Acids, Bases and Salts
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-5
Notes
Topics to be learn :
- Arrhenious theory of acids and bases
- Concentration of an acid or a base
- pH of a solution
- Reactivity of acids and bases
- Salts
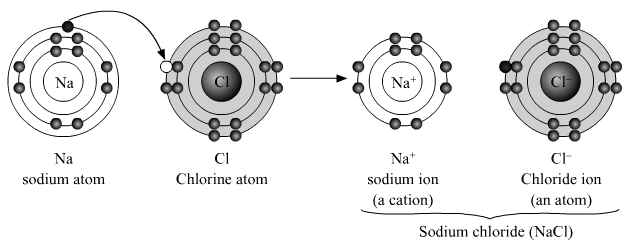
Ionic compounds:
- There are three types of ionic compounds and these are acids, bases and salts.
- The molecule of an ionic compound has two constituents, namely, cation (positive ion/ basic radical) and anion (negative ion/ acidic radical).
- The force of attraction between one positive charge on a cation and one negative charge on an anion is called the ionic bond.
Example : Sodium chloride (NaCl).
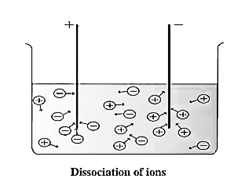
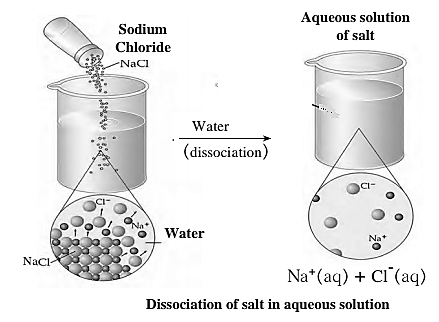
Dissociation of Ionic Compounds: When a solid ionic compound begins to dissolve in water, the water molecules push themselves in between the ions of the compound and separate them from each other. It means, an ionic compound dissociates during the formation of an aqueous solution.
Example : NaCl(s) \(\frac{water}{dissociation}\)> Na+(aq) + Cl¯(aq)
Acid : A substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to H+ ion as the only cation is called an acid.
HCl \(\frac{water}{dissociation}\)> H+(aq) + Cl¯(aq)
HNO3 \(\frac{water}{dissociation}\)> H+(aq) + NO3¯(aq)
Base: A substance which on dissolving in water gives rise to the OH¯ ion as the only anion is called a base.
Example : NaOH, Ca(OH)2
NaOH \(\frac{water}{dissociation}\)> Na+(aq) + OH¯(aq)
Ca(OH)2 \(\frac{water}{dissociation}\)> Ca2+(aq) + 2OH¯(aq)
Classification of acids and bases : Strong and weak acids, bases and alkali.
Strong acid : An acid, on dissolving in water, dissociates completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains H+ ions and the concerned acidic radicals. This is called a strong acid.
Examples : HCl, HNO3, H2S04
Weak acid : An acid, on dissolving in water, does not dissociate completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains H+ ions and the concerned acidic radicals in small proportion along with a large proportion of the undissociated molecules of the acid. This is called a weak acid.
Examples : H2CO3 (carbonic acid), CH3COOH (acetic acid).
Strong Base : A base, on dissolving in water, dissociates completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains OH¯ ions and the concerned basic radicals. This is called a strong base.
Examples : NaOH, KOH
Weak base : A base, on dissolving in water, does not dissociate completely, and the resulting aqueous solution contains OH¯ ions and the concerned basic radicals in small proportion along with a large proportion of the undissociated molecules of the base. This is called a weak base.
Example : NH4OH
Alkali : The bases which are highly soluble in water. are called alkali.
Examples : NaOH, KOH, While NH3 is a weak alkali:
Basicity Of acids : The number of H+ ions obtainable by the dissociation of one molecule of an acid is called its basicity.
Acidity of bases : The number of OH¯ ions obtainable by the dissociation of one molecule of a base is called its acidity.
