Chapter-6-Classification of Plants
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Science & Technology-Chapter-6
Solution
Question 1:
Match the proper terms from columns A and C with the description in column B.
| 'A' | 'B' | 'C' |
| Thallophyta | Seeds are formed in fruits | Fern |
| Bryophyta | No natural covering on seeds | Cycas |
| Pteridophyta | These plants mainly grow in water | Tamarind |
| Gymnosperms | These plants need water for reproduction | Moss |
| Angiosperms | Tissues are present for conduction of water and food | Algae |
A
B
C
Thallophyta
These plants mainly grow in water
Algae
Bryophyta
These plants need water for reproduction
Moss
Pteridophyta
Tissues are present for conduction of water and food
Fern
Gymnosperms
No natural covering on seeds
Cycas
Angiosperms
Seeds are formed in fruits
Tamarind
Question 2:
Complete the sentences by filling in the blanks and explain those statements.
(angiosperms, gymnosperms, spore, bryophyta, thallophyta, zygote)
1. .................... plants have soft and fibre-like body.
2..................... is called the ‘amphibian’ of the plant kingdom.
3.In pteridophytes, asexual reproduction occurs by .................... formation and sexual reproduction occurs by ....................formation.
4. Male and female flowers of ....................are borne on different sporophylls of the same plant.
1. Thallophytaplants have soft and fibre-like body. 2. Bryophyteis called the ‘amphibian’ of the plant kingdom. 3. In pteridophytes, asexual reproduction occurs bysporeformation and sexual reproduction occurs by zygote formation. 4. Male and female flowers of gymnospermsare borne on different sporophylls of the same plant.
Question 3:
Answer the following questions in your own words.
1. Write the charateristics of subkingdom Phanerogams.
Plants that bear seeds are called Phanerogams. In these plants, seeds are formed after Reproduction. They show characteristics like- Phanerogams are further subdivided into gymnosperms and angiosperms on the basis of seeds which are enclosed in a fruit or not. Gymnosperms produce seeds which are not enclosed by fruit and hence are called naked seeds whereas angiosperms produce seeds which are enclosed in fruits.
2. Distinguish between monocots and dicots.
Example Maize, Jowar Example: Sunflower,beans
Monocots
Dicots
The embryo in a monocot seed has one cotyledon.
The embryo in a dicot seed has two cotyledons.
The sepals or petals are in 3 parts or in multiples of three.
The sepals or petals are in 4 or 5parts or in their multiples.
The stem vascular bundles are scattered.
The stem vascular bundles are arranged in a ring.
Leaves show parallel venation.
Leaves show reticulated venation.
They have fibrous or adventitious roots.
They have a tap-root system.
3. Write a paragraph in your own words about the ornamental plants called ferns.
Ferns are ornamental plants seen in gardens. They are called ornamentals as they beautify the place wherever they grow.
4. Sketch, label and describe the Spirogyra.
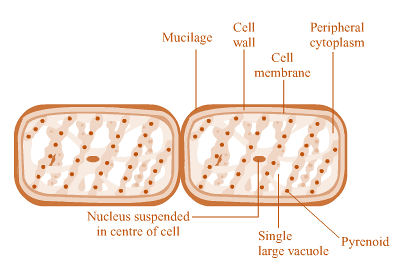
4. Write the characteristics of the plants belonging to division Bryophyta.
The characteristics of bryophytes are-
Question 4:
Sketch and label the figures of the following plants and explain them into brief.
(i) Marchantia
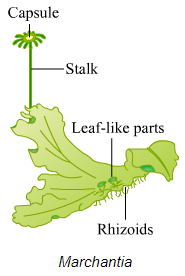
(ii) Funaria
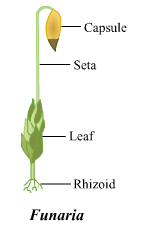
(iii) Fern

(iv) Spirogyra.
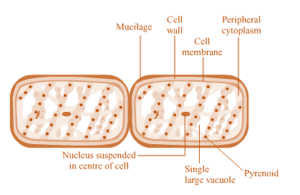
Question 5:
Collect a monocot and dicot plant available in your area. Observe the plants carefully and describe them in scientific language.
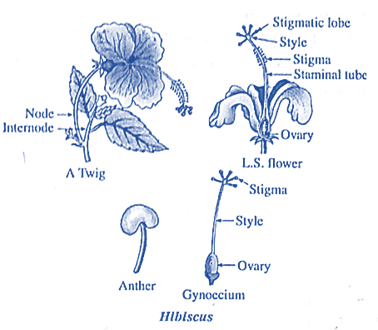
(1) Onion (Allium cepa) : An onion is monocotyledonous because the veins in the leaves are parallel, it has a fibrous root system and only one seed cotyledon . A small herb with tunicated bulb Root : Fibrous Stem : Underground stem (bulb) Leaves : Hollow and tubular Flower : Complete, bisexual Perianth : Made up of 6 lobes, arranged in two whorls of 3 each Androecium : Made up of 6 stamens, Epiphyllous Gynoecium : Tricarpellary, syncarpous, ovary sperior. (2) Hibiscus (A dicot plant) : Root : Tap root Stem : Erect and branched Leaf : Simple, alternate, with reticulate, venation Flower : Pedicillate, complete, bisexual Calyx : Sepals-5, Gamosepalous Corolla : Petals-5, Gamopetalous Androecium : Stamen indefinite. Filaments are united to form a staminal tube. The staminal tube bears kidney shaped anthers. Gynoecium ; Pentacarpellary, syncarpous.

Question 6:
Which criteria are used for the classification of plants? Explain with reasons.
Plants are divided on the basis of various characteristics like:
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Science & Technology - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 5: Acids, Bases and Salts - view online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 7: Energy Flow in Ecosystem - Online Solution |

🖕🏻