Question 1.
Complete the following sentences by choosing the appropriate words from the brackets.
(Inheritance, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction, chromosomes, DNA, RNA, gene)
a. Hereditary characters are transferred from parents to offsprings by ............, hence they are said to be structural and functional units of heredity.
b. Organisms produced by ............ show minor variations.
c. The component which is in the nuclei of cells and carries the hereditary characteristics is called .............
d. Chromosomes are mainly made up of .............
e. Organisms produced through ............ show major variations.
Answer :
a. Hereditary characters are transferred from parents to offsprings by gene, hence they are said to be structural and functional units of heredity.
b. Organisms produced by asexual reproduction show minor variations.
c. The component which is in the nuclei of cells and carries the hereditary characteristics is called chromosome.
d. Chromosomes are mainly made up of DNA.
e. Organisms produced through sexual reproduction show major variations.
[collapse]
Question 2.
Explain following.
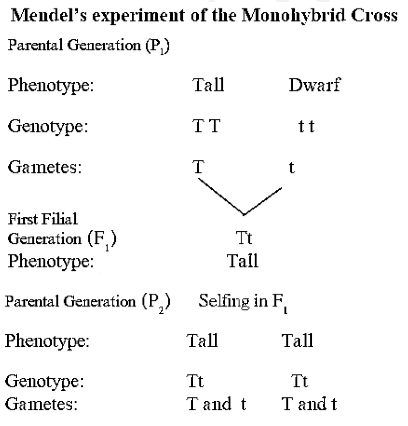
a. Explain Mendel’s monohybrid progeny with the help of any one cross.
Answer :
When the characteristics are sent to the next generation, they follow certain rules. The Mendel’s laws are based on these findings.
Monohybrid cross : Monohybrid cross is the cross of mating involving only one pair of contrasting characters or traits. '
- In P1 generation tall and dwarf plants were used for the cross. The progeny developed through such cross were all tall. Therefore, Mendel called tallness as a dominant character.
- In the F1 generation all the plants are tall as the tallness is the dominant character. The dwarf plant was not obtained and thus dwarfness is the recessive character.
- Though in F1 generation all the plants were tall, the character of dwarfness was hidden in them. Thus the phenotype of all the F1 individuals was tall but their genotypes were of heterozygous type.
- When two such F1 plants were crossed with each other it was seen that there were two types of phenotypes in F2 generation. These were tall and dwarf.
- In the F2 generation three types of genotypes are obtained viz. homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive and heterozygous.
- According to the data collected after the experiments of Mendel, out of 929 pea plants, 705 were tall and 224 were short.
- This shows that in F2 generation there is phenotypic ratio of 3 tall : 1 dwarf whereas genotypic ratio was 1TT : 2Tt : 1tt.
First Filial Generation (F2):
| Male gamet à
Female gamet ¯
|
T |
t |
| T |
TT (Tall) |
Tt (Tall) |
| t |
Tt (Tall) |
tt (Dwarf) |
[collapse]
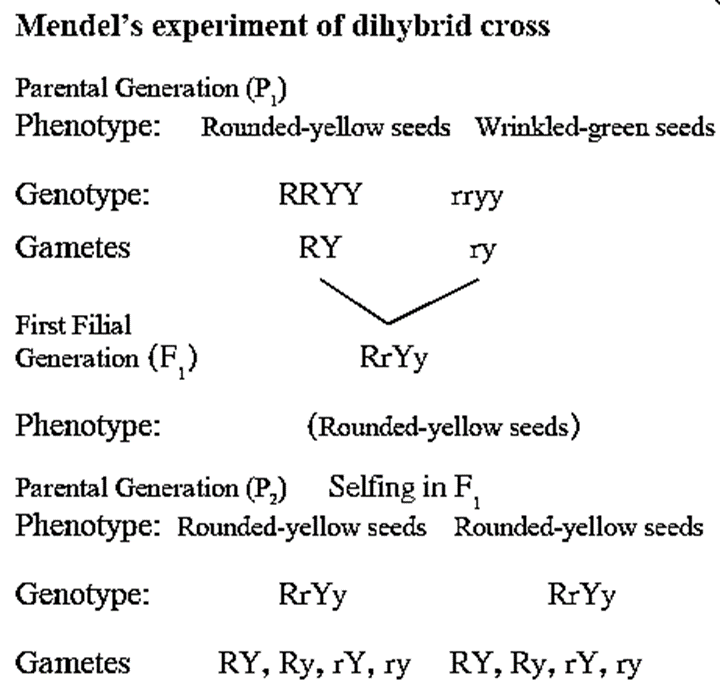
b. Explain Mendel’s dihybrid ratio with the help of any one cross.