Concentration of acid and base : The proportion of a solute in a solution is called the concentration of the solute in the solution. When the concentration of a solute in its solution is high, it is a concentrated solution. When the concentration of a solute in its solution is low, it is a dilute solution. To express the concentration of a solution, several units are used. Grams per litre : The mass of solute in grams dissolved in one litre of the solution is called gram per litre (g/ L). Molarity (M) : The number of moles of the solute dissolved in one litre of the solution is called the molarity (M) of the solution.
The pH of solution: pH is a number which indicates the acidic or basic nature of a solution. It helps in measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
pH scale : On the pH scale we can measure pH from 0 (very acidic solution) to 14 (very alkaline solution). pH is a number which indicates the strength of the acidic or basic nature of a solution.
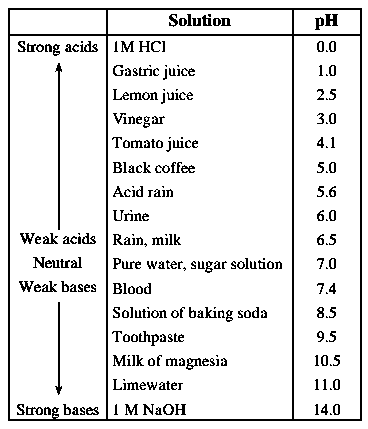
The scale used for measuring hydrogen ion concentration in a solution is termed as pH scale.
- The higher the hydronium ion concentration, the lower is the pH value.
- When pH value is in between 0 to 7, the solution is acidic in nature
- When pH value is in between 7 to 14, the solution is alkaline/ basic in nature. Neutral solution has a pH equal to 7.
Pure water has a pH of 7 it means pure water has [H+] = 1 x 10-7 mol/L.
pH 7 indicates a neutral solution.
At 25°C, the concentration of H+ ions in 1 M solution of HCl is 1 x 10° mol/L.
While in a 1 M NaOH solution, the concentration of H+ ions is 1 x 10-14 mol/L.
Universal indicator : A universal indicator is a mixture of several indicators in specific proportions which gives different colours at different pH values of the pH scale.

Neutralization : An acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water is called the neutralization.
HCL(aq) + NaOH(aq) —> NaCl(aq) + H20
Reaction of acids with metals : When a metal reacts with dilute acid, the reactive metal displaces hydrogen from the acid to release hydrogen gas. At the same time, the metal is converted into basic radical which combines with the acidic radical from the acid to form the salt. Metal + Dilute acid —> Salt + H2 gas MgO(s), + 2HCl(aq) —> MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) —> ZnCl2(aq) + H2(s)
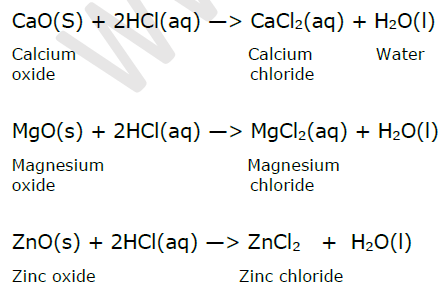
Reaction of acids with oxides of metals : When a metal oxide reacts with an acid it forms corresponding salt and water. Metallic oxides are basic oxides. Metal oxide + Dilute acid —> Salt + Water
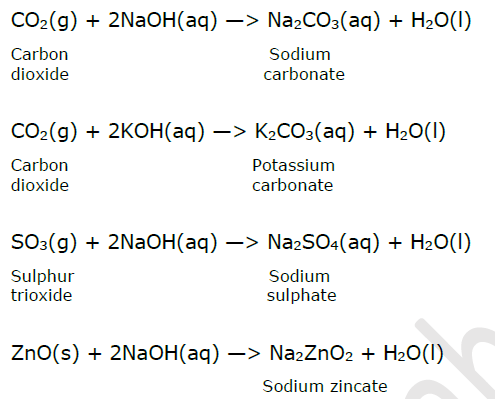
Reactivity of base with non-metallic oxides : When a non-metallic oxide reacts with a base, it forms salt and water. Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. Non-metallic oxide + Base —> Salt + Water
Reaction of acids with carbonates and bicarbonates of metals : When a metal carbonate or metal bicarbonate reacts with an acid, it forms corresponding salt and carbon dioxide gas.

