Exogenetic Processes Part-1
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-3
Solution
Question 1.
Answer in brief.
(a) What is mechanical weathering ?
Breaking or weakening of rocks without any change in their chemical composition is called mechanical weathering. Types : Exfoliation, granular weathering and block disintegration are the types of mechanical weathering. Reasons : Mechanical weathering mainly occurs because of the following reasons :
(b) What are the main types of chemical weathering?
Chemical weathering : The process of decomposition of rocks by changes in the chemical composition of it is called chemical weathering. Water is a universal solvent. The solubility increases because the matter has dissolved in water. And those materials which do not dissolve easily in water get dissolved in such solutions. As its effect, chemical weathering occurs. Carbonation, solution and oxidation are the main types of chemical weathering.
(c) How does biological weathering occur?
Biological weathering : Biological weathering occurs due to human beings, animals and plants.
(d) Distinguish between weathering and mass wasting.
Question 2.
Write whether the statements are true or false. Correct the incorrect ones.
(a) Climate affects earthquakes.
False
(b) Mechanical weathering is less effective in humid climates.
True
(c) Mechanical weathering happens on a large scale in dry climates.
True
(d) The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles is called weathering.
Answer :
(e) Lateritic rocks are formed through exfoliation.
False
Question 3.
Complete the flowchart below.
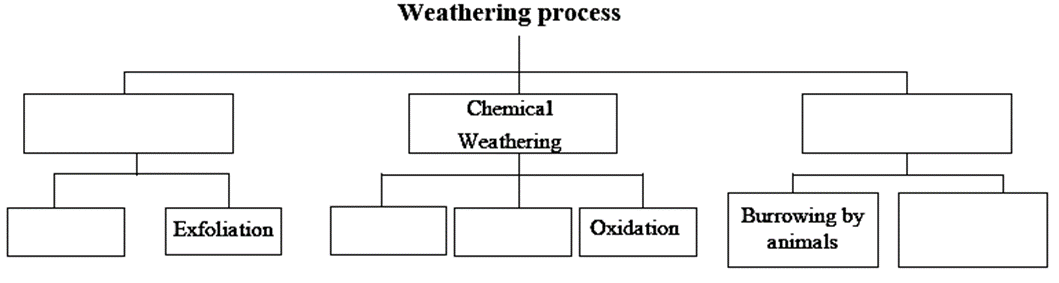
***This type of questions are excluded in the revised pattern
Question 4.
Identify the type of weathering from the given description.
(a) Some animals live inside the grounds by making burrows.
Biological weathering
(b) The rock rusts.
Chemical weathering
(c) Water which has accumulated in the crevices of the rocks freezes. Consequently, the rock breaks.
Mechanical weathering
(d) The pipes supplying water in colder regions break.
Mechanical weathering
(e) Sand formation occurs in deserts
Mechanical weathering
Click on link to get PDF from store
Chapter-3-Exogenetic Processes Part-1-Notes
Chapter-3-Exogenetic Processes Part-1-Solutions
Class 9 Geography PDF Set :
All Chapters Notes (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Solutions (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Notes+Solutions (24-PDF) Rs.80-Buy
Class 9 Social Science PDF Set :
All Notes- Social Science Notes(Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Notes+Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (56-PDF) Rs.175-Buy
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 2: Endogenetic Movements - online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 4: Exogenetic Processes Part-2 - online Solution |
