Cell Structure and Micro-organisms
Based on Maharashtra Board General Science Chapter 11-Audio Notes, Solution, Video, PDF, Test
Notes
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Cell:
The body of all living organisms is made up of minute component called cell. The number of cells are different and specific for every living organism.
(1) Cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. Cellular organization is the primary characteristic of all living organisms.
Structural organization of Book -Flow Chart
| Letters -> | Words -> | Sentences-> | Paragraphs-> | Chapters-> | Book |
Structural organization of Living organisms -Flow Chart
Cell ->Tissue -> Organ -> Organ System -> Body – Living Organisms.
History of cell science :
(1) Robert Hooke in 1665 discovered cells.
(2) M. J. Schleiden and Theodore Schwann in 1838, gave a theory about cellular structure.
(3) Rudolph Virchow in 1885, stated that all cells are formed from pre-existing cells.
Measurement and observation of cells:
(1) Anton van Leeuwenhoek constructed first microscope in 1673. For the first time he observed live bacterial and protozoan cells under this microscope.
(2) Cells are minute in size and can be seen only with a compound microscope.
(3) The units used for measuring the sizes of cellular structure is micrometre and nanometre.
1 centimetre =10 millimetres.
1 millimetre = 1000 micrometres.
1 micrometre (or micron) = 1000 nanometres.
Shapes of the cells:
(1) The shapes of cells show great variation which is mainly related to their functions.
(2) Circular, rod-shaped, columnar, spiral, oval, rectangular, etc. are the different shapes of the cells observed.
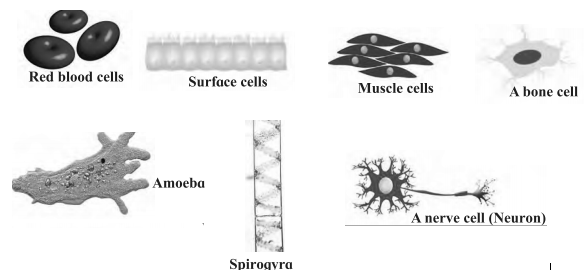
Components of the cell:
(1) Every cell has many cell components which are specific in their function. These components are called cell organelles. They carry out different life processes.
(2) Cell organelles are studied with the help of the electron microscope which has magnifying power of (2 x 109) i.e. two billion times their actual size.
(3) Cells are of two main types, viz.
- Prokaryotic cells (in microbes).
- Kukaryotic cells, (Plant cells and Animal cells.)
(4) Cell wall: The outermost covering of a cell which is seen only in plant cells. Cell wall gives definite shape to the cells, Animal cells lack the cell wall.
(5) The plasma membrane : or cell membrane is a thin extremely delicate and flexible covering, In plant cells it is inside the cell wall. In animal cell it is the outermost covering of the cells.
(6) Cytoplasm : The liquid part in the cell, except the nucleus is called cytoplasm. It is present in the space between the plasma membrane and nucleus. In the cytoplasm the cell organelles are scattered.
(7) Cell organelles :
- Nucleus :
- Structure : Porous double membrane around it. Lodges chromosomes and genes.
- Functions : Gives orders of protein synthesis.
- Peculiarities : Controls all functions of the cell.
- Endoplasmic reticulum and the ribosomes attached to it :
- Structure : Sprawling net-like.
- Functions : Ribosomes : Protein synthesis.
- Peculiarities : Transport system of the cell.
- Golgi bodies:
- Structure : several flat sacs.
- Functions : The proper distribution of proteins.
- Peculiarities :
- Plastids:
- Structure : With double membrane.
- Functions : Performing photosynthesis.
- Peculiarities : Present only in plant cells.
- Mitochondria:
- Structure : Spindle shaped, with double membrane.
- Functions : Produce energy.
- Peculiarities : Power house of the cell.
- Vacuoles :
- Structure : Empty space like a bubble.
- Functions : Throw out waste products of the cell.
- Peculiarities : Only one big vacuole in plant cells. Many small ones in animal cells.
- Lysosomes :
- Structure : Spherical bag with enzymes.
- Functions : Destroy cell by lysis.
- Peculiarities : Suicidal bags of the cell.
Plant Cell :
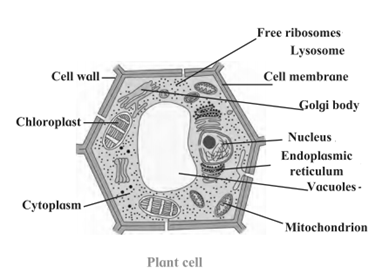
- Plant cells have cell wall made up of cellulose.
