Endogenetic Movements
Maharashtra Board-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-2
Solution
Question 1.
Tick in front of the correct option
(a) On which of the following are slow movements in the earth’s interior dependent?
(i) Landforms
(ii) Velocity
(iii) Direction
(ii) Velocity
(b) When waves divert from each other, what do they create
(i) Compression
(ii) Tension
(iii) Mountain
(ii) Tension
(c) For the formation of a rift valley, which of the following processes should occur in the earth’s crust?
(i) Compression
(ii) Tension
(iii) Weathering
(ii) Tension
(d) Which of these is a fold mountain?
(i) The Satpudas
(ii) The Himalayas
(iii) The Western Ghats
(ii) The Himalayas
(e) The formation of extensive plateaus is a result of which type of movements ?
(i) Mountain-building
(ii) Continent-building
(iii) Horizontal
(ii) Continent-building
Question 2.
Give geographical reasons.
(a) Buildings collapsed at the foothills of the Himalayas because of an earthquake. Before collapsing they were moving forward and backward.
(b) There is a difference in the formation of the Meghalaya Plateau and the Deccan Plateau.
(i) Formation of the Meghalaya Plateau: (ii) Formation of Deccan Plateau : In this way, there is a difference in the formation of the Meghalaya Plateau and the Deccan Plateau.
(c) Most of the volcanoes are found on the plate boundaries.
Thus, most of the volcanoes are found on the plate boundaries.
(d) The Barren Island is becoming conical in shape.
Therefore, the Barren Island is becoming conical in shape.
(e) Volcanic eruptions can cause earthquakes.
Question 3.
Identify and name the internal movement.
(a) Tsunamis are generated in coastal areas.
Sudden movement
(b) The Himalayas are an example of fold mountains.
Slow movement (c) Molten magma is thrown out of the earth’s mantle.
Sudden movement
(d) Rift valley is formed because of faulting.
Slow movement
Question 4.
Arrange the following statements in chronological order in which an earthquake occurs.
(a) The earth’s surface vibrates
(b) The plates suddenly move.
(c) Due to the movements in the mantle, compression goes on increasing.
(d) Along the weak points ( faultlines) rocks break apart.
(e) Stored energy is released in the form of seismic waves.
(b) The plates suddenly move. (c) Due to the movements in the mantle, compression goes on increasing. (d) Along the weak points, (fault-lines) rocks break apart. (e) Stored energy is released in the form of seismic waves. (a) The earth’s surface vibrates.
Question 5.
Distinguish between -
(a) Block Mountain and Fold Mountain
Block Mountain
Fold Mountain
Because of internal movement, horizontal waves moving away from each other are formed. This causes tension on the layers of rocks. This leads to formation of faults in the rocks.
Energy is transferred from the interior of the earth. Because of these energy waves and pressure working towards each other and in horizontal direction, the layers of the soft rocks form folds.
When a part of the earth’s crust in between two parallel faults is lifted, it looks like a block. Such a landform is known as a block mountain.
If the pressure is very high, large scale folds are formed and as a result, the surface of the earth gets uplifted and fold mountains are formed.
For example, Black Forest Mountains in Europe, the Meghalaya Plateau in India.
For example, the Himalayas, the Rockies, the Andes, the Alps.
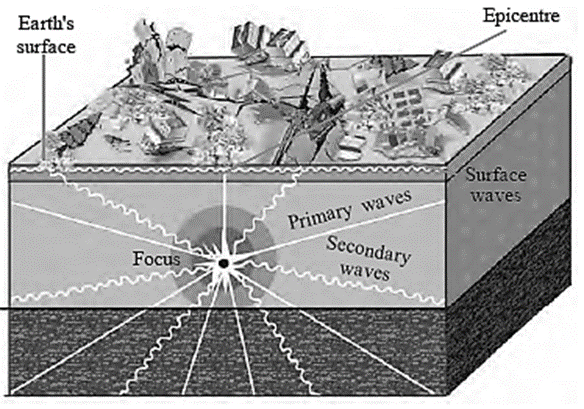
(b) Primary and Secondary Seismic Waves
Primary Seismic Waves
Secondary Seismic Waves
The seismic waves that reach the earth first, immediately after the energy is released in the interior are called primary seismic waves.