Answer :
- The cross involving two pairs of contrasting characters is known as a dihybrid cross.
- Two pairs of contrasting characters, namely seed shape and seed colour were considered by Mendel.
- The characters of round and yellow seeds are dominant characters while wrinkled and green seeds are recessive characters.
- In parental (P1) generation, a plant with round and yellow seeds was crossed with a plant bearing wrinkled and green seeds. RRYY (round and yellow) was one parent while rryy (wrinkled and green) was another parent.
- Each pair of genes segregates independently from the other.
- RRYY parents produced RY type of gametes, and rryy parents produced ry type of gametes.
- In F1 generation all the offsprings produced had genotype RrYy and their phenotype was yellow and round.
- The F1 generation produced four different types of gametes, viz. RY, Ry, rY and rY- of these, RY and ry were parental combinations whereas Ry and rY were recombination.
- From four male gametes and from four female gametes, 16 different combinations are produced as follows : (Refer to the table)
- The phenotypic ratio produced was 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 which is called a dihybrid ratio.
First Filial Generation (F2):

Phonotypic ratio:
- Round-Yellow : 9
- Wrinkled-Yellow : 3
- Round-Green : 3
- Wrinkled-Green : 1
Genotypicratio = 1:1:2:2:4:2:2:1:1
RRYY -1, RRYy -2, RRyy -1, RrYY -2, RrYy -4, Rryy -2, rrYY -1, rrYy -2, rryy -1
[collapse]
c. Distinguish between monohybrid and dihybrid cross.
Answer :
| Monohybrid cross |
Dihybrid cross |
| The cross in which only one pair of contrasting characters is involved is known as monohybrid cross. |
The cross in which only two pairs of contrasting characters are involved is known as dihybrid cross. |
| A monohybrid cross is useful in determining the dominance of genes. |
A dihybrid cross is useful in studying the assortment of the offspring. |
| Monohybrid crosses yield a phenotypic ratio of 3 : 1 in the F2 generation. |
Dihybrid crosses yield a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1in the F2 generation. |
| Example- a cross between tall and dwarf plant |
Example- a cross between tall plant having red flower and a dwarf plant having white flower |
[collapse]
d. Is it right to avoid living with a person suffering from a genetic disorder?
Answer :
No, it is not right to avoid living with a person suffering from a genetic disorder. Genetic disorders are not communicable diseases that would be transmitted to people who come in contact with people with genetic disorders. It is transmitted only from parents to offspring. Similarly, it is never cured. The genetic disorder is formed in the embryonic stage due to abnormal genome. This spreads to all the cells of the patient. Later in life it is incurable. Such people need help and support. Few borderline syndromes are given remedial education and made self-sufficient. The parents of syndrome also need lots of empathy and support
[collapse]
Question 3.
Answers the following questions in your own words.
a. What is meant by ‘chromosome’. Explain its types.
Answer :
- Chromosomes are in definite number in the nucleus of every cell.
- They are seen only at the time of cell division. Each chromosome is made up of DNA, RNA and proteins.
- The nucleotides present in the DNA molecule form the sequences. Thus the sequence with which the nucleotides are arranged in the DNA molecules is called gene. The segments of DNA thus form genes. The genes are carried to the next generation via chromosomes. This is the important function of the chromosomes.
