The Earth and The Graticule
Class 6th-Geography-Chapter-1
Notes
|
Topics to be Learn :
|
The Graticule : The parallels and meridians on the globe form a net that is called a graticule . This facilitates determining the location of a place.
Click here to View Figure-1
Figure :
Limitations of determining the location of a place on the earth :
- Any monument is located at a particular place on the earth. However, when people from different places tell its direction from their respective places, their answers vary.
- Thus, the use of directions and sub-directions alone does not help us to accurately describe the location of a particular place on the earth.
- Therefore, it becomes necessary to use the exact system to state the precise location of any place on the earth.
Earth's huge size and making of a globe :
Angular distance :
Click here to View Figure-2
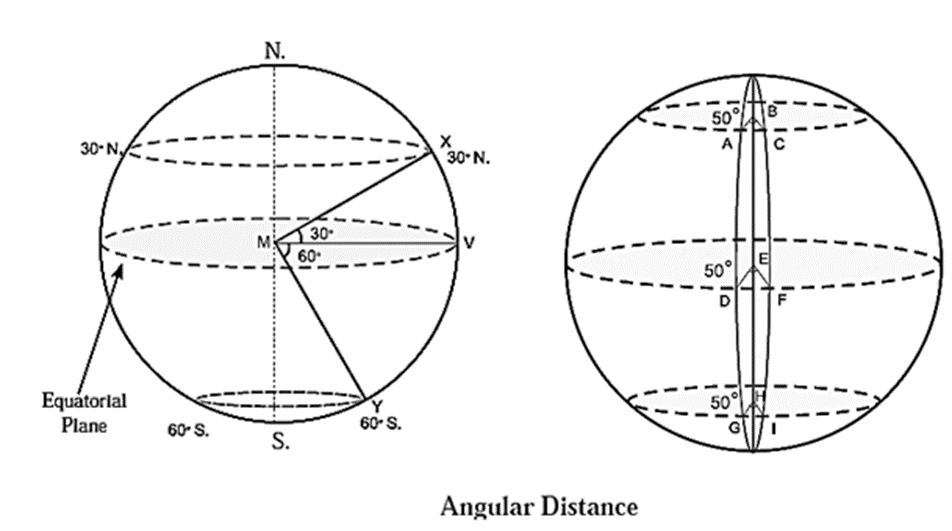
- The location of any place on the earth is determined with reference to the centre of the earth.
- Any point on the earth makes an angle with the plane of the equator. The measure of this angle is used in determining the location of that point.
Parallels of latitudes :
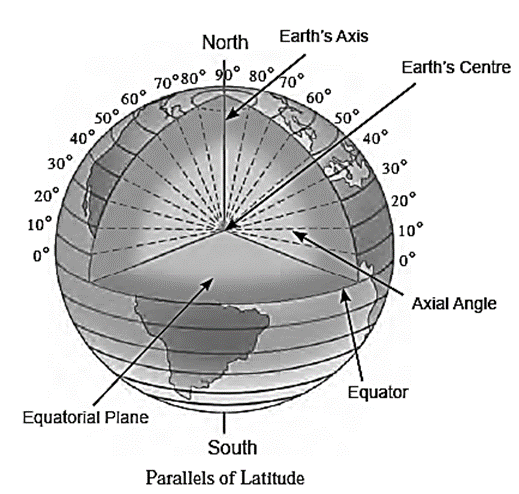
- The east-west circles created at some angular distance from the centre of the earth are called parallels of latitudes.
- The angular distances of all parallels are measured in degrees and are called latitudes
- The parallels of latitudes are parallel to one another.
- Parallels of latitudes are imaginary horizontal lines.
Click here to View Figure-3
Equator : The equator is considered as a 0° parallel. It is the largest parallel, and also known as a Great Circle.
Hemisphere : The equator bisects the earth into north and south parts. The one to the north is called the Northern Hemisphere and the one to the south is called the Southern Hemisphere.
Towards the north and the south of the equator, parallels of latitudes progressively become smaller and smaller in size but their angular value goes increasing.
North Pole and the South Pole : At the north and the south ends of the earth's axis, the parallels appear as points These are called the North Pole and the South Pole.
The total number of parallels on the earth :
Labelling of a parallel :
- While labelling the value of a parallel, it is necessary to mention whether it is in the Northern Hemisphere or in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Th6 parallels from the Northern Hemisphere are referred to as 5°N, 35°N, etc. Similarly, the parallels from the Southern Hemisphere are referred to as 5°S. 30°S, etc.
Meridians of longitudes :
- The north-south semicircles created at some angular distance from the centre of the earth, are called meridians of longitudes.
- The angular distances of all meridians are measured in degrees and are called longitudes.
- Meridians of longitudes are imaginary vertical lines.
Click here to View Figure-4

0° Meridian : 0° meridian is also known as the Prime Meridian. The angular distances of the other meridians are measured from the Prime Meridian.
180° Meridian : 0° meridian and 180° meridian lie opposite on the globe, forming a circle, This circle divides the earth into east and west parts. The one to the east is called the Eastern Hemisphere and the one to the west is called the Western Hemisphere.
The total number of meridians on the earth :
Labelling of a meridian :
- While labelling the value of a meridian, it is necessary to mention whether it is in the Eastern Hemisphere or in the Western Hemisphere.
- The meridians from the Eastern Hemisphere are referred to as 10° E, 25° E, etc.
- Similarly, the meridians from the Western Hemisphere are referred to as 10° W 25° W. etc.
- 0° meridian is known as the Prime Meridian. Therefore, 0° meridian is not labelled as 0° E or 0° W. It is labelled only as 0° meridian.
The distance between parallels and meridians :
The values of parallels and meridians in degrees, minutes and seconds :
Various systems for determining locations on the earth :
Indian Regional Positioning system :
Useful links :
| Main Page : Class 6th MSBSHSE – Geography - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Next Chapter : Chapter-2-Let us Use the Graticule - Online Notes |