- The cytoplasm of the plant cells is lesser, granular and not dense.
- There is a single large vacuole located in centre which pushes the cytoplasm to one end.
- There are no lysosomes.
- The mitochondria are few in number.
- Plastids are present only in plant cells.
- Single or more but large vacuoles present.
- The vacuoles are filled up with cell sap.
Animal Cell :
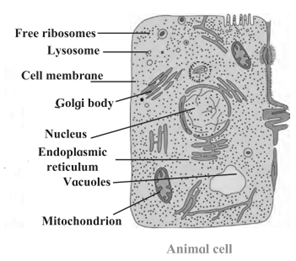
- Animal cells do not have cell wall.
- The cytoplasm of animal cells is more granular and dense.
- The cytoplasm is uniformly distributed in the cell.
- Lysosomes are present in the animal cells,
- The mitochondria are greater in number as compared to the plant cells.
- Plastids are absent in the animal cells.
- Vacuoles are few and temporarily formed.
- The vacuoles are filled with food or excretory matter,
Prokaryotic cell : Prokaryotic cells are about 1 to 10 um in size
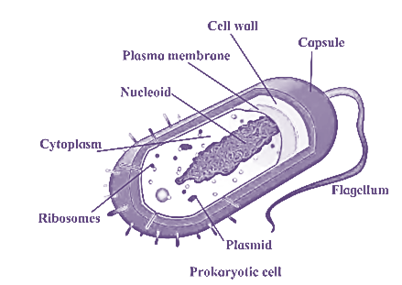
- The nucleus of prokaryotic cell is not distinct.
- Due to the absence of nuclear membrane, the nuclear material comes in contact with the cytoplasm.
- The cell organelles if present are without membranes.
- There is indistinct nucleoid in which prokaryotic DNA is present. There is a single chromosome.
- Mitochondria are absent in prokaryotic cells.
- Chlorophyll is present in the vesicles and not in plastids.
- Prokaryotic cells are found in blue-green algae and bacteria.
Eukaryotic cell : Eukaryotic cells are about 5 to 100 pm in size.
- The nucleus of eukaryotic cell is distinct, with nuclear membrane, nucleoli and nucleoplasm.
- Due to the presence of nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm and cytoplasmn never come in physical contact with each other.
- The cell organelles are always bound with membranes.
- The nucleus is distinct with more than one chromosomes.
- Mitochondria are present in eukaryotic cells.
- Chlorophyll is always inside the chloroplasts.
- Eukaryotic cells are found in highly evolved plants and animals.
[/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Micro-organisms :
The living organisms on the earth which are all around us, but we are unable to see them are called micro-organisms. They can be seen only under compound microscope.
| Q. Categories the following organisms into two groups, according to size —amoeba, paramecium, euglena, snail, elephant, pigeon, worms.
Ans.
|
Occurrence of micro-organisms :
- Micro-organisms are present everywhere, in the air, water, soil, food. sewage, garbage and also in the bodies of plants, animals and humans.
- Some are solitary living singly, e.g., amoeba, paramoecium while some live in colonies.
Observation and measurement of micro-organisms :
- Since microorganisms are smaller than 100 micrometres in size, they are observed only under microscope.
- If a magnification of more than 1000 x is needed then an electron microscope is used to observe those micro-organisms.
Nature of micro-organisms :
- Micro-organisms are prokaryotic cells.
- It lacks membrane bound cell organelles. It has only plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleoid.
- Unicellular micro-organisms : Micro-organisms having a single cell e.g., Bacteria and virus.
- Multicellular micro-organisms : Micro-organisms having many cells e.g. Fungus
and algae.
Growth of micro-organisms :
- Specific environment for growth and reproduction.
- During adverse conditions, micro-organisms form a thick covering or cyst around themselves and remain dormant. On return of favorable conditions, they come out of the protective covering to continue with their life.
- Aerobic microbes need oxygen for their growth. Anaerobic microbes do not need
- Some micro-organisms survive even in extreme and adverse conditions. e.g. ocean floor, polar regions, hot water springs etc.
Classification of micro-organisms :
Micro-organisms are broadly classified into algae, fungi, protozoa, bacteria and viruses. This classification is based on the shape and the life processes
Useful micro-organisms :
(1) Some micro-organisms carry out decomposing of waste and convert it into fertilisers. Farm waste, human excreta, wet garbage, etc. is used in a biogas plant to produce biogas und fertilizer with the help of microbes. Sewage is also treated with microbes for quick decomposition of the organic compounds in it. Microbes thus keep the environment clean by decomposition process.