Examples from everyday life :
Salts :
(i) A neutral salt is formed by the neutralization reaction between a strong acid and a strong base. The aqueous solution of a neutral salt has pH equal to 7.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) —> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
. Neutral
(ii) An acidic salt is formed by the neutralization reaction between a strong acid and a weak base. The pH of the aqueous solution of an acidic salt is less than 7.
HNO3(aq) + NH4OH(aq) —> NH4NO3(aq) + H2O(l)
(iii) A basic salt is formed by the neutralization reaction between a weak acid and a strong base. The pH of an aqueous solution of a basic salt is greater than 7.
NaOH(aq) + CH3COOH(aq) -—> CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l)
Water of crystallization : Ionic compounds are crystalline in nature. These crystals are formed as a result of definite arrangement of ions. In the crystals fixed number of water molecules are included in this arrangement. This is the water of crystallization.
On heating or just by keeping, the water of crystallization is lost and the crystalline shape of that part is lost.
Examples : Blue vitriol CuSO4·5H2O (copper sulphate) Crystalline ferrous sulphate FeSO4·7H2O Crystalline washing soda Na2CO3·1OH2O Crystalline alum K2SO4·Al2(SO4)3·24H2O
Ionic compounds and electrical conductivity : NaCl and CuSO4 are salts. H2SO4 is a strong acid and NaOH is a strong base.
These compounds dissociate completely in their aqueous solutions and are electricity conductors.
Electrolytic cell : An assembly that consists of a container electrolyte and electrodes dipped in it, is called on an electrolytic cell.
Electrodes : When there is a liquid or solution in the circuit, two rods, or wires or plates are immersed in it. These are called electrodes.
The electrode connected to the negative terminal of a battery by means of a conducting wire is called a cathode.
The electrode connected to the positive terminal of a battery by means of conducting wire is called an anode.
The different uses of an electrolytes are
(1) electrolysis (2) electroplating.
Electrolysis : It is necessary for the liquid/solution to have a large number of dissociated ions for electrolysis to take place.
Therefore, substances which undergo dissociation to great extent in the liquid state or a solution are called electrolytes.
Salts, strong acids and strong bases are electrolytes.
Electrolytes are good conductors of electricity in their liquid or solution state.
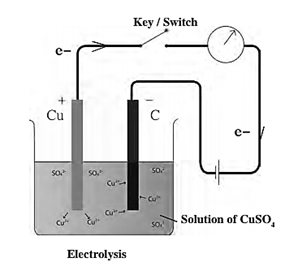
Electrolysis of water : Write the electrode reactions and explain them. When electric current is passed through water containing a few drops of an acid or a few drops of a base, it dissociates to give H+ ions and OH¯ ions. Hydrogen gas is formed near the cathode and oxygen gas near the anode. This is called electrolysis of water. Cathode reaction : 2H2O(l)+ 2e¯ —> H2(g) + 2OH¯ (aq) Anode reaction : 2H2O(l) —> O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e¯
Q. Butter milk spoils if kept in a copper or brass container.
Ans. Brass or copper reacts with organic acid i.e. lactic acid present in butter milk and poisonous salts are formed. Hence, butter milk spoils if kept in a copper or brass container.
Q. Ferrous sulphate crystals turn white on heating.
Distinguish between Acids and Bases : Acids have one or more H+ ions. Substance which donates a proton Acids turn blue litmus red. pH value less than 7.0 Oxides of non-metals form acids. It neutralizes a base to give salt and water. Examples : HCl, H2SO4, H3PO4 Bases have one or more OH" ions. Substance which accepts a proton Bases turn red litmus blue. pH value greater than 7.0 Oxides of metals form bases. It neutralizes an acid to give salt and water Examples : NaOH, Ca(OH)2
Acids
Bases
Acids have sour taste.
Bases have bitter taste.
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 4-Measurements of Matter - online Notes Next Chapter : Chapter 6: Classification of plants -online Notes |
Very nice 👍👍 thank you so much for this 💕🤗 and maths ke lectures ley lo live please once again thanks 🙏
👌🏻