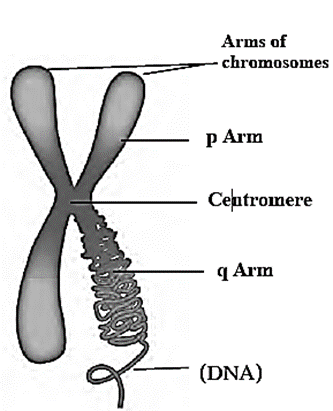
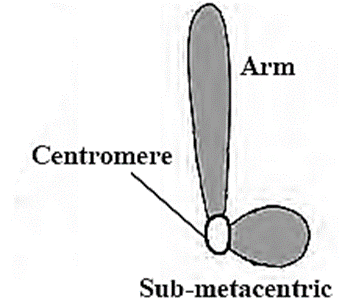
- There ‘Primary constriction’ or ‘Centromere’ present on each chromosome which divides the chromosome into two parts. Each part is called an ‘arm’. The centromere has a specific position in each chromosome.
Depending upon the position of centromere and the length of the arms of the chromosome, there are four types of chromosomes.
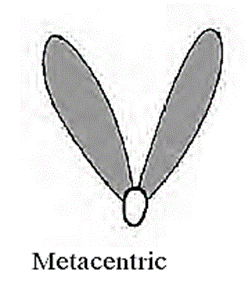
1. Metacentric :
- Structure : The centromere is exactly at the mid-point in this chromosome.
- Pattern : This chromosome looks like the English letter ‘V’.
- Arm : The arms of this chromosome are equal in length.
2. Sub-metacentric :
- Structure : The centromere is somewhere near the mid-point in this chromosome
- Pattern : It looks like English letter ‘L’.
- Arm : One arm is slightly shorter than the other.
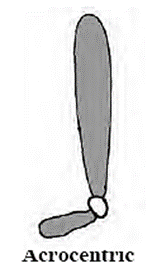
3. Acrocentric :
- Structure : The centromere is near one end of this chromosome
- Pattern : It looks like the English letter ‘j’.
- Arm : One arm is much smaller than other.
4. Telocentric :
- Structure : The centromere is right at the end of this chromosome.
- Pattern : This chromosome look like the English letter ‘i’.
- Arm : This chromosome consists of only one arm.

Types of chromosomes according to their function :
- Homologous chromosomes : If the pair consists of similar chromosomes by shape and organization, they are called homologous chromosomes.
- Heterologous chromosomes : If the chromosomal pairs are not similar they are called heterologous chromosomes.
- Sex chromosomes or allosomes : The chromosomal pair that decides the sex of the sexually reproducing organisms.
- Somatic chromosomes or autosomes : Chromosomes that decide the body characters other than sex.
[collapse]
b. Describe the structure of the DNA molecule.
Answer :
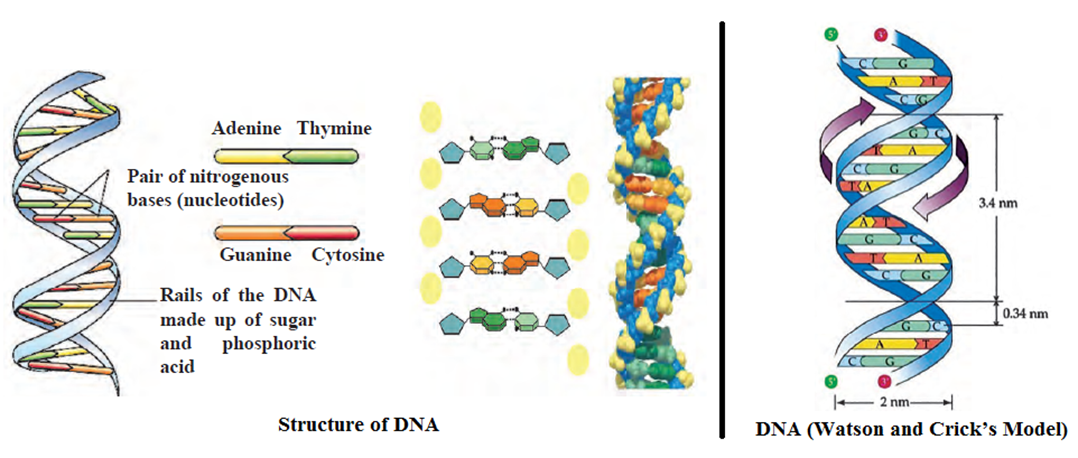
- Watson and Crick proposed the model for DNA structure in 1953.
