Observing Space : Telescopes
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-18
Solution
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks with the proper words.
a. The wavelength of visible light is between …….. and ………
b. GMRT is used for ……. waves.
c. A certain X-ray telescope is named after scientist ………..
d. The first scientist to use a telescope for space observation was. ................... .
e. The biggest optical telescope in India is situated at ……….
a. The wavelength of visible light is between 400 nmand 800 nm. b. GMRT is used for radiowaves. c. A certain X-ray telescope is named after scientist Subramanian Chandrashekhar. d. The first scientist to use a telescope for space observation was Galileo. e. The biggest optical telescope in India is situated at Aryabhatt Research Institute of Experimental Sciences, Nanital.
Question 2.
Form pairs
| ‘A’ Groups | ‘B’ Groups |
| (i) X-rays | (a) GMRT |
| (ii) Optical telescope | (b) ISRO |
| (iii) Indian radio | (c) Hubble telescope |
| (iv) Launching | (d) Chandra artificial satellites |
‘A’ Groups
‘B’ Groups
(i) X-rays
(d) Chandra artificial satellites
(ii) Optical telescope
(c) Hubble telescope
(iii) Indian radio
(a) GMRT
(iv) Launching
(b) ISRO
Question 3.
What are the difficulties in using ground based optical telescopes? How are they overcome?
The difficulties faced in using ground based telescopes due to which it does not make good quality observations are: This issue is overcome either of the following ways :
Question 4.
Which type of telescopes can be made using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens? Draw diagrams of these telescopes.
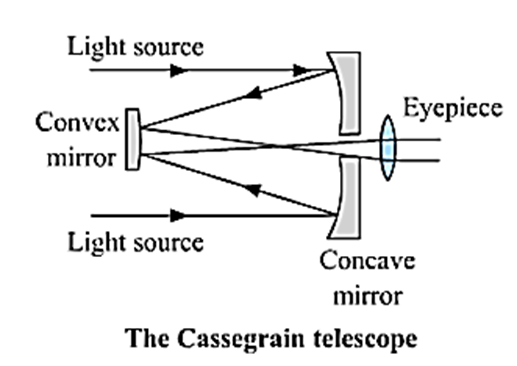
Reflecting types of telescopes can be made using a concave mirror, convex mirror, plane mirror and a lens. Reflecting type of telescopes is mainly of two types: Cassegrain telescope : In this telescope, the light rays after reflection from the concave mirror, are reflected back towards it by a small convex mirror. Then the rays pass through the eyepiece placed at the back of the concave mirror as shown. The eyepiece produces a magnified image of the source.
Newtonian telescope : Light rays coming from a heavenly body (distant object) get reflected by the concave mirror. Before the reflected rays converge at the focus of the concave mirror, it is again reflected by the plane mirror as shown. As a result, the rays pass through the eyepiece and we get a magnified image of the body.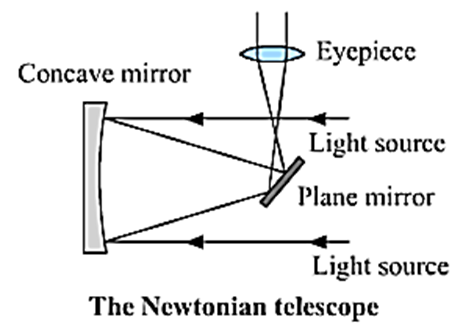
Question 5.
Study the figure and answer the following questions

[/spoiler]
a. What type of telescope is shown in the figure?
Telescope shown in the diagram is Newtonian type of telescope.
b. Label the main parts of the telescope.
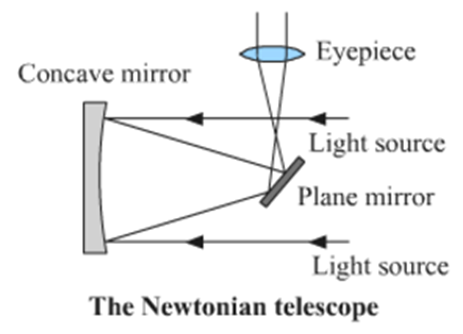
c. Which type of mirror does the telescope use?
Both plane and spherical mirror is used in this telescope. The spherical mirror is a concave mirror.
d. What other type of telescope uses a curved mirror?
Another telescope which uses a concave mirror is Cassegrain type of optical telescope.
e. Explain the working of the above telescope.
The telescope shown above has a concave mirror, a plane mirror and an eyepiece. This is a Newtonian type of telescope.
Question 6.
Answer the following questions.
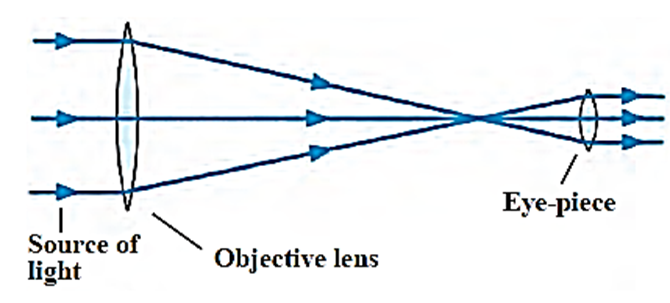
a. Explain the construction of Galileo’s telescope.
In 1906, Galileo constructed a telescope which provides an erect image of an object only with the help of two lenses. The Galileo's telescope consists of two lenses located at the ends of a long tube as shown in the figure below. Both lenses are arranged in a such a way that the distance between them can be adjusted. The objective was a convex lens and eye piece was a concave lens.
b. Explain the construction of a radio telescope.
These telescopes are used to see radio waves coming from space. Many heavenly bodies like stars, planets, galaxies, emit radiations other than visible light like X-rays, gamma rays, infrared rays, etc. Radio Telescopes capable to receive and produce images from such rays. It has one or more dishes of parabolic shape. The rays coming from the distant source are first reflected by these dishes which converges at the focus. A radio receiver is placed at the focal point, which gathers the information. The gathered information is then passed on to a computer which analyses it and construct an image of the source. A giant radio telescope can be formed by linking mini radio telescopes together. Giant Wave Radio Telescope (GMRT) is erected at Narayangaon near Pune. This large radio telescope is actually an interconnected 30 parabolic dishes spread over 25 sq. km area.

c. Why are optical telescopes located in uninhabited places on mountains?
Optical telescopes situated on the surface of Earth, does not produce images of good quality of the following reasons: Thus, optical telescopes are located in uninhabited places and on higher altitudes such as on top of mountains to reduce the above problems in appreciable amount.
d. Why can an X-ray telescope not be based on the earth?
X-ray telescope cannot be based on the Earth because X-rays cannot reach up to surface of the earth due to certain constraints like atmosphere, temperature, air pressure, cloud cover, etc.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 17:Introduction to Biotechnology - online Solution |