The seismic waves that reach the earth after the primary seismic Waves are called secondary seismic waves.
Primary seismic waves can travel through all the three mediums i.e. liquid, solid and gaseous.
Secondary seismic waves can travel only through the solid medium.
The particles lying in the way of primary seismic waves move to and fro in the direction of energy transfer.
The particles lying in the way of secondary seismic waves move up and down in the direction of energy transfer.
Compared to secondary seismic waves, the primary seismic waves are less destructive.
Compared to primary seismic waves, the secondary seismic waves are more destructive.
(c) Earthquakes and volcanoes
Earthquakes
Volcanoes
Sometimes, due to rapid earth movements below the surface, the crust is subjected to a tremendous stress. This energy gets released suddenly resulting in trembling of the surface of the earth. This sudden trembling of the earth’s surface is called an earthquake.
A process in which hot solid, liquid and gaseous materials are thrown out of from the mantle of the earth onto the surface of the earth, is called volcanic eruption/volcanoes.
Due to earthquake, the land may not erupt or subside. Land may erupt or subside with a smaller extent.
Due to volcanoes, the land erupts up to great extent and as a result cone shapes mountains or volcanic plateaus are formed.
During earthquake, molten magma may not come out on the surface of the earth.
During volcanic eruption, molten magma comes out on the surface of the earth.
Question 6.
Answer in brief
(a) Give reasons why an earthquake occurs.
An earthquake occurs due to the following reasons :
(b) Which type of movements have led to the formation of the major fold mountains in the world?
(c) How is the magnitude of the earthquake related to the collapse of houses
(d) What are the effects of earthquakes on the earth’s surface and human life?
(A) Effects on the earth’s surface : (B) Effects on human life :
(e) Explain the types of seismic waves.
Seismic waves : The seismic waves can be divided into primary, secondary and surface waves as follows : Primary or ‘P’ waves : These waves are the first one to reach the surface of the earth after the energy is emitted in the earth’s interior. Secondary or ‘S’ waves : The waves which reach the earth’s surface after the primary waves are called secondary waves. Surface waves or ‘L’ waves : These waves are generated after the main ‘P’ waves and ‘S’ waves reach the epicenter.
(f) Explain the types of volcanoes on the basis of periodicity of eruption with examples.
Types of volcanoes on the basis of periodicity of eruption : The following are the types of volcanoes on the basis of periodicity of eruption :
Question 7.
Show the epicentre, focus and the primary, secondary and surface waves of an earthquake with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
***This type of questions are excluded in the revised pattern
Question 8.
Show the following on a given outline map of the world.
(a) Mt. Kilimanjaro
(b) Mid-Atlantic Earthquake zone
(c) Mt. Fuji
(d) Krakatoa
(e) Mt. Vesuvius
Activity based, student should do it by self.
Click on link to get PDF from store
MSBSHSE-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-2-Endogenetic Movements-Notes
MSBSHSE-Class 9-Geography-Chapter-2-Endogenetic Movements-Solutions
Class 9 Geography PDF Set :
All Chapters Notes (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Solutions (12-PDF) Rs.50-Buy
All Chapters Notes+Solutions (24-PDF) Rs.80-Buy
Class 9 Social Science PDF Set :
All Notes- Social Science Notes(Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (28-PDF) Rs.95-Buy
All Notes+Solutions- Social Science (Hist.+Civic+Geo) (56-PDF) Rs.175-Buy
Useful links :
| Main Page : - Maharashtra Board Class 9th Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 1: Distributional Maps - online Solution Next Chapter : Chapter 3: Exogenetic Processes Part-1 - online Solution |
