRT has enabled scientists to study Solar System, Solar winds, Pulsar, Supernova and interstellar hydrogen clouds.
Salient features of radio telescopes :
Limitation of telescopes erected on the earth :
Telescope in space :
- To get rid of problems in situating telescope on the earth, scientists have successfully placed the telescope in the space. Images obtained by the telescope placed in the space are bright and clear.
- In 1990 National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) of USA launched an optical telescope ‘Hubble’ in space. The lens of this telescope is 94 inches in diameter and orbiting the earth at a height of 589 km above in space.
- In 1999 NASA launched the X-ray telescope ‘Chandra’ in Space. This telescope has an ability to grasp (receive) X-rays from heavenly objects. Chandra telescope has given us useful information about stars and galaxies. The telescope is named after the famous Indian scientist Subramanian Chandrashekhar.
Contribution of Indian Space Research Organisation : This institute was established in 1969 with the aim of developing technology for making and launching of artificial satellites.
Astrosat : In 2015, ISRO launch an artificial satellite Astrosat. This satellite has ultraviolet and X-ray telescopes and detectors. Most of the parts used in the satellites are made in India. With the help of Astrosat, Indian scientists are studying various aspects of the universe.
Active telescopes in space : List of some of the important active telescopes in space are as follows : All the scores are active even today. Examples of each type of the telescope is given above. There are hundreds of such telescopes functioning in space today.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 17:Introduction to Biotechnology - online Notes |

Your notes is a very smart notes
This notes lern isiliye