(2) Micro-organisms in the soil and the root nodules of leguminous plants convert
atmospheric nitrogen into its compounds. Due to them soil Fertility increases and
the protein content of the pules also increase.
(3) Microbes produce milk products like cards, butter, buttermilk, cheese, paneer, etc. from the milk.
(4) Processes like tanning of skin production of ropes and strings from agave are done with the help of microbes.
(5) With help of process of bacterial fermentation, alcohol from grains and fruits, bread from flour as well as production of acetic acid, citric acid, lactic acid, vitamin antibiotics, we are produced
(6) Microbes are used in removing a layer of oil slick floating in ocean or lake. Such oil slicks are fallen due to accidental spillage.
Harmful micro-organisms :
(1) Micro-organisms spoil the food. In hot and humid air there is fugal attack on food.
(2) Microbes produce enterotoxins and cause food toxic resulting into food poisoning.
(3) Harmful microbes cause diseases in plants, animals and human. Amoebiasis, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis, gastro are caused by water and food borne microbes.
(4) Microbes cause diseases like malaria, dengue, elephantiasis, yellow fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, etc. These diseases are caused after mosquito transfers the microbes into human body. Common cold, cough, diphtheria, pneumonia, tuberculosis are diseases of respiratory tract which are caused by microbes.
Pathogens : Disease-producing micro-organisms :
- Pathogens are present in water bodies contaminated with sewage and dirt.
- They are also in the food left uncovered in unhygienic conditions.
- The food contaminated with houseflies or contaminated water if consumed, can Cause various diseases of the alimentary canal, like amoebiasis, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis, gastro, etc.
- When a patient having an infection of the respiratory tract sneezes or coughs many pathogens are released in the air. A healthy person contracts such infections through pathogens.
- When there are heaps of garbage, drains, stagnant water, etc. mosquito gets a breeding ground. Through the bite of a female mosquito different types of microbes enter the body.
[/responsivevoice]
[responsivevoice voice="UK English Female" rate="0.8" pitch="0.8" buttontext="Listen to this"]
Q. What happens to the sweetmeat or bread forgotten in a lunch-box for three or four days?
Ans. If sweet meat is not consumed in time it becomes rotten and hence cannot be eaten. The microbes make the sweetmeats bad. The bread usually shown growth of fungus over it, if kept just like that in a lunch box.
Food poisoning: When some microbes grow in the food they produce toxic compound called enterotoxins. This toxin makes the food poisonous. If such spoiled food is consumed
it results into vomiting and loose motions. A round layer of white scum or black particles on the food is an indication of fungal growth. It grows quickly on the moist and stale food.
Q. What do we do with such spoilt food? Why?
Ans. We throw away the spoilt food. Consuming such food will cause harm to health. So we do not eat it.
Care of food :
(1) Always eat fresh and properly covered food.
(2) Always drink clean and boiled water,
(3) Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze,
(4) Keep surroundings clean by not allowing garbago and water to accumulate around
your house.
Fermentation : Fermentation is the chemical process of conversion of a carbon compound into its another type by the action of micro-organisms. During the process of fermentation, heat, some gases and carbon dioxide are evolved.
In the process of fermentation the volume of material rises. Thus this reaction is used
in the production of various common foodstuffs. e.g., The flour is fermented to produce bread. In batter of idli and dosa, dough, fruit juices, etc. microbial process is used. This enables production of new compounds as the microbes grow.
Antibiotics and vaccines :
• Antibiotics cure diseases like tuberculosis, typhoid, cholera, etc.
• Domestic animals are also given antibiotic treatment against various diseases
• Plant diseases are controlled with the help of antibiotics.
• A vaccine that gives immunity against a particular disease is also produced with the help of microbes in a laboratory. [/responsivevoice]
| Contaminated medium | Disease |
| Uncleanliness near water body.
Uncovered and spoilt food |
Amoebiasis, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis,
gastro—diseases of alimentary canal. |
| Air | Common cold, cough, diphtheria, pneumonia, tuberculosis. |
| Bite of mosquito | malaria, dengue, elephantiasis, yellow fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, |
| View Solutions of this Chapter ← Click |
| Main Page : Class 7th MSBSHSE – General Science - All chapters notes, solutions, videos, test, pdf.
Previous Chapter : Chapter 10 : Disaster Management - Online notes Next Chapter : Chapter 12 : The Muscular System and Digestive System in Human Beings - Online Notes |