- According DNA structure proposed by Watson and Crick, the DNA molecule is a double helix.
- Each strand of this helix is made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made up of a phosphoric acid, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogenous base.
- Nitrogenous bases are of two types, viz. purines and pyrimidines. The purines are of two types, viz. adenine and guanine. Pyrimidines are of two types, viz, cytosine and thymine.
- The helices have hydrogen bonds with opposite sides. The adenine always pairs with thymine with double hydrogen bonds while cytosine always pairs with guanine with triple hydrogen bond.
- The deoxyribose sugar and the phosphoric acid alternate with each other and are arranged on the outer side of each helix.
- The genes in the form of nucleotide sequence are located on the DNA molecule which is transmitted through parental DNA to offspring.
[collapse]
c. Express your opinion about the use of DNA fingerprinting.
Answer :
- DNA fingerprinting is the ultramodern technique. The sequence of genes in the DNA of any person can be understood using this technique.
- This technique is used to identify the criminals in forensic cases.
- Identification of the unclaimed dead bodies can also be done using DNA fingerprinting.
- The DNA sequence of mother, father and child match with each other. In case of disputed parentage, therefore DNA fingerprinting technique is used.
- If unknown remains are obtained during excavation, then they can be identified using the same technique.
[collapse]
d. Explain the structure, function and types of RNA.
Answer :
- The RNA is a nucleic acid that is found both in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm. It is made up of single strand that is twisted upon itself.
- The components of RNA are nucleotides which are made up of ribose sugar, phosphoric acid and the nitrogenous bases.
- The four types of nitrogenous substances in the RNA are adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. Thymine is not present in the RNA molecules, of these adenine and guanine are purines while cytosine and uracil are the pyrimidines of the RNA.
- RNA is found both in nucleus as well as in cytoplasm.
- The RNA is of three types according to its functions.
Types of RNA according to their function :
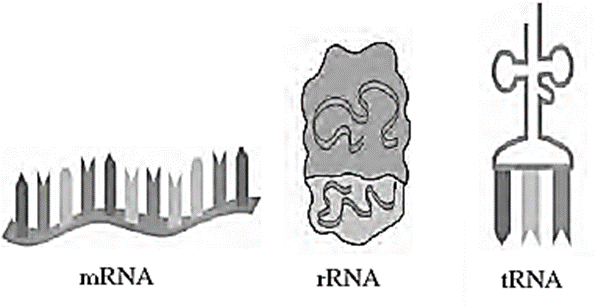
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) : Carries the information of protein synthesis from genes i.e. DNA chain in the cell nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm which produce the proteins, is called messenger RNA.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) : The molecule of RNA which is a component of the ribosome organelle is called a ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes helps in function of protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA) : The RNA molecule which, according to the message of the mRNA carries the amino acid up to the ribosomes is called transfer RNA.
[collapse]
e. Why is it necessary for people to have their blood examined before marriage?
Answer :
It is necessary for people to have their blood examined before marriage because the genetic disorders are transmitted only by reproduction. If a carrier/sufferer of a genetic disorder marries a person who is also a carrier/ sufferer of the disorder, then there are chances that disorder will be passed on to the offsprings.
E.g. Sickle-cell anaemia, thalassaemia, different types of syndrome conditions, etc. may be present in such children. By performing blood tests on prospective husband and wife, the chances of having abnormal children can be understood. The genetic disorders cannot be cured any time. It comes with the birth and ends with the death.
Moreover, if one wants to be protected from the dreadful disease like AIDS, then the blood test of our prospective spouse should be done in time.
If the Rh blood group is incompatible with each other, the disorder of erythroblastosis foetalis can occur resulting in death or retardation of the child.
If mother is Rh negative and father is Rh positive the children born to such couple may have many problems. Taking into consideration all these facts, it becomes evident that people should have their blood examined before marriage.
[collapse]
Question 4.
Write a brief note on each.
a. Down syndrome
Answer :
- Down syndrome is a disorder arising due to autosomal abnormality.
- Down syndrome was the first discovered and described chromosomal disorder in human beings.
- This disorder is also called trisomy 21 as the 21st chromosome occurs thrice in such patients. Due to extra 21st chromosome, in each cell of Down syndrome there are 47 chromosomes.
- These children are mentally retarded due to improper brain growth. Their main symptoms include short height, short wide neck, flat nose, short fingers, scanty hair, single horizontal crease on the palm.
- They have short life span ranging to about 16 to 20 years.
[collapse]
b. Monogenic disorders
Answer :
- Monogenic disorders: Monogenic disorders are genetic disorders which are caused by a mutation in a single gene. This mutation may be present on one or both the chromosomes.
- When there is mutation in any single gene into a defective gene, it causes disorders which are called monogenic disorders.
- There are about 4000 different disorders of this type.
- Due to abnormal genes, the protein synthesis does not take place properly. Therefore, their products are either produced in deficient amounts or are not produced at all. It causes abnormal metabolism leading to death at a tender age.
- Some of the examples of monogenic disorders are sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, polycystic kidney etc.
[collapse]
c. Sickle cell anaemia: symptoms and treatment.
Answer :
Symptoms of sickle-cell anaemia :
- Swelling of hands and legs,
- Pain in joints,
- Severe general body aches,
- Frequent colds and cough,
- Constant low grade fever,
- Exhaustion,
- Pale face,
- Low haemoglobin content.
Treatment/ Remedies :
- There is no particular treatment for sickle cell anemia, the treatments which are available provide symptomatic relief from the symptoms associated with this disorder.
- Premarital blood check up should be done as this disease spreads only through reproduction.
- A carrier or sufferer should never marry with another carrier or sufferer. Or if they marry they should not have children.
- A person suffering from sickle cell anaemia should regularly and daily take a tablet of folic acid.
[collapse]
Question 5.
How are the items in groups A, B and C inter-related?
| A |
B |
C |
| Leber hereditary optic neuropathy |
44+XXY |
Pale skin,white hairs |
| Diabetes |
45+X |
Men are sterile |
| Albinism |
Mitochondrial disorder |
Women are sterile |
| Turner syndrome |
Polygenic disorder |
This disorder arises during development of zygote. |
| Klinefelter syndrome |
Monogenic disorder |
Effect on blood-glucose level |
Answer :
| A |
B |
C |
| Leber hereditary optic neuropathy |
Mitochondrial
disorder |
This disorder arises during development of zygote. |
| Diabetes |
Polygenic disorder |
Effect on blood-glucose level |
| Albinism |
Monogenic disorder |
Pale skin,white hairs |
| Turner syndrome |
45+X |
Women are sterile |
| Klinefelter syndrome |
44+XXY |
Men are sterile |
[collapse]
Question 6.
Filling the blanks based on the given relationship.
a. 44+X:Turner syndrome: :44+XXY:- ..............
b. 3:1 Monohybrid: : 9:3:3:1 : .............
c. Women : Turner syndrome : : Men : .......
Answer :
a. 44+X:Turner syndrome: :44+XXY:- Klinefelter syndrome
b. 3:1 Monohybrid: : 9:3:3:1 : Dihybrid cross
c. Women : Turner syndrome : : Men : Klinefelter syndrome
[collapse]
Question 7.
Complete the tree diagram below based on types of hereditary disorders.
Answer :

[